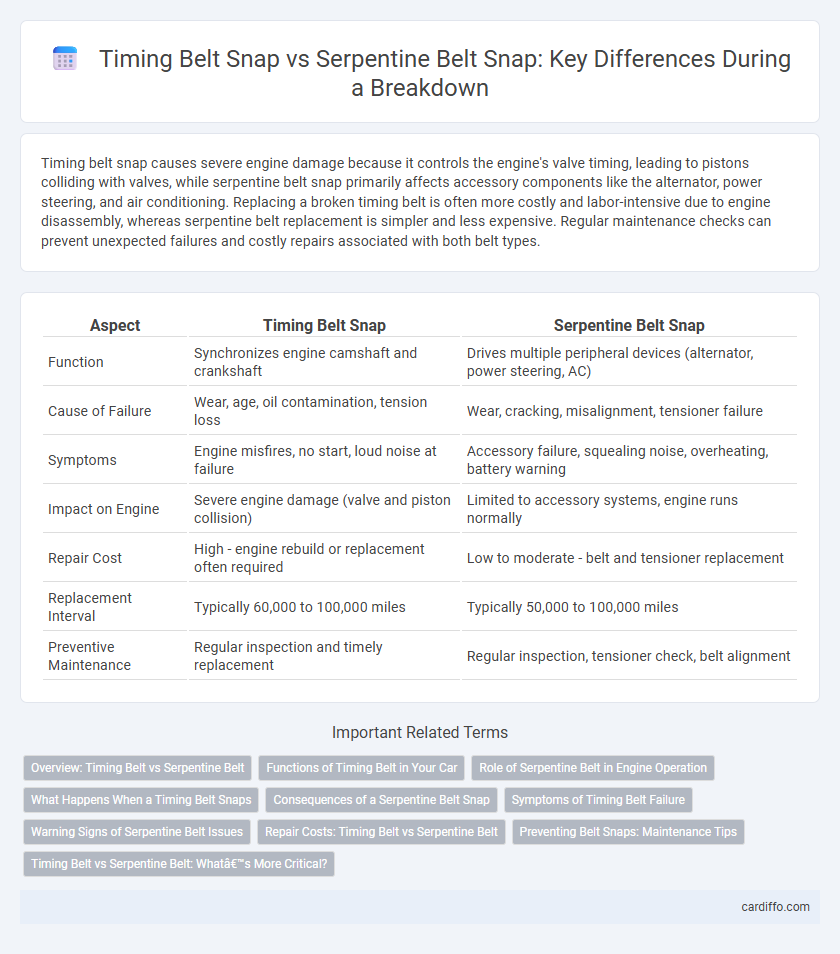
Timing belt snap causes severe engine damage because it controls the engine's valve timing, leading to pistons colliding with valves, while serpentine belt snap primarily affects accessory components like the alternator, power steering, and air conditioning. Replacing a broken timing belt is often more costly and labor-intensive due to engine disassembly, whereas serpentine belt replacement is simpler and less expensive. Regular maintenance checks can prevent unexpected failures and costly repairs associated with both belt types.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Timing Belt Snap | Serpentine Belt Snap |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Synchronizes engine camshaft and crankshaft | Drives multiple peripheral devices (alternator, power steering, AC) |
| Cause of Failure | Wear, age, oil contamination, tension loss | Wear, cracking, misalignment, tensioner failure |
| Symptoms | Engine misfires, no start, loud noise at failure | Accessory failure, squealing noise, overheating, battery warning |
| Impact on Engine | Severe engine damage (valve and piston collision) | Limited to accessory systems, engine runs normally |
| Repair Cost | High - engine rebuild or replacement often required | Low to moderate - belt and tensioner replacement |
| Replacement Interval | Typically 60,000 to 100,000 miles | Typically 50,000 to 100,000 miles |
| Preventive Maintenance | Regular inspection and timely replacement | Regular inspection, tensioner check, belt alignment |
Overview: Timing Belt vs Serpentine Belt
A timing belt synchronizes the engine's camshaft and crankshaft, ensuring precise valve timing critical for engine performance, while a serpentine belt drives multiple peripheral devices like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Timing belt failure often leads to severe engine damage due to misaligned valves and pistons, whereas serpentine belt failure typically results in accessory failure and vehicle breakdown without immediate engine harm. Replacing the timing belt at manufacturer-recommended intervals is crucial for preventing catastrophic engine damage, while serpentine belts generally have a longer lifespan but require timely inspection for cracks or wear.
Functions of Timing Belt in Your Car
The timing belt synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring precise engine valve timing for optimal combustion and engine performance. A timing belt snap can cause severe engine damage due to the abrupt loss of synchronization, often leading to costly repairs. Unlike the serpentine belt, which powers peripheral components such as the alternator and power steering pump, the timing belt is critical for maintaining engine mechanical integrity.
Role of Serpentine Belt in Engine Operation
The serpentine belt drives multiple engine components such as the alternator, water pump, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor, making its integrity crucial for overall engine function. A serpentine belt snap causes immediate loss of essential systems, leading to engine overheating, battery drain, and steering difficulties. Unlike a timing belt, which controls engine timing, the serpentine belt's failure disrupts auxiliary systems, often resulting in a breakdown requiring prompt repair.
What Happens When a Timing Belt Snaps
When a timing belt snaps, the engine's camshaft and crankshaft lose synchronization, causing valves to collide with pistons in interference engines, resulting in severe internal damage. This can lead to bent valves, piston damage, and costly repairs, often requiring engine rebuild or replacement. Unlike a serpentine belt failure that affects accessories like power steering and alternator, a timing belt failure directly impacts engine operation and can cause complete engine failure.
Consequences of a Serpentine Belt Snap
A serpentine belt snap can cause immediate loss of power steering, alternator function, and air conditioning, leading to reduced vehicle control and increased safety risks. Unlike a timing belt snap, which often results in catastrophic engine damage, a serpentine belt failure mainly affects auxiliary systems but can still cause the engine to overheat if the water pump stops functioning. Prompt replacement of a broken serpentine belt is essential to prevent further mechanical issues and maintain safe vehicle operation.
Symptoms of Timing Belt Failure
Timing belt failure typically causes engine misfires, rough idling, and a sudden loss of power as the belt controls the precise timing of engine valves. Unlike serpentine belt snaps, timing belt failure can lead to severe engine damage due to valve and piston collisions in interference engine designs. Symptoms such as ticking noises from the engine or difficulty starting are key indicators of an impending timing belt snap.
Warning Signs of Serpentine Belt Issues
A serpentine belt snap often occurs without much warning, but early signs include squealing noises, visible cracks, and fraying on the belt surface. Reduced performance of accessories like the alternator, power steering, or air conditioning may indicate serpentine belt wear or tension problems. Timely inspection and replacement are crucial to prevent sudden breakdowns caused by serpentine belt failure.
Repair Costs: Timing Belt vs Serpentine Belt
Repair costs for a timing belt snap typically range from $500 to $1,000 or more due to the labor-intensive process of accessing and replacing internal engine components. In contrast, repairing a serpentine belt snap usually costs between $100 and $200, as it involves easier access and replacement without major engine disassembly. Timing belt failure can also cause severe engine damage, increasing repair expenses, while serpentine belt issues mainly affect accessory systems with lower associated costs.
Preventing Belt Snaps: Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection and timely replacement of timing belts and serpentine belts are critical to preventing sudden breakdowns caused by belt snaps. Using manufacturer-recommended tensioning tools ensures optimal belt tension, reducing the risk of premature wear or failure. Maintaining proper belt alignment and avoiding exposure to oil or contaminants significantly extends belt lifespan and vehicle reliability.
Timing Belt vs Serpentine Belt: What’s More Critical?
A timing belt snap can cause severe engine damage by disrupting the synchronization between the crankshaft and camshaft, leading to catastrophic failure in interference engines. In contrast, a serpentine belt snap typically results in the loss of accessories such as the alternator, power steering, and air conditioning but rarely causes engine damage. Therefore, while both failures require immediate attention, timing belt failure is more critical due to its direct impact on engine integrity and expensive repairs.
Timing belt snap vs serpentine belt snap Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com