Private registration protects your personal information by keeping your contact details hidden in domain records, enhancing privacy and reducing spam. Commercial registration emphasizes branding and business identity, often including services like bulk domain management, SSL certificates, and professional email setups. Choosing between private and commercial registration depends on prioritizing confidentiality or leveraging business-focused tools for online presence.
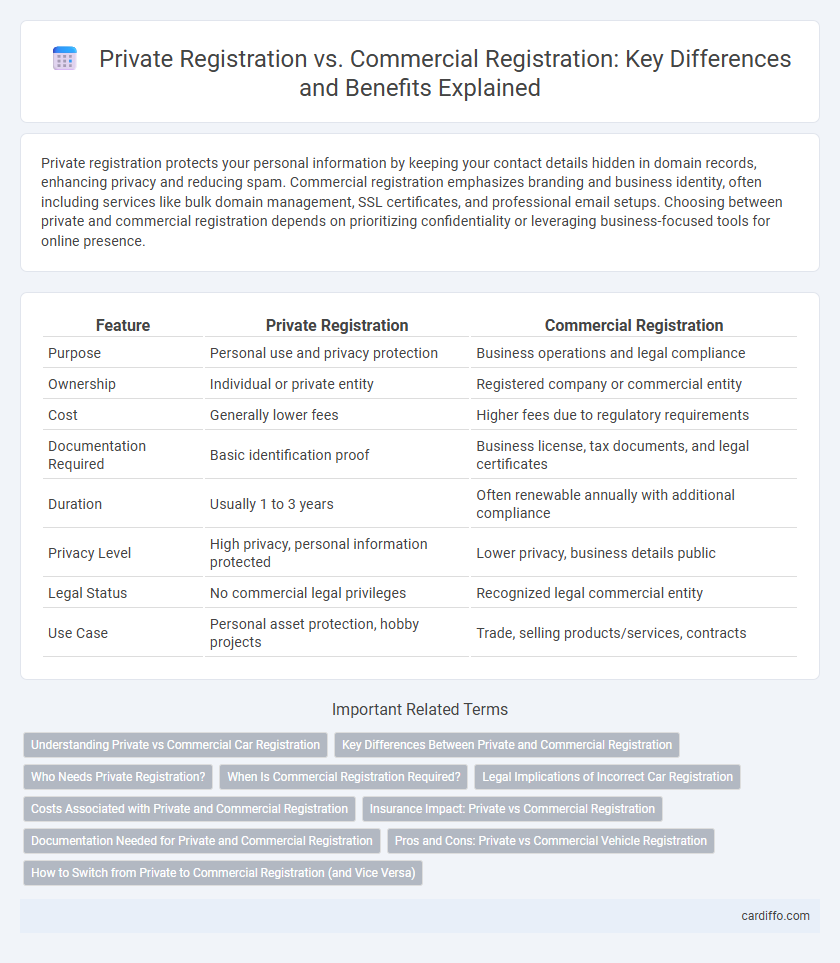
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Private Registration | Commercial Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Personal use and privacy protection | Business operations and legal compliance |
| Ownership | Individual or private entity | Registered company or commercial entity |
| Cost | Generally lower fees | Higher fees due to regulatory requirements |
| Documentation Required | Basic identification proof | Business license, tax documents, and legal certificates |
| Duration | Usually 1 to 3 years | Often renewable annually with additional compliance |
| Privacy Level | High privacy, personal information protected | Lower privacy, business details public |
| Legal Status | No commercial legal privileges | Recognized legal commercial entity |
| Use Case | Personal asset protection, hobby projects | Trade, selling products/services, contracts |
Understanding Private vs Commercial Car Registration
Private car registration refers to the process where individuals register their vehicles for personal use, ensuring ownership is legally recognized and recorded under their name. Commercial registration applies to vehicles used for business purposes, including goods transport or passenger services, requiring compliance with additional regulations and higher fees. Understanding the distinction helps vehicle owners select the appropriate registration type based on usage, affecting insurance, taxation, and legal obligations.
Key Differences Between Private and Commercial Registration
Private registration is typically used for individual or small business purposes and offers enhanced privacy by concealing personal information from public databases. Commercial registration applies to businesses engaged in commercial activities and requires disclosure of company details to ensure transparency and legal compliance. Key differences include privacy levels, disclosure requirements, and the nature of entity use, with private registration favoring confidentiality and commercial registration prioritizing regulatory adherence.
Who Needs Private Registration?
Individuals who prioritize privacy and wish to keep their personal information confidential on domain name registries need Private Registration. This service shields personal details such as name, address, and contact information from public WHOIS databases, reducing exposure to spam, identity theft, and unauthorized solicitations. Private Registration is ideal for private website owners, bloggers, and small business owners seeking to maintain anonymity online.
When Is Commercial Registration Required?
Commercial registration is required when a business engages in activities aimed at generating profit, such as selling goods or providing services publicly. Unlike private registration, which is typically used for sole proprietors or informal enterprises, commercial registration ensures compliance with local regulations and grants legal recognition to entities operating commercially. This process is crucial for businesses exceeding specific revenue thresholds or employing multiple staff members, as mandated by jurisdictional laws.
Legal Implications of Incorrect Car Registration
Incorrect car registration can result in severe legal consequences, including fines, vehicle impoundment, and potential criminal charges, particularly when using private registration improperly for commercial purposes. Private registration is intended solely for personal use, whereas commercial registration legally authorizes business-related vehicle activity, ensuring compliance with tax, insurance, and safety regulations. Failure to maintain accurate registration status may void insurance coverage and lead to liability issues in accidents or inspections, emphasizing the necessity of correct classification.
Costs Associated with Private and Commercial Registration
Private registration typically involves lower upfront costs, including basic registration fees and minimal ongoing expenses, making it ideal for individual use or small-scale operations. Commercial registration often incurs higher fees due to additional requirements such as liability coverage, regulatory compliance, and periodic renewals mandated by business operations. Businesses should also budget for potential costs related to legal consultations and insurance premiums that are commonly associated with commercial registration.
Insurance Impact: Private vs Commercial Registration
Private registration typically results in lower insurance premiums due to limited usage and reduced risk profiles compared to commercial registration. Commercial registration often leads to higher insurance costs as vehicles are exposed to increased liability, heavier usage, and stricter regulatory requirements. Insurance policies for commercial vehicles generally include broader coverage options to address the higher risks associated with business operations.
Documentation Needed for Private and Commercial Registration
Private registration requires a government-issued ID, proof of address, and sometimes a social security number or taxpayer identification. Commercial registration demands more extensive documentation, including business licenses, articles of incorporation, tax identification numbers, and proof of ownership or authorization to operate. Both processes may require additional documents specific to the jurisdiction or industry for verification and compliance.
Pros and Cons: Private vs Commercial Vehicle Registration
Private vehicle registration offers lower fees and simpler renewal processes, making it ideal for personal use and individual ownership. Commercial vehicle registration requires higher fees and stricter compliance with safety and operational standards, but provides benefits like tax deductions and access to commercial insurance. Choosing between private and commercial registration depends on the vehicle's intended use, with private suited for personal driving and commercial necessary for profit-related transport and logistics.
How to Switch from Private to Commercial Registration (and Vice Versa)
Switching from private to commercial registration or vice versa requires updating your business classification with the relevant government authority, such as the Department of Motor Vehicles or business registration office. Submit the necessary application forms, provide supporting documentation like proof of business use or personal use, and pay applicable fees to complete the transition. Ensure all vehicle insurance policies and tax records reflect the updated registration type to maintain compliance and avoid penalties.
Private Registration vs Commercial Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com