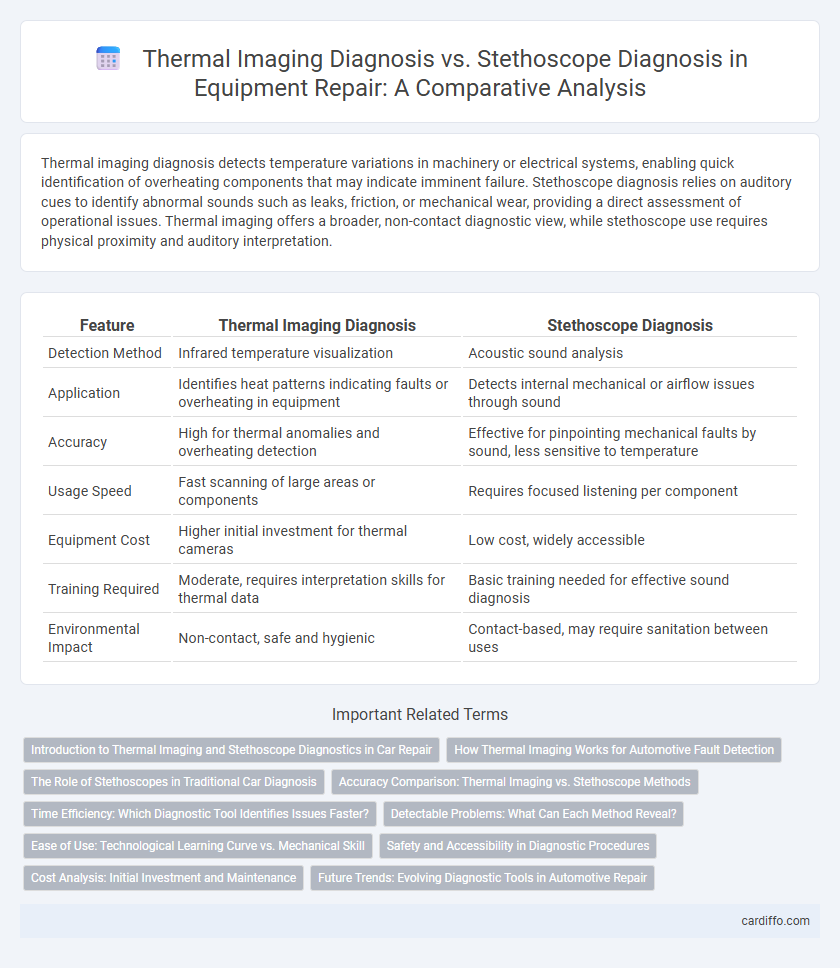
Thermal imaging diagnosis detects temperature variations in machinery or electrical systems, enabling quick identification of overheating components that may indicate imminent failure. Stethoscope diagnosis relies on auditory cues to identify abnormal sounds such as leaks, friction, or mechanical wear, providing a direct assessment of operational issues. Thermal imaging offers a broader, non-contact diagnostic view, while stethoscope use requires physical proximity and auditory interpretation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Thermal Imaging Diagnosis | Stethoscope Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Method | Infrared temperature visualization | Acoustic sound analysis |
| Application | Identifies heat patterns indicating faults or overheating in equipment | Detects internal mechanical or airflow issues through sound |
| Accuracy | High for thermal anomalies and overheating detection | Effective for pinpointing mechanical faults by sound, less sensitive to temperature |
| Usage Speed | Fast scanning of large areas or components | Requires focused listening per component |
| Equipment Cost | Higher initial investment for thermal cameras | Low cost, widely accessible |
| Training Required | Moderate, requires interpretation skills for thermal data | Basic training needed for effective sound diagnosis |
| Environmental Impact | Non-contact, safe and hygienic | Contact-based, may require sanitation between uses |
Introduction to Thermal Imaging and Stethoscope Diagnostics in Car Repair
Thermal imaging diagnostics in car repair utilize infrared cameras to detect and visualize temperature variations, revealing overheating components, electrical faults, and inefficient cooling systems with precise thermal maps. Stethoscope diagnostics involve using a mechanic's stethoscope to listen for abnormal sounds such as engine knock, bearing noise, or air leaks, providing real-time acoustic detection of mechanical issues. Combining thermal imaging and stethoscope tools enhances the accuracy of vehicle diagnostics by addressing both thermal anomalies and sound-based symptoms.
How Thermal Imaging Works for Automotive Fault Detection
Thermal imaging detects automotive faults by capturing infrared radiation emitted from engine components, revealing temperature anomalies that indicate overheating, electrical shorts, or fluid leaks. This method provides a non-contact diagnostic approach, allowing technicians to identify issues early without disassembling parts, which is more efficient compared to stethoscope diagnosis that relies on sound detection. Infrared cameras produce detailed thermal maps, enabling precise localization of problems such as coolant blockages or bearing failures in real-time.
The Role of Stethoscopes in Traditional Car Diagnosis
Stethoscopes have been essential in traditional car diagnosis by enabling mechanics to identify engine and exhaust noises that indicate potential issues such as misfires, bearing failures, or air leaks. This tool provides an immediate, tactile sense of mechanical problems without requiring advanced technology, making it valuable for initial diagnostics. While thermal imaging offers detailed temperature analysis, stethoscopes remain a cost-effective and accessible option for detecting irregular sound patterns in automotive repair.
Accuracy Comparison: Thermal Imaging vs. Stethoscope Methods
Thermal imaging diagnosis offers higher accuracy by detecting temperature variations and underlying issues that are invisible to the naked ear, unlike the traditional stethoscope which relies on auditory cues and can miss subtle anomalies. Studies indicate thermal imaging can identify early-stage faults in machinery and building systems with up to 90% accuracy, whereas stethoscope diagnosis typically achieves around 65-70% accuracy. This technological advantage makes thermal imaging a superior choice for precise and non-invasive repair diagnostics.
Time Efficiency: Which Diagnostic Tool Identifies Issues Faster?
Thermal imaging diagnosis detects temperature anomalies in electrical and mechanical systems within seconds, providing rapid pinpointing of faults often invisible to the naked eye. Stethoscope diagnosis relies on acoustic detection of irregular sounds, which can be time-consuming and requires specialized skill to interpret subtle audio cues accurately. The non-contact, real-time data capture of thermal imaging significantly enhances time efficiency in identifying issues compared to the more manual process of using a stethoscope.
Detectable Problems: What Can Each Method Reveal?
Thermal imaging diagnosis detects temperature anomalies indicating electrical faults, fluid leaks, and mechanical wear invisible to the naked eye, while stethoscope diagnosis identifies auditory signs of issues such as valve leaks, bearing faults, and air or gas flow irregularities. Thermal imaging excels at revealing hidden heat patterns linked to insulation failures, motor overloads, and overheating components, whereas a stethoscope is effective for pinpointing abnormal vibrations, friction, and mechanical noises during operation. Combining both methods enhances diagnostic accuracy by covering both thermal and acoustic indicators of equipment problems.
Ease of Use: Technological Learning Curve vs. Mechanical Skill
Thermal imaging diagnosis offers intuitive user interfaces that reduce the technological learning curve compared to traditional stethoscope diagnosis, which relies heavily on refined mechanical skills developed through extensive practice. While thermal imaging devices enable quick visualization of temperature variations without requiring specialized auditory training, stethoscopes demand precise acoustic interpretation and physical dexterity. The ease of use in thermal imaging accelerates diagnostic efficiency, particularly for technicians with limited clinical experience.
Safety and Accessibility in Diagnostic Procedures
Thermal imaging diagnosis enhances safety by providing non-contact temperature assessments, reducing exposure to harmful substances or environments compared to traditional stethoscope diagnosis. This method increases accessibility by enabling remote evaluations and quicker identification of abnormal heat patterns, which is critical in early problem detection. Stethoscopes require close physical proximity, limiting their use in hazardous or hard-to-reach locations, whereas thermal imaging supports safer, broader diagnostic applications.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Thermal imaging diagnosis requires a higher initial investment, typically ranging from $2,000 to $10,000 for quality equipment, compared to stethoscopes, which generally cost between $20 and $300. Maintenance costs for thermal imagers include calibration and occasional sensor replacements, potentially adding hundreds of dollars annually, whereas stethoscopes have minimal maintenance expenses, primarily related to cleaning and occasional diaphragm replacement. The cost-effectiveness of each tool depends on the diagnostic scope and frequency, with thermal imaging offering advanced capabilities at a higher long-term financial commitment.
Future Trends: Evolving Diagnostic Tools in Automotive Repair
Thermal imaging diagnosis enhances automotive repair by detecting heat patterns and electrical faults invisible to the naked eye, enabling early fault identification that stethoscope diagnosis cannot match. Future trends indicate widespread integration of thermal imaging with AI analytics for predictive maintenance, reducing vehicle downtime and repair costs. Advanced sensor fusion combining thermal data and acoustic signals promises more accurate, non-invasive diagnostics, revolutionizing precision in automotive repair services.
Thermal imaging diagnosis vs stethoscope diagnosis Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com