Single-owner registration simplifies legal control and decision-making by assigning property rights to one individual, ensuring streamlined management and clear responsibility. Multi-owner registration distributes ownership among several parties, promoting shared investment and collaboration but requiring consensus for major decisions. Choosing between single-owner and multi-owner registration depends on the desired balance between autonomy and collective participation in property management.
Table of Comparison
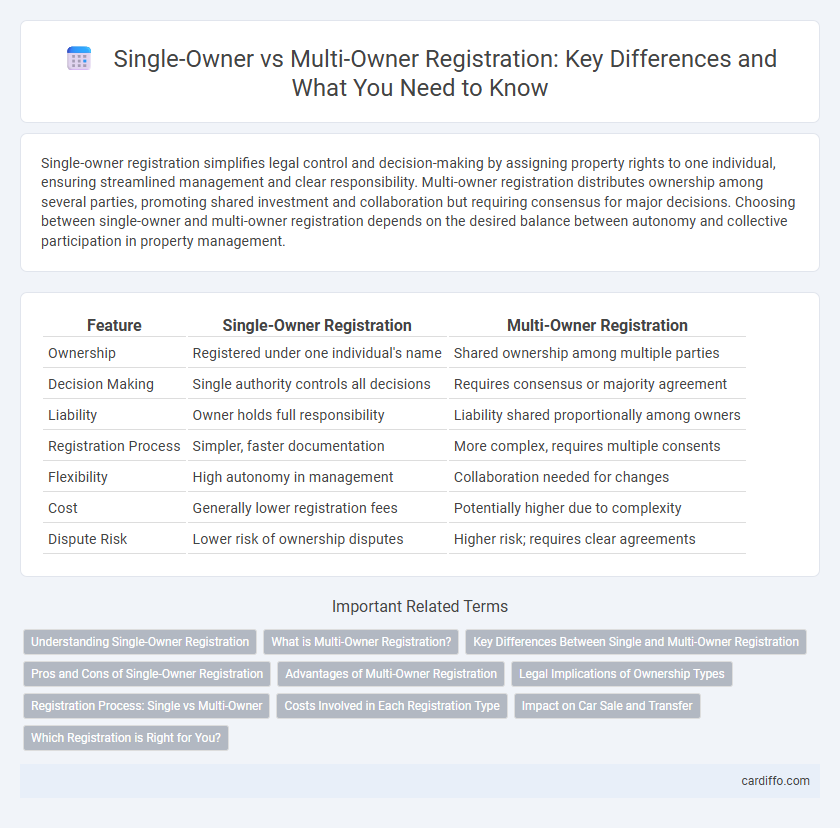
| Feature | Single-Owner Registration | Multi-Owner Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Registered under one individual's name | Shared ownership among multiple parties |
| Decision Making | Single authority controls all decisions | Requires consensus or majority agreement |
| Liability | Owner holds full responsibility | Liability shared proportionally among owners |
| Registration Process | Simpler, faster documentation | More complex, requires multiple consents |
| Flexibility | High autonomy in management | Collaboration needed for changes |
| Cost | Generally lower registration fees | Potentially higher due to complexity |
| Dispute Risk | Lower risk of ownership disputes | Higher risk; requires clear agreements |
Understanding Single-Owner Registration
Single-owner registration grants full control and legal ownership rights to one individual, simplifying decision-making and liability management. This registration type streamlines documentation and tax reporting processes as only one owner is accountable. It is ideal for sole proprietors or individuals seeking clear ownership boundaries without shared responsibilities.
What is Multi-Owner Registration?
Multi-owner registration allows multiple individuals or entities to jointly register a property or asset, establishing shared ownership rights and responsibilities. This method enhances legal clarity by defining each owner's interest, facilitating smoother transactions and dispute resolution. Multi-owner registration is commonly used in business partnerships, co-owned real estate, and joint ventures to ensure transparent and equitable management.
Key Differences Between Single and Multi-Owner Registration
Single-owner registration grants exclusive control and decision-making authority to one individual, simplifying legal responsibilities and management. In contrast, multi-owner registration involves shared ownership rights, requiring consensus among parties for actions and distributing liabilities proportionally. Understanding these distinctions impacts governance, dispute resolution, and financial obligations.
Pros and Cons of Single-Owner Registration
Single-owner registration offers streamlined decision-making and simplified management, reducing administrative overhead and potential conflicts among owners. However, it concentrates liability and financial responsibility solely on one individual, which may increase personal risk in case of legal or financial issues. Limited access to diverse resources and expertise compared to multi-owner registration can also hinder growth opportunities.
Advantages of Multi-Owner Registration
Multi-owner registration enhances asset security by distributing ownership rights among multiple individuals, reducing the risk of unilateral decisions or fraud. It facilitates streamlined decision-making and shared responsibility, promoting transparency and trust among co-owners. This registration method also enables efficient succession planning, ensuring smoother transfer of ownership in case of an owner's incapacity or death.
Legal Implications of Ownership Types
Single-owner registration grants full legal control and responsibility over the property, simplifying decision-making but increasing liability for any disputes or debts. Multi-owner registration introduces shared legal rights and obligations, requiring clear agreements to manage ownership percentages, transfer restrictions, and conflict resolution. Understanding the legal framework of each ownership type is essential to protect interests and ensure compliance with property laws.
Registration Process: Single vs Multi-Owner
The single-owner registration process requires submitting details and documentation tied to one individual, simplifying verification and reducing administrative steps. Multi-owner registration involves collecting and validating information from all parties, requiring additional coordination to ensure each owner's consent and legal compliance. This complexity often results in longer processing times and more stringent review to secure unanimous agreement among co-owners.
Costs Involved in Each Registration Type
Single-owner registration typically involves lower administrative fees and simpler paperwork, resulting in reduced overall costs compared to multi-owner registration. Multi-owner registration often incurs higher expenses due to the need for additional documentation, shared legal fees, and potential costs related to dispute resolution agreements. Businesses and property owners should carefully evaluate these cost differences when choosing between single-owner and multi-owner registration to optimize budget efficiency.
Impact on Car Sale and Transfer
Single-owner registration simplifies the car sale and transfer process by allowing ownership to be transferred quickly to a new buyer without requiring consent from multiple parties. Multi-owner registration can complicate the sale and transfer since all registered owners must agree and sign off, potentially causing delays and legal disputes. Clear documentation and consensus among multi-owners are essential to ensure smooth transactions and avoid ownership conflicts during a vehicle sale.
Which Registration is Right for You?
Single-owner registration offers full control and simplified decision-making, ideal for solo entrepreneurs or sole proprietors seeking streamlined management. Multi-owner registration benefits partnerships and joint ventures by allowing shared responsibilities, diversified expertise, and combined financial resources. Choosing the right registration depends on your business structure, liability preferences, and operational goals.
Single-Owner Registration vs Multi-Owner Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com