Personal registration is designed for individual users who need to access services or create accounts for non-business purposes, ensuring a streamlined and straightforward process tailored to private use. Commercial registration caters to businesses and organizations, often requiring additional documentation and compliance with legal standards to verify business legitimacy and support commercial activities. Differentiating between personal and commercial registration helps optimize user experiences and maintain regulatory compliance across various platforms.
Table of Comparison
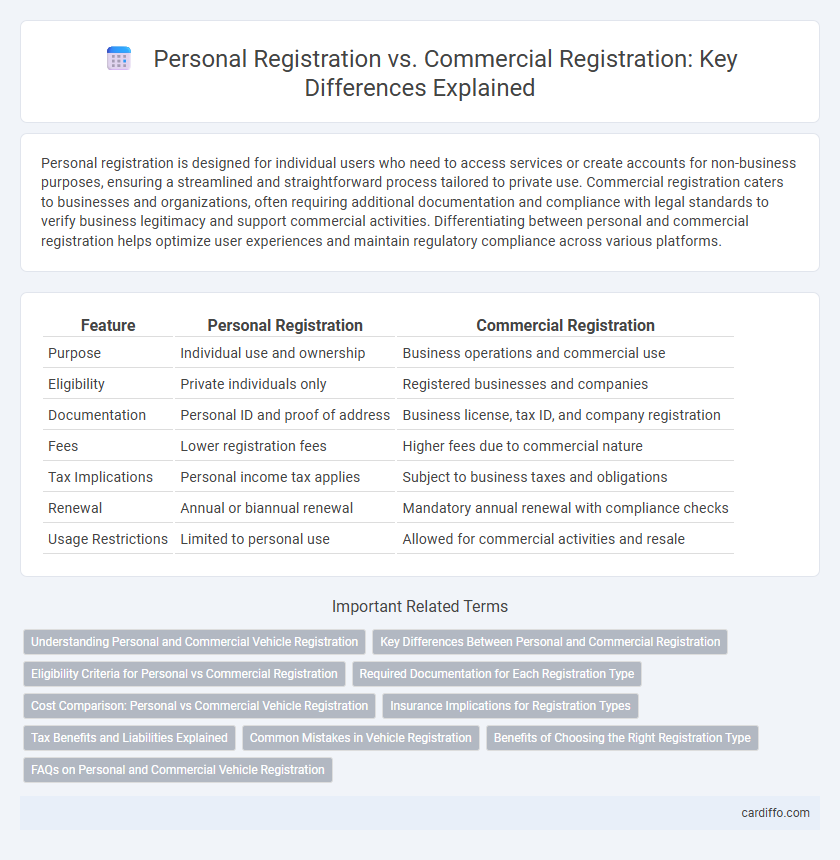
| Feature | Personal Registration | Commercial Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Individual use and ownership | Business operations and commercial use |
| Eligibility | Private individuals only | Registered businesses and companies |
| Documentation | Personal ID and proof of address | Business license, tax ID, and company registration |
| Fees | Lower registration fees | Higher fees due to commercial nature |
| Tax Implications | Personal income tax applies | Subject to business taxes and obligations |
| Renewal | Annual or biannual renewal | Mandatory annual renewal with compliance checks |
| Usage Restrictions | Limited to personal use | Allowed for commercial activities and resale |
Understanding Personal and Commercial Vehicle Registration
Personal vehicle registration involves registering a vehicle owned by an individual for private use, typically requiring proof of ownership, identification, and insurance. Commercial vehicle registration applies to vehicles used for business purposes, often subject to different regulations, higher fees, weight limits, and additional safety inspections. Understanding the distinctions ensures compliance with local DMV requirements and avoids penalties related to misclassification.
Key Differences Between Personal and Commercial Registration
Personal registration typically applies to individual users registering for services or accounts without a business purpose, while commercial registration is intended for entities conducting business activities. Key differences include legal requirements, such as the need for business licenses and tax identification for commercial registration, which are not required for personal registration. Commercial registration often involves stricter verification processes and documentation to ensure compliance with industry regulations and tax laws.
Eligibility Criteria for Personal vs Commercial Registration
Personal registration eligibility requires individuals to be of legal age, possess a valid identification document, and have a residential address proof. Commercial registration demands businesses to provide a valid business license, taxpayer identification number, and proof of commercial activity at a registered business address. Both types often necessitate compliance with local regulations and submission of required documentation for verification.
Required Documentation for Each Registration Type
Personal registration requires a valid government-issued ID, proof of address, and a birth certificate or social security number for identity verification. Commercial registration demands additional documents such as business licenses, tax identification numbers, articles of incorporation, and partnership agreements to validate commercial operations. Both registration types mandate completed application forms and relevant fees to process the registration effectively.
Cost Comparison: Personal vs Commercial Vehicle Registration
Personal vehicle registration typically incurs lower fees compared to commercial vehicle registration due to differences in tax rates, insurance premiums, and regulatory requirements. Commercial vehicle registration costs often include higher licensing fees, additional permits, and increased insurance expenses reflecting the vehicle's business use. Understanding these cost disparities helps individuals and businesses budget accurately for vehicle ownership and operation expenses.
Insurance Implications for Registration Types
Personal registration typically offers lower insurance premiums due to reduced risk associated with non-commercial use, while commercial registration often results in higher premiums reflecting increased liability exposure. Insurance policies for commercial vehicles require broader coverage to account for business-related risks such as cargo damage and employee liability. Understanding the insurance implications of registration types is crucial for selecting appropriate coverage and managing overall costs effectively.
Tax Benefits and Liabilities Explained
Personal registration typically subjects individuals to simplified tax rates and fewer deductible expenses, minimizing liabilities but limiting tax benefits. Commercial registration allows for broader tax deductions on business expenses and potential access to credits, increasing tax benefits while also imposing stricter liabilities such as corporate taxes and compliance requirements. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize tax strategy by balancing obligations with eligible benefits in personal versus commercial contexts.
Common Mistakes in Vehicle Registration
Common mistakes in vehicle registration often involve confusing personal registration with commercial registration requirements, leading to incorrect documentation submission. Many individuals fail to accurately classify their vehicle's intended use, resulting in improper fee payments and non-compliance with state regulations. Ensuring correct vehicle classification and understanding distinct liability obligations are crucial for a smooth registration process.
Benefits of Choosing the Right Registration Type
Selecting the appropriate registration type--personal or commercial--maximizes legal protections and tax advantages tailored to individual or business needs. Personal registration typically offers simplicity and privacy for individual use, while commercial registration ensures compliance with business laws and access to trade benefits. Making an informed choice enhances operational efficiency and safeguards assets in the long term.
FAQs on Personal and Commercial Vehicle Registration
Personal vehicle registration involves the process of recording privately owned cars under an individual's name for legal road use, typically requiring proof of identity, ownership, and insurance. Commercial vehicle registration applies to vehicles used for business purposes, mandating additional documentation such as commercial insurance, tax permits, and sometimes special licensing due to the nature of usage. Common FAQs address differences in fees, renewal periods, and documentation requirements distinguishing personal registrations from commercial vehicle registrations.
Personal Registration vs Commercial Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com