Private sale registration involves transferring ownership of a vehicle between individual parties without commercial intent, typically requiring fewer documentation and lower fees. Commercial registration applies to vehicles used for business purposes, mandating compliance with stricter regulations, higher fees, and additional documentation such as proof of business operation. Understanding the distinctions ensures proper legal compliance and avoids penalties during the vehicle registration process.
Table of Comparison
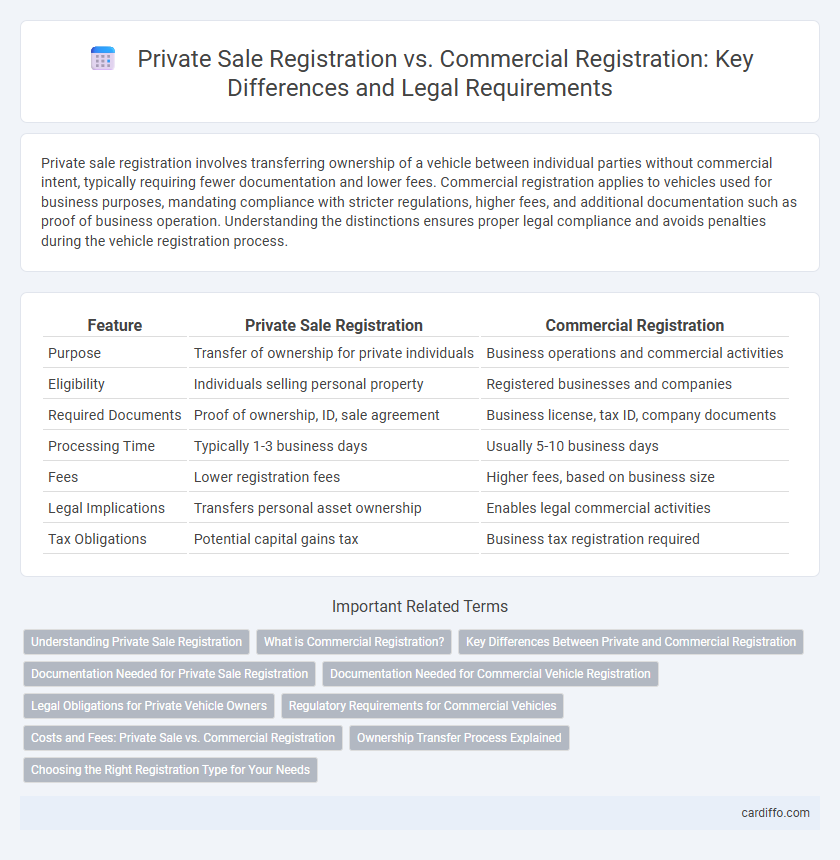
| Feature | Private Sale Registration | Commercial Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Transfer of ownership for private individuals | Business operations and commercial activities |
| Eligibility | Individuals selling personal property | Registered businesses and companies |
| Required Documents | Proof of ownership, ID, sale agreement | Business license, tax ID, company documents |
| Processing Time | Typically 1-3 business days | Usually 5-10 business days |
| Fees | Lower registration fees | Higher fees, based on business size |
| Legal Implications | Transfers personal asset ownership | Enables legal commercial activities |
| Tax Obligations | Potential capital gains tax | Business tax registration required |
Understanding Private Sale Registration
Private Sale Registration involves documenting the transfer of ownership between private individuals without dealer involvement, ensuring legal recognition and compliance with local vehicle laws. Unlike Commercial Registration, which applies to businesses and requires additional permits and taxes, Private Sale Registration typically entails fewer fees and simpler paperwork. Understanding the necessary documents, such as the title transfer form, bill of sale, and proof of insurance, is crucial for a successful private sale registration process.
What is Commercial Registration?
Commercial registration refers to the legal process through which a business entity is officially recorded with government authorities, enabling it to operate legally within a specific jurisdiction. It involves the submission of essential documents such as business name, ownership details, and business activity descriptions, which are necessary for compliance with regulatory requirements. This registration distinguishes commercial enterprises from private sales, ensuring transparency, accountability, and eligibility for business-related licenses and tax obligations.
Key Differences Between Private and Commercial Registration
Private sale registration typically involves the transfer of ownership between individual buyers and sellers without business involvement, focusing on personal asset transactions. Commercial registration pertains to business-related transfers, requiring compliance with regulatory standards, including tax documentation and licensing specific to commercial entities. Key differences lie in the legal requirements, transaction purposes, and the level of regulatory scrutiny applied to ensure proper tax and legal adherence in commercial versus private sales.
Documentation Needed for Private Sale Registration
Private Sale Registration requires essential documentation including a valid government-issued ID, proof of vehicle ownership such as the title or bill of sale, and a completed registration application form. Sellers must provide a notarized bill of sale to verify the transaction, while buyers need to present proof of insurance and payment of applicable taxes and fees. Unlike Commercial Registration, Private Sale Registration typically does not require extensive corporate documents or commercial vehicle permits.
Documentation Needed for Commercial Vehicle Registration
Commercial vehicle registration requires comprehensive documentation including the vehicle's original invoice, proof of insurance, emission test certificates, and a commercial use permit. Owners must also provide proof of identity, address, and a valid driver's license, alongside specialized forms such as the commercial vehicle registration application and tax receipts. Unlike private sale registration, commercial registration often involves additional endorsements and compliance with regulatory standards for business operation and safety inspections.
Legal Obligations for Private Vehicle Owners
Private sale registration requires the transfer of ownership through a bill of sale and submission to the local DMV, ensuring the new owner assumes legal responsibility and liability. Commercial registration mandates additional documentation such as proof of business use, commercial insurance, and compliance with safety regulations tailored for vehicles used in commerce. Legal obligations for private vehicle owners focus on accurate title transfer, timely registration renewal, and adherence to state emissions and safety inspections.
Regulatory Requirements for Commercial Vehicles
Commercial vehicle registration requires adherence to strict regulatory standards including proof of insurance, compliance with safety inspections, and obtaining proper permits for commercial use. Unlike private sale registration, which typically involves verifying ownership and basic vehicle information, commercial registration mandates additional documentation such as tax identification numbers and proof of business operation. Regulatory requirements also encompass emissions testing and adherence to weight and size limits governed by federal and state transportation authorities.
Costs and Fees: Private Sale vs. Commercial Registration
Private sale registration typically incurs lower costs and minimal fees as it involves the transfer of ownership between individuals without the need for extensive documentation. Commercial registration demands higher fees due to additional requirements such as business licenses, permits, and compliance with regulatory standards. The cost disparity reflects the administrative complexity and legal obligations associated with commercial vehicle use compared to private ownership.
Ownership Transfer Process Explained
Private sale registration involves a straightforward ownership transfer process where the seller and buyer complete the necessary paperwork, submit the required documents--such as the signed title deed and proof of identification--to the relevant motor vehicle department, and pay applicable fees to update the vehicle's ownership records. Commercial registration for ownership transfer requires additional steps, including compliance with business licensing, verification of commercial use, and adherence to regulatory standards, which often entails submitting commercial invoices, business permits, and updated insurance information alongside standard transfer documents. Both processes ensure legal transfer of ownership, but commercial registrations demand more stringent documentation and regulatory compliance due to the vehicle's commercial application.
Choosing the Right Registration Type for Your Needs
Choosing the right registration type depends on your specific requirements: Private Sale Registration is ideal for individual sellers dealing in limited quantities, offering simpler procedures and lower fees, while Commercial Registration suits businesses with ongoing sales, enabling higher transaction volumes and compliance with regulatory standards. Assess your transaction frequency, business scale, and tax obligations to determine the appropriate registration type. Proper selection ensures legal compliance, optimized tax benefits, and streamlined operations tailored to private or commercial activities.
Private Sale Registration vs Commercial Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com