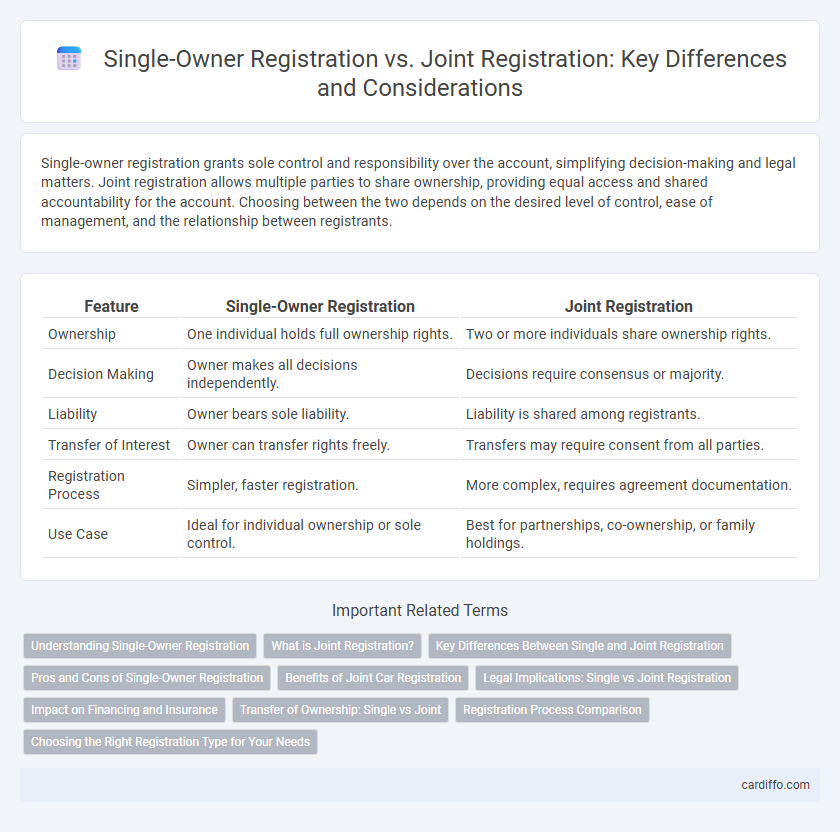
Single-owner registration grants sole control and responsibility over the account, simplifying decision-making and legal matters. Joint registration allows multiple parties to share ownership, providing equal access and shared accountability for the account. Choosing between the two depends on the desired level of control, ease of management, and the relationship between registrants.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Single-Owner Registration | Joint Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | One individual holds full ownership rights. | Two or more individuals share ownership rights. |
| Decision Making | Owner makes all decisions independently. | Decisions require consensus or majority. |
| Liability | Owner bears sole liability. | Liability is shared among registrants. |
| Transfer of Interest | Owner can transfer rights freely. | Transfers may require consent from all parties. |
| Registration Process | Simpler, faster registration. | More complex, requires agreement documentation. |
| Use Case | Ideal for individual ownership or sole control. | Best for partnerships, co-ownership, or family holdings. |
Understanding Single-Owner Registration
Single-owner registration assigns ownership rights solely to one individual, simplifying control and decision-making over the registered asset. This type of registration ensures that legal and financial responsibilities rest entirely with the single owner, minimizing disputes commonly associated with joint ownership. Choosing single-owner registration allows for straightforward asset management and clear transfer protocols in legal or financial transactions.
What is Joint Registration?
Joint registration allows two or more individuals to hold ownership of an asset or account simultaneously, providing shared control and rights. This type of registration is commonly used for bank accounts, property titles, and investment portfolios, enabling co-owners to manage and access the asset collectively. Beneficial for couples, business partners, or family members, joint registration ensures that the asset passes directly to surviving owners without probate.
Key Differences Between Single and Joint Registration
Single-owner registration designates one individual as the sole account holder, granting exclusive control and responsibility over the account. Joint registration involves two or more individuals sharing ownership rights, allowing all parties to access and manage the account equally. Crucial distinctions include control authority, liability implications, and inheritance procedures, with single registration offering straightforward management while joint registration facilitates shared decision-making and survivorship benefits.
Pros and Cons of Single-Owner Registration
Single-owner registration offers complete control over the account, allowing the individual to make decisions independently without requiring consent from others, which streamlines management and reduces potential conflicts. However, it lacks the benefit of shared responsibility and protection, making the single owner solely liable for all activities and decisions associated with the account. This form of registration is optimal for those seeking full autonomy but may pose risks in terms of asset security and succession planning.
Benefits of Joint Car Registration
Joint car registration offers shared ownership rights, enabling both parties to have equal legal access and responsibilities for the vehicle. It simplifies insurance processes, often resulting in reduced premiums by leveraging combined driving records. Furthermore, joint registration facilitates smoother asset transfer in case of sale or inheritance, providing stronger protection for co-owners.
Legal Implications: Single vs Joint Registration
Single-owner registration grants complete control and sole legal responsibility over the asset, simplifying decision-making but exposing the individual to full liability. Joint registration distributes legal ownership among all parties, requiring consensus for major decisions and potentially complicating liability issues. Understanding the distinct legal implications of single versus joint registration is crucial for effective asset management and risk allocation.
Impact on Financing and Insurance
Single-owner registration simplifies the financing process by allowing a single credit profile to be assessed, often resulting in quicker loan approvals and straightforward insurance underwriting. Joint registration involves multiple owners, which can complicate financing due to combined credit evaluations and potentially higher insurance premiums reflecting shared liability. Lenders may offer better rates for single-owner registrations, while joint registrations provide risk distribution but require careful coordination between parties for insurance claims and loan obligations.
Transfer of Ownership: Single vs Joint
Single-owner registration allows for straightforward transfer of ownership, with only one party required to authorize and complete the process, minimizing delays and legal complexities. Joint registration necessitates the consent of all registered parties to transfer ownership, ensuring shared control but potentially slowing down the transaction if any co-owner disagrees or delays approval. This distinction impacts the ease and speed of ownership transfer, influencing decisions in estate planning and asset management.
Registration Process Comparison
Single-owner registration involves one individual completing the entire registration process, simplifying documentation and approval procedures. Joint registration requires all parties to provide identification and consent, often resulting in longer processing times due to multiple validations. Verification steps and legal responsibilities differ between both methods, impacting the overall registration timeline and management rights.
Choosing the Right Registration Type for Your Needs
Single-owner registration provides exclusive control and simplifies decision-making for individual asset management, ideal for those seeking full authority over their accounts or properties. Joint registration allows multiple owners to share rights and responsibilities, enhancing flexibility and offering benefits such as survivorship rights and easier access for spouses or business partners. Evaluating factors like control preferences, legal implications, and the nature of the asset helps determine the optimal registration type tailored to personal or collaborative ownership needs.
Single-Owner Registration vs Joint Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com