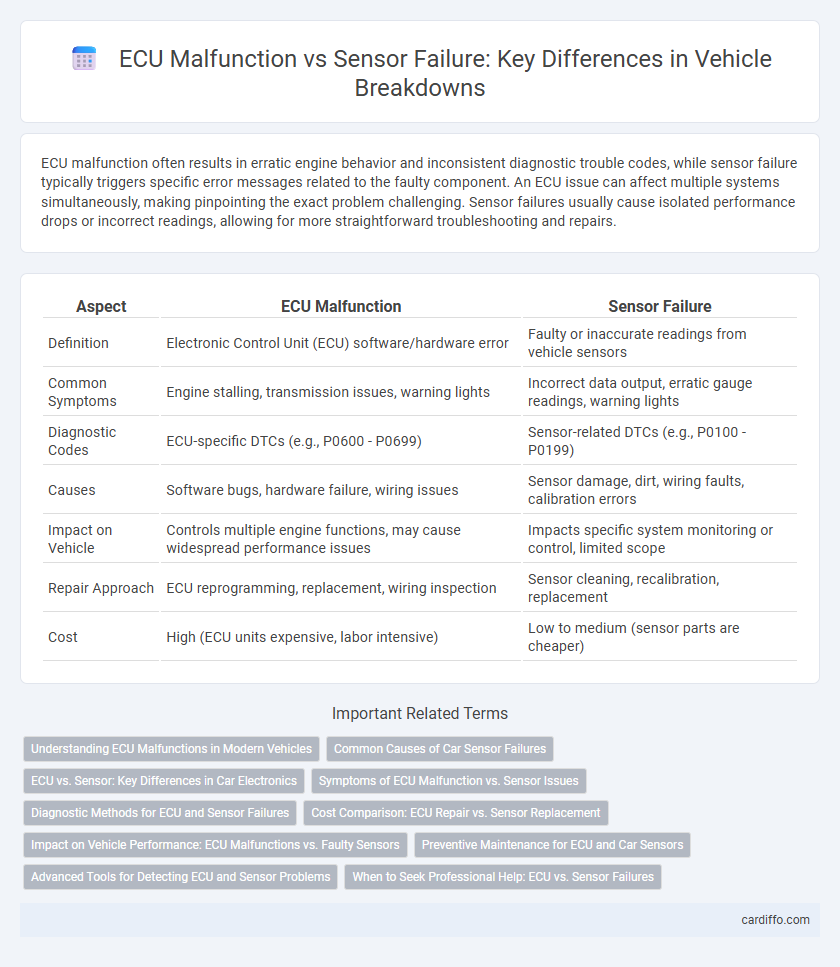
ECU malfunction often results in erratic engine behavior and inconsistent diagnostic trouble codes, while sensor failure typically triggers specific error messages related to the faulty component. An ECU issue can affect multiple systems simultaneously, making pinpointing the exact problem challenging. Sensor failures usually cause isolated performance drops or incorrect readings, allowing for more straightforward troubleshooting and repairs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | ECU Malfunction | Sensor Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electronic Control Unit (ECU) software/hardware error | Faulty or inaccurate readings from vehicle sensors |
| Common Symptoms | Engine stalling, transmission issues, warning lights | Incorrect data output, erratic gauge readings, warning lights |
| Diagnostic Codes | ECU-specific DTCs (e.g., P0600 - P0699) | Sensor-related DTCs (e.g., P0100 - P0199) |
| Causes | Software bugs, hardware failure, wiring issues | Sensor damage, dirt, wiring faults, calibration errors |
| Impact on Vehicle | Controls multiple engine functions, may cause widespread performance issues | Impacts specific system monitoring or control, limited scope |
| Repair Approach | ECU reprogramming, replacement, wiring inspection | Sensor cleaning, recalibration, replacement |
| Cost | High (ECU units expensive, labor intensive) | Low to medium (sensor parts are cheaper) |
Understanding ECU Malfunctions in Modern Vehicles
ECU malfunctions in modern vehicles often arise from software glitches, wiring issues, or internal component failures, disrupting engine performance and safety systems. Differentiating between ECU failure and sensor malfunction is critical, as sensors relay essential data while the ECU processes this information to control vehicle functions. Accurate diagnosis using specialized tools ensures effective repairs, preventing misdiagnoses that could overlook underlying ECU defects or sensor faults.
Common Causes of Car Sensor Failures
Car sensor failures often result from exposure to extreme temperatures, moisture intrusion, and physical damage caused by road debris or improper installations. Wiring issues such as corrosion, short circuits, or loose connections also contribute significantly to sensor malfunctions. These factors lead to inaccurate data transmission to the ECU, causing engine performance problems and triggering warning lights.
ECU vs. Sensor: Key Differences in Car Electronics
An ECU malfunction disrupts the central computer system that controls engine performance, fuel injection, and ignition timing, often leading to widespread vehicle issues. In contrast, a sensor failure impacts only specific data inputs such as oxygen levels or temperature, causing localized misreads without total engine control loss. While ECU faults require major diagnostics and potential replacement, sensor failures are typically simpler to identify and repair, affecting overall car electronics and drivability differently.
Symptoms of ECU Malfunction vs. Sensor Issues
ECU malfunctions often cause erratic engine behavior, such as sudden stalling, inconsistent idling, or failure to start, accompanied by illuminated check engine lights and diagnostic trouble codes related to the ECU itself. Sensor failures typically result in inaccurate data transmission, causing symptoms like poor fuel economy, rough engine performance, or misfires, with trouble codes pointing to specific sensors like oxygen sensors, throttle position sensors, or mass airflow sensors. Differentiating between ECU and sensor issues requires specialized diagnostic tools to interpret error codes and monitor real-time data streams from the vehicle's onboard systems.
Diagnostic Methods for ECU and Sensor Failures
Diagnostic methods for ECU malfunctions primarily involve scanning the vehicle's onboard diagnostic system using an OBD-II scanner to retrieve error codes that indicate specific ECU faults. Sensor failures are identified by analyzing sensor output data for irregularities, cross-checking with reference sensor values, and performing physical inspections or functional tests using multimeters or oscilloscopes. Advanced diagnostics may include ECU bench testing and software reflashing to isolate and resolve control module issues distinct from sensor errors.
Cost Comparison: ECU Repair vs. Sensor Replacement
ECU repair costs are typically higher than sensor replacement due to the complexity and central role of the ECU in vehicle systems. Sensor replacements usually involve lower parts and labor expenses, often ranging between $50 to $300, whereas ECU repairs can exceed $500 to $1,200 depending on the vehicle model and fault severity. Choosing sensor replacement over ECU repair can result in significant savings, especially when the malfunction is isolated to sensor failure rather than the control unit itself.
Impact on Vehicle Performance: ECU Malfunctions vs. Faulty Sensors
ECU malfunctions disrupt critical engine control processes, causing erratic performance, stalling, or complete vehicle shutdown, while faulty sensors primarily transmit incorrect data, leading to suboptimal fuel efficiency, poor acceleration, or inaccurate diagnostics. In cases of ECU failure, the vehicle may enter limp mode to prevent further damage, significantly limiting drivability, whereas sensor failures generally result in warning lights and degraded system responsiveness without immediate engine stoppage. Both issues compromise safety, but ECU malfunctions incur higher repair costs and downtime due to complex hardware and software diagnostics.
Preventive Maintenance for ECU and Car Sensors
Regular preventive maintenance of the ECU and car sensors significantly reduces the risk of breakdowns caused by ECU malfunctions or sensor failures. Routine diagnostic checks and software updates ensure optimal ECU performance, while sensor inspections prevent inaccurate data transmission that can lead to engine issues. Proper cleaning and timely replacement of faulty sensors contribute to extending the lifespan of both the ECU and vehicle components.
Advanced Tools for Detecting ECU and Sensor Problems
Advanced diagnostic tools like oscilloscopes and scan tools equipped with real-time data analysis excel in pinpointing ECU malfunctions versus sensor failures by monitoring signal integrity and communication protocols. These tools utilize ECU-specific error codes and sensor output patterns to differentiate between internal control unit faults and external input discrepancies. Employing such technologies significantly reduces diagnostic time, improving breakdown response and repair accuracy in automotive systems.
When to Seek Professional Help: ECU vs. Sensor Failures
Recognizing the difference between ECU malfunction and sensor failure is crucial for timely vehicle repair, as ECU issues often require specialized diagnostic tools and expertise beyond typical sensor replacements. Persistent warning lights, erratic engine behavior, or inability to read sensor data suggest ECU problems warranting professional intervention. Sensor failures, while sometimes repairable through part replacements, should also prompt expert evaluation if standard troubleshooting does not resolve the fault.
ECU malfunction vs sensor failure Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com