Transmission slip occurs when the engine's power is not fully transferred to the drivetrain, causing a delay in acceleration without the vehicle coming to a complete stop. Transmission stall, however, is a more severe issue where the engine RPM drops and the vehicle may stop moving under load despite being in gear. Understanding the difference helps in diagnosing whether the problem lies in clutch wear, torque converter failure, or hydraulic system malfunctions.
Table of Comparison
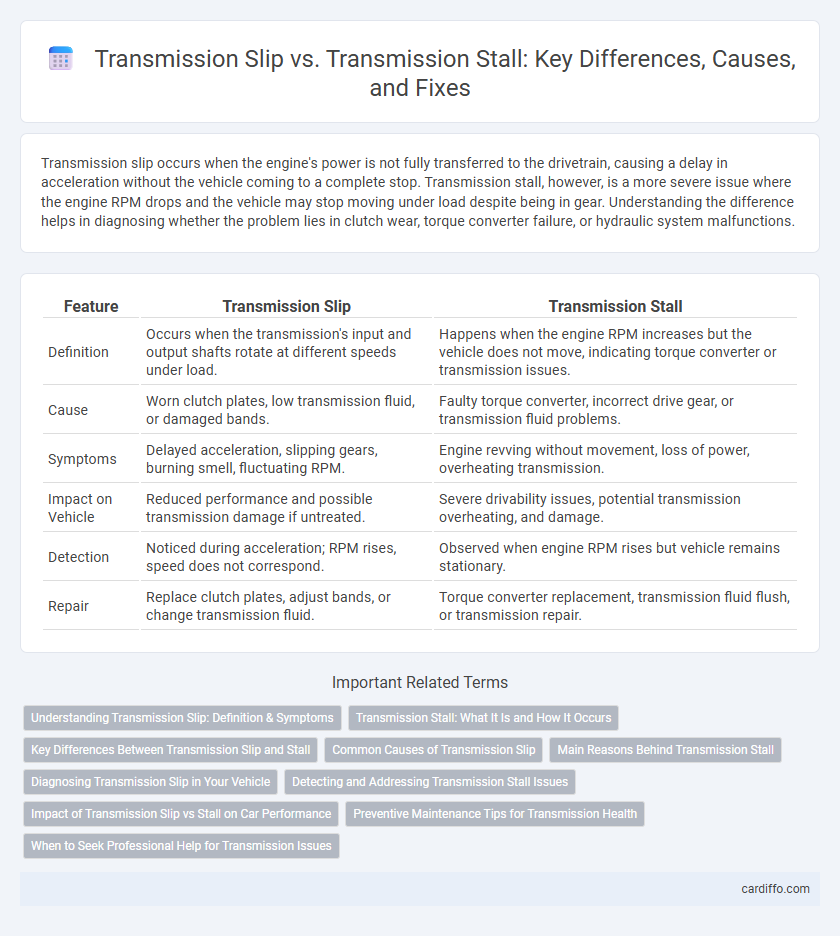
| Feature | Transmission Slip | Transmission Stall |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Occurs when the transmission's input and output shafts rotate at different speeds under load. | Happens when the engine RPM increases but the vehicle does not move, indicating torque converter or transmission issues. |
| Cause | Worn clutch plates, low transmission fluid, or damaged bands. | Faulty torque converter, incorrect drive gear, or transmission fluid problems. |
| Symptoms | Delayed acceleration, slipping gears, burning smell, fluctuating RPM. | Engine revving without movement, loss of power, overheating transmission. |
| Impact on Vehicle | Reduced performance and possible transmission damage if untreated. | Severe drivability issues, potential transmission overheating, and damage. |
| Detection | Noticed during acceleration; RPM rises, speed does not correspond. | Observed when engine RPM rises but vehicle remains stationary. |
| Repair | Replace clutch plates, adjust bands, or change transmission fluid. | Torque converter replacement, transmission fluid flush, or transmission repair. |
Understanding Transmission Slip: Definition & Symptoms
Transmission slip occurs when the transmission's input and output speeds do not match, causing a delay or loss of power transfer between the engine and wheels. Common symptoms include erratic acceleration, engine revs increasing without corresponding vehicle speed, and delayed or harsh gear shifts. Identifying transmission slip early helps prevent severe damage and costly repairs by addressing issues like worn clutch plates or low transmission fluid.
Transmission Stall: What It Is and How It Occurs
Transmission stall occurs when the engine RPM rises without a corresponding increase in vehicle speed, indicating a failure in power transfer from the engine to the transmission. It often results from internal transmission issues such as worn clutch plates, low transmission fluid, or a faulty torque converter causing the transmission to momentarily lock up under load. Identifying transmission stall involves monitoring for sudden drops in acceleration, odd noises, and overheating, which signal the need for prompt mechanical inspection to prevent severe drivetrain damage.
Key Differences Between Transmission Slip and Stall
Transmission slip occurs when the transmission fails to engage properly, causing delayed or erratic gear shifts without a complete loss of power, often resulting from worn clutches or low transmission fluid. Transmission stall, on the other hand, causes the engine to unexpectedly lose power and shut off, commonly due to torque converter issues or severe mechanical failure in the transmission system. Key differences lie in symptom manifestation: slip leads to improper acceleration and gear slipping, while stall results in engine shutdown and inability to move the vehicle.
Common Causes of Transmission Slip
Transmission slip occurs when the transmission fails to engage properly, causing delayed or incomplete gear shifts frequently caused by low transmission fluid, worn-out clutch plates, or a malfunctioning torque converter. Transmission stall, by contrast, happens when the engine unexpectedly stops or loses power due to issues like fuel delivery problems or ignition system failures. Common causes of transmission slip include fluid contamination, overheating, or internal component wear, which degrade the transmission's ability to maintain proper hydraulic pressure and friction for effective gear engagement.
Main Reasons Behind Transmission Stall
Transmission stall primarily occurs due to issues such as low transmission fluid levels, worn torque converter clutches, or faulty shift solenoids disrupting hydraulic pressure. These factors prevent the transmission from engaging gears properly, causing engine revs to rise without corresponding vehicle movement. Unlike transmission slip, which involves delayed or irregular gear shifts, transmission stall signals a more severe internal malfunction often linked to mechanical or electronic component failure.
Diagnosing Transmission Slip in Your Vehicle
Transmission slip occurs when engine power is not effectively transferred to the wheels, causing delayed acceleration or fluctuating RPMs without corresponding speed increase. Diagnosing transmission slip involves checking transmission fluid levels and quality, inspecting clutch packs or bands for wear, and using diagnostic tools to detect error codes indicating solenoid malfunctions or valve body issues. Recognizing symptoms like slipping gears, burning smell, or erratic shifting can pinpoint underlying transmission problems before they escalate into costly repairs.
Detecting and Addressing Transmission Stall Issues
Transmission stalls occur when the engine unexpectedly loses power due to excessive load or fluid pressure issues, unlike transmission slip where gears fail to engage properly. Detecting transmission stall involves monitoring abnormal engine behavior such as hesitation during acceleration and unusual shifts in RPM, often linked to low transmission fluid or worn components. Addressing transmission stall requires fluid level checks, filter replacements, and sometimes valve body inspections to restore proper hydraulic pressure and gear engagement.
Impact of Transmission Slip vs Stall on Car Performance
Transmission slip reduces power delivery by allowing the transmission to rotate faster than the engine output, leading to delayed acceleration and increased fuel consumption. Transmission stall causes the engine to bog down or stop unexpectedly, resulting in poor drivability and potential engine damage. Both issues degrade overall car performance, but slip primarily affects efficiency while stall directly impacts vehicle control and safety.
Preventive Maintenance Tips for Transmission Health
Regularly check and maintain proper transmission fluid levels and quality to prevent transmission slip and stall, as degraded fluid can cause overheating and wear. Schedule routine inspections for worn clutch plates and transmission bands to identify early signs of slipping or stalling issues. Use manufacturer-recommended transmission fluids and avoid harsh driving conditions to extend transmission life and ensure smooth gear engagement.
When to Seek Professional Help for Transmission Issues
Transmission slip often manifests as delayed acceleration or irregular gear shifts, while transmission stall results in the engine ceasing to respond during gear engagement. Persistent symptoms such as slipping or stalling require immediate professional diagnosis to prevent severe damage to the transmission system. Seeking expert assistance at the first sign of transmission irregularities ensures timely repairs and avoids costly replacements.
Transmission slip vs transmission stall Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com