Resident registration for pets requires proof of local residence and compliance with municipal regulations, ensuring pets are accounted for within community safety frameworks. Non-resident registration typically applies to temporary pet stays or owners living outside the municipality, often requiring additional documentation and adherence to different rules. Understanding these distinctions helps streamline the registration process and ensures pets are properly listed regardless of the owner's residency status.
Table of Comparison
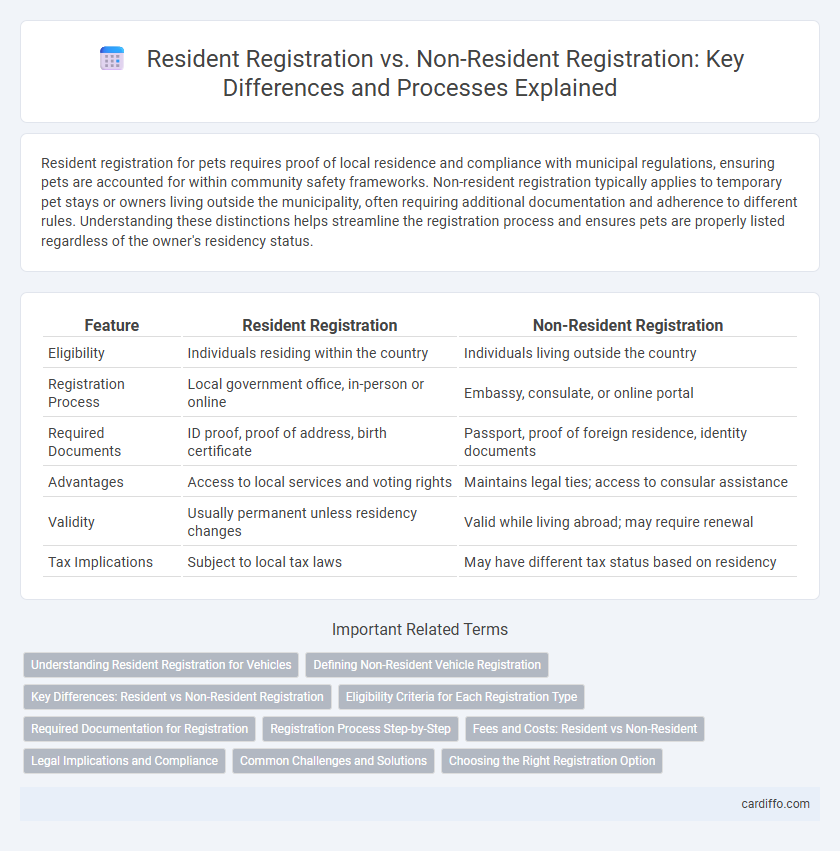
| Feature | Resident Registration | Non-Resident Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Individuals residing within the country | Individuals living outside the country |
| Registration Process | Local government office, in-person or online | Embassy, consulate, or online portal |
| Required Documents | ID proof, proof of address, birth certificate | Passport, proof of foreign residence, identity documents |
| Advantages | Access to local services and voting rights | Maintains legal ties; access to consular assistance |
| Validity | Usually permanent unless residency changes | Valid while living abroad; may require renewal |
| Tax Implications | Subject to local tax laws | May have different tax status based on residency |
Understanding Resident Registration for Vehicles
Resident registration for vehicles requires the owner to register the vehicle in the jurisdiction where they primarily reside, ensuring compliance with local laws and tax obligations. This process typically involves submitting proof of residency, vehicle identification documents, and paying applicable registration fees, which vary by region. Understanding the distinctions between resident and non-resident registration helps avoid penalties and facilitates proper vehicle insurance coverage.
Defining Non-Resident Vehicle Registration
Non-resident vehicle registration allows individuals who do not permanently reside in a state or country to legally register their vehicles for temporary use within that jurisdiction. This registration type typically requires proof of residency elsewhere, temporary stay documentation, and compliance with local vehicle regulations. Non-resident registration facilitates lawful operation and legal accountability for vehicles owned by out-of-state or foreign residents during their visits.
Key Differences: Resident vs Non-Resident Registration
Resident registration involves enrolling individuals who live permanently within a specific jurisdiction, ensuring access to local services and legal rights. Non-resident registration applies to individuals temporarily present or without permanent residence, often limiting eligibility for benefits or voting rights. Key differences include duration of stay, eligibility for social services, and legal obligations tied to residency status.
Eligibility Criteria for Each Registration Type
Resident registration requires individuals to have a primary place of residence within the jurisdiction and typically mandates continuous physical presence for a specified period, often six months or more. Non-resident registration is available for those who maintain legal ties, such as property ownership or business interests within the area, but do not reside there permanently. Eligibility criteria for non-residents usually include proof of sustained connection without meeting residency duration requirements.
Required Documentation for Registration
Resident registration requires proof of local residency such as a utility bill, government-issued ID, or lease agreement, along with personal identification documents like a passport or birth certificate. Non-resident registration demands additional documents, including a valid visa, international passport, and sometimes a letter of authorization or proof of temporary stay. Both processes necessitate accurate completion of registration forms and may require biometric data submission depending on jurisdiction.
Registration Process Step-by-Step
The resident registration process involves submitting proof of residency, identity verification, and completing an application form at the local municipal office, followed by receiving a resident registration certificate. Non-resident registration requires providing valid identification, proof of non-residency status, and completing an online or in-person application, often involving additional documentation such as employment or study verification. Both processes typically conclude with a confirmation receipt or registration number to access government services or benefits.
Fees and Costs: Resident vs Non-Resident
Resident registration fees are typically lower due to local subsidies and streamlined processing, often ranging between $50 to $150 depending on the jurisdiction. Non-resident registration incurs higher costs, commonly exceeding $200, reflecting additional administrative efforts and lack of local fee discounts. These financial differences impact budgeting decisions for individuals and businesses considering their registration status.
Legal Implications and Compliance
Resident registration requires individuals to comply with local laws mandating accurate address documentation, which affects taxation, voting rights, and access to public services. Non-resident registration often involves additional legal scrutiny related to visa status, tax obligations, and eligibility for government benefits, with penalties for non-compliance varying by jurisdiction. Understanding these distinctions ensures adherence to regulatory requirements and minimizes risks of legal penalties or loss of rights.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Resident registration often faces challenges such as proof of address verification and documentation inconsistencies, while non-resident registration struggles with verifying foreign credentials and maintaining updated contact information. Both processes can benefit from implementing integrated digital platforms that enable secure data sharing and real-time updates. Deploying AI-driven verification tools reduces errors and expedites approval, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of registration systems.
Choosing the Right Registration Option
Selecting between Resident Registration and Non-Resident Registration depends on the individual's primary place of stay and tax obligations. Resident Registration is ideal for those living within the country for more than 183 days annually, ensuring compliance with local laws and access to resident benefits. Non-Resident Registration suits individuals with temporary or infrequent presence, minimizing tax liabilities while maintaining legal recognition.
Resident Registration vs Non-Resident Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com