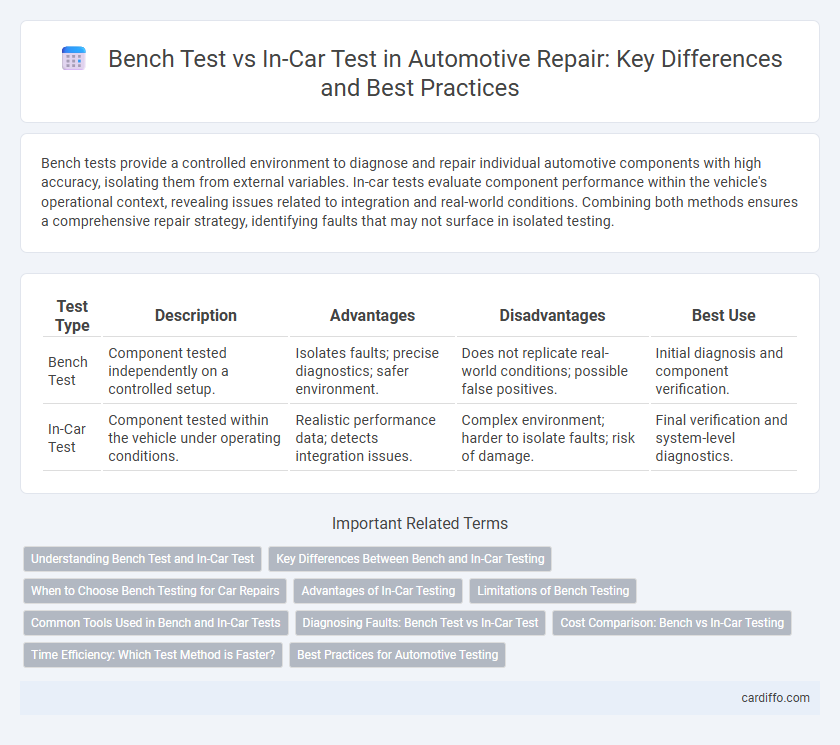
Bench tests provide a controlled environment to diagnose and repair individual automotive components with high accuracy, isolating them from external variables. In-car tests evaluate component performance within the vehicle's operational context, revealing issues related to integration and real-world conditions. Combining both methods ensures a comprehensive repair strategy, identifying faults that may not surface in isolated testing.
Table of Comparison
| Test Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bench Test | Component tested independently on a controlled setup. | Isolates faults; precise diagnostics; safer environment. | Does not replicate real-world conditions; possible false positives. | Initial diagnosis and component verification. |
| In-Car Test | Component tested within the vehicle under operating conditions. | Realistic performance data; detects integration issues. | Complex environment; harder to isolate faults; risk of damage. | Final verification and system-level diagnostics. |
Understanding Bench Test and In-Car Test
Bench test involves evaluating vehicle components in a controlled environment using specialized equipment to simulate operating conditions, enabling precise measurement of performance and faults. In-car test requires installing the component back into the vehicle to observe real-world functionality and interaction with other systems under actual driving conditions. Both tests complement each other by combining controlled diagnostics with practical validation to ensure thorough repair and reliability.
Key Differences Between Bench and In-Car Testing
Bench testing involves evaluating automotive components in a controlled environment outside the vehicle, allowing for precise measurement of performance parameters without external variables. In-car testing assesses the same components within the operational context of the vehicle, capturing real-world conditions such as temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and interactions with other systems. Key differences include the controlled conditions of bench tests versus the dynamic and integrative nature of in-car tests, which influence diagnostic accuracy and repair effectiveness.
When to Choose Bench Testing for Car Repairs
Bench testing is ideal for diagnosing automotive components like fuel injectors, alternators, and sensors outside the vehicle to isolate faults without interference from other systems. It allows technicians to simulate operating conditions precisely, ensuring accurate performance evaluation and reducing diagnostic time. Choose bench testing when component removal is feasible and the goal is to verify part functionality independently from the car's electrical or mechanical systems.
Advantages of In-Car Testing
In-car testing provides real-world conditions that accurately reflect vehicle performance, allowing precise diagnosis of issues under actual operating loads and environments. This method captures dynamic engine behaviors, electrical system responses, and sensor interactions that bench tests cannot replicate. In-car testing enhances reliability by validating repairs in the vehicle's natural operational context, reducing misdiagnosis and repeated repairs.
Limitations of Bench Testing
Bench testing provides controlled conditions for diagnosing individual automotive components, but it cannot replicate the complex interactions and environmental factors present in an actual vehicle. Limitations include the inability to simulate real-world operating conditions such as vibration, temperature fluctuations, and electrical loads that affect component performance. In contrast, in-car testing allows technicians to assess the integrated system functionality, revealing issues that may not appear during isolated bench tests.
Common Tools Used in Bench and In-Car Tests
Common tools used in bench tests include oscilloscopes, multimeters, and signal generators to diagnose electronic control units (ECUs) and sensors outside the vehicle. In-car tests typically involve scan tools, diagnostic trouble code (DTC) readers, and portable oscilloscopes to monitor live data and system interactions under real driving conditions. Both testing methods rely heavily on specialized adapters and connectors to interface with vehicle modules for accurate fault detection and repair verification.
Diagnosing Faults: Bench Test vs In-Car Test
Bench tests offer controlled conditions to diagnose faults by isolating components from the vehicle's electrical system, enabling precise measurement of voltage, resistance, and continuity without external interference. In-car tests provide real-world diagnostics by observing component behavior under actual operating conditions, capturing dynamic interactions and intermittent faults that bench tests might miss. Combining both methods enhances fault diagnosis accuracy, leveraging bench tests for detailed component analysis and in-car tests for system-level performance verification.
Cost Comparison: Bench vs In-Car Testing
Bench testing incurs lower initial costs due to controlled laboratory conditions and standardized equipment, reducing the need for specialized on-site tools. In-car testing involves higher expenses related to vehicle availability, real-time diagnostics, and potential labor-intensive procedures within confined spaces. Overall, bench tests offer a cost-effective solution for early diagnostics, while in-car tests justify their higher cost through complex, real-world condition assessments.
Time Efficiency: Which Test Method is Faster?
Bench testing enables rapid diagnosis by isolating components in a controlled environment, significantly reducing the time required compared to in-car tests. In-car testing often involves additional steps such as vehicle setup and reassembly, leading to longer overall testing durations. For time-sensitive repairs, bench testing offers a faster turnaround without compromising diagnostic accuracy.
Best Practices for Automotive Testing
Bench tests provide a controlled environment to assess automotive components' functionality and identify faults without interference from other vehicle systems. In-car tests validate the performance of repaired parts under real-world conditions, ensuring compatibility and reliability in operational scenarios. Combining bench and in-car testing optimizes diagnostic accuracy and repair quality, minimizing repeat failures and enhancing vehicle safety.
Bench Test vs In-Car Test Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com