Resealing gaskets restores their ability to prevent leaks by applying new sealant, extending the lifespan of the existing gasket without the need for full replacement. Replacing gaskets is necessary when damage, wear, or deformation compromises their functionality beyond repair, ensuring a reliable, long-term seal. Choosing between resealing and replacing depends on the gasket's condition, material type, and the application's pressure and temperature requirements.
Table of Comparison
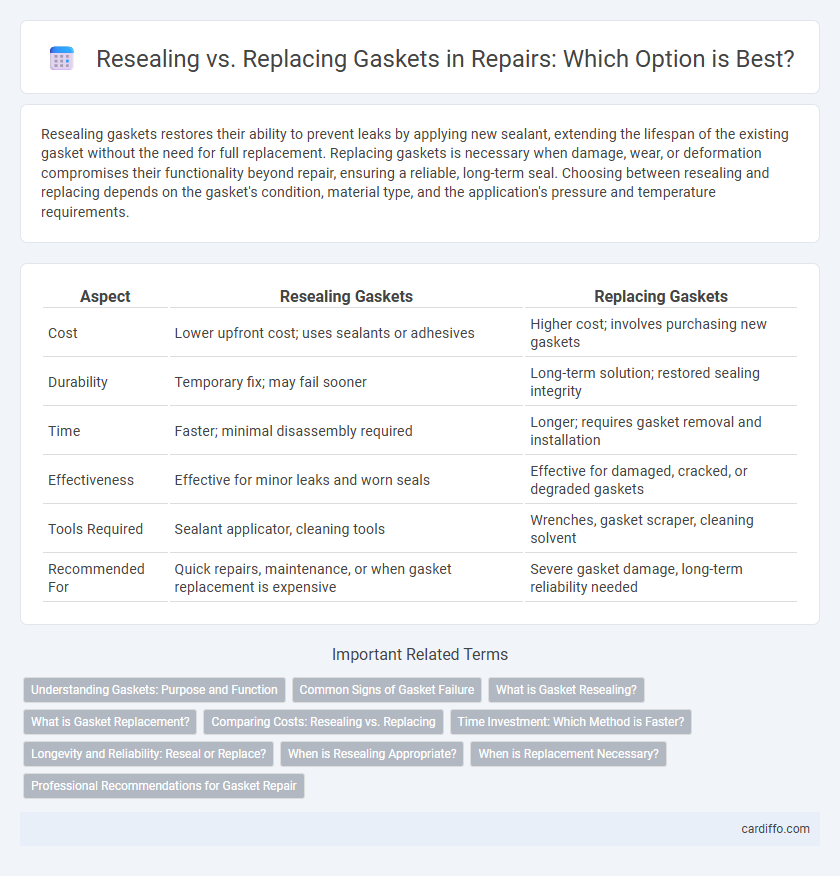
| Aspect | Resealing Gaskets | Replacing Gaskets |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower upfront cost; uses sealants or adhesives | Higher cost; involves purchasing new gaskets |
| Durability | Temporary fix; may fail sooner | Long-term solution; restored sealing integrity |
| Time | Faster; minimal disassembly required | Longer; requires gasket removal and installation |
| Effectiveness | Effective for minor leaks and worn seals | Effective for damaged, cracked, or degraded gaskets |
| Tools Required | Sealant applicator, cleaning tools | Wrenches, gasket scraper, cleaning solvent |
| Recommended For | Quick repairs, maintenance, or when gasket replacement is expensive | Severe gasket damage, long-term reliability needed |
Understanding Gaskets: Purpose and Function
Gaskets serve as critical seals that prevent fluid leaks and maintain pressure between two joined surfaces in machinery and engines. Proper resealing preserves gasket integrity by restoring its sealing capability without the cost and labor of full replacement. Replacing gaskets becomes necessary when damage, wear, or deformation compromises the seal, risking equipment performance and safety.
Common Signs of Gasket Failure
Common signs of gasket failure include visible fluid leaks, unusual engine noises, and overheating. Warped or damaged surfaces caused by prolonged gasket failure can exacerbate issues, leading to decreased engine performance and potential damage. Identifying symptoms early helps determine whether resealing or replacing gaskets is necessary to maintain optimal system integrity.
What is Gasket Resealing?
Gasket resealing involves restoring the seal of an existing gasket by applying sealant or tightening bolts to prevent leaks without removing and replacing the entire gasket. This process is cost-effective and quicker than full gasket replacement, making it ideal for minor leaks or maintenance where the gasket material is still intact. Effective resealing ensures engine components or machinery maintain proper pressure and fluid containment, extending the lifespan of the gasket and reducing downtime.
What is Gasket Replacement?
Gasket replacement involves removing the old, worn gasket and installing a new one to restore a proper seal between two surfaces, preventing leaks and ensuring optimal performance. This process is essential when the gasket is damaged, brittle, or unable to maintain an effective seal due to wear or chemical exposure. Replacing gaskets helps maintain equipment integrity, avoids costly repairs, and improves operational efficiency compared to resealing methods that may only provide a temporary fix.
Comparing Costs: Resealing vs. Replacing
Resealing gaskets typically costs less than replacing due to lower material expenses and reduced labor time. However, resealing may offer only a temporary fix, leading to recurring repairs and cumulative costs. Replacing gaskets demands higher upfront investment but ensures long-term durability and fewer maintenance interventions.
Time Investment: Which Method is Faster?
Resealing gaskets typically requires less time because it involves applying sealant directly to the existing gasket, avoiding the need for extensive disassembly. Replacing gaskets often takes longer due to the necessity of removing and cleaning parts before installing a new gasket to ensure a proper seal. For quicker repairs, resealing is generally the preferred method unless gasket damage necessitates replacement.
Longevity and Reliability: Reseal or Replace?
Resealing gaskets extends the lifespan of existing seals by restoring their integrity without the need for full replacement, offering a cost-effective solution for maintaining equipment reliability. Replacing gaskets, however, provides a complete renewal that ensures optimal sealing performance and reduces the risk of future leaks, enhancing long-term durability. Evaluating factors like material wear, environmental conditions, and critical operational demands helps determine whether resealing or replacing will deliver greater longevity and reliability.
When is Resealing Appropriate?
Resealing gaskets is appropriate when the gasket material remains intact without cracks or severe wear, and the leak is due to minor surface imperfections or improper installation. This method saves time and cost by restoring the seal without complete gasket removal, especially in non-critical applications or where gasket degradation is minimal. Regular inspection for oil or fluid leaks helps determine if resealing can extend the gasket's service life before deciding on full replacement.
When is Replacement Necessary?
Replacement of gaskets becomes necessary when visible damage such as cracks, warping, or severe wear compromises the seal's integrity, causing persistent leaks despite resealing attempts. High-temperature exposure or chemical corrosion can degrade gasket material, necessitating replacement to restore proper functionality. Routine inspection often reveals when the gasket no longer maintains adequate compression, indicating that resealing is insufficient and full replacement is required.
Professional Recommendations for Gasket Repair
Professional recommendations for gasket repair emphasize resealing when the gasket shows minor wear or slight leaks, as this approach preserves the original part and reduces costs. Replacing gaskets is advised when damage is extensive, deformation is visible, or repeated leaks occur, ensuring long-term reliability and preventing further equipment damage. Expert technicians assess gasket material compatibility, pressure ratings, and operating conditions to determine the most effective repair strategy.
Resealing vs replacing gaskets Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com