Dealer registration involves enrolling a business entity that sells products or services, usually requiring additional documentation such as business licenses and tax identification numbers. Individual registration is designed for single users, focusing primarily on personal information without the need for extensive business credentials. Choosing between dealer and individual registration depends on the nature of the user's activities and legal requirements for commerce or service provision.
Table of Comparison
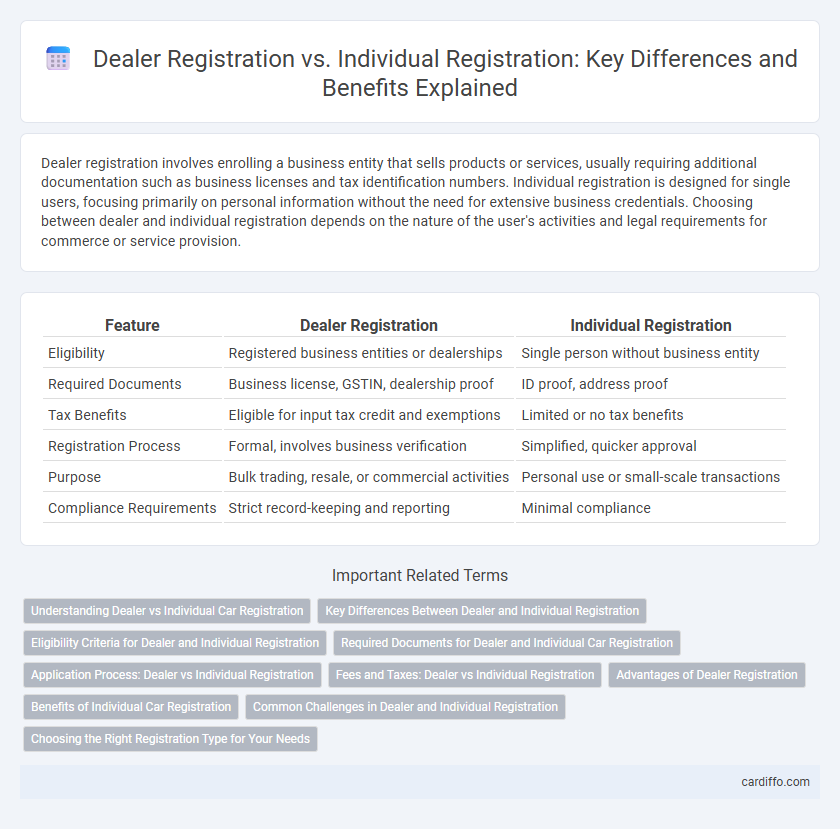
| Feature | Dealer Registration | Individual Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Registered business entities or dealerships | Single person without business entity |
| Required Documents | Business license, GSTIN, dealership proof | ID proof, address proof |
| Tax Benefits | Eligible for input tax credit and exemptions | Limited or no tax benefits |
| Registration Process | Formal, involves business verification | Simplified, quicker approval |
| Purpose | Bulk trading, resale, or commercial activities | Personal use or small-scale transactions |
| Compliance Requirements | Strict record-keeping and reporting | Minimal compliance |
Understanding Dealer vs Individual Car Registration
Dealer registration allows automotive businesses to register multiple vehicles under a single account, facilitating inventory management, wholesale transactions, and resale activities, while individual registration is designed for private vehicle owners to register a single car for personal use. Understanding the differences in documentation requirements, fees, and eligibility criteria is crucial as dealer registration often requires a business license, dealer bond, and compliance with state regulations, whereas individual registration typically involves proof of ownership, insurance, and personal identification. Choosing the appropriate registration type ensures adherence to legal standards and smooth processing, impacting taxation, liability, and resale processes in the automotive market.
Key Differences Between Dealer and Individual Registration
Dealer registration involves enrolling as a business entity authorized to buy, sell, or trade products in bulk, often requiring compliance with specific regulatory standards and tax obligations. Individual registration is typically for personal use or occasional transactions and demands simpler documentation focusing on identity verification rather than business credentials. Key differences include the scope of transactions, legal responsibilities, and the documentation requirements tailored to commercial versus personal activities.
Eligibility Criteria for Dealer and Individual Registration
Dealer registration requires businesses to have a federal employer identification number (FEIN) and proof of valid business licenses, ensuring compliance with state and federal regulations. Individual registration mandates applicants to present a government-issued photo ID and proof of residency, confirming personal identity and local eligibility. Both registration types often require background checks and adherence to specific operational standards relevant to the industry.
Required Documents for Dealer and Individual Car Registration
Dealer registration requires business documents such as a valid dealership license, tax identification number, proof of business insurance, and reseller's permit, alongside vehicle-specific paperwork including manufacturer's certificates of origin. Individual registration necessitates personal identification like a driver's license, proof of vehicle ownership (title or bill of sale), proof of insurance, and residency documentation such as a utility bill. Both processes demand distinct sets of documents reflecting the nature of the registrant, with dealer registration emphasizing business credentials and individual registration focusing on personal identification and ownership.
Application Process: Dealer vs Individual Registration
Dealer registration requires submitting business licenses, tax identification numbers, and proof of dealership authorization, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Individual registration involves providing personal identification, address verification, and sometimes background checks to confirm eligibility. Both processes demand accurate documentation but differ primarily in the scope of required credentials reflecting business versus personal status.
Fees and Taxes: Dealer vs Individual Registration
Dealer registration often involves higher fees and more complex tax obligations compared to individual registration due to business licensing, resale permits, and inventory taxes. Individual registration typically incurs lower upfront fees and simpler personal tax responsibilities, focusing on personal use or limited resale. Understanding these differences is crucial for compliance and cost management in vehicle or product registration processes.
Advantages of Dealer Registration
Dealer registration offers significant advantages including access to wholesale pricing, bulk purchase options, and priority inventory availability, which individual registration typically lacks. Registered dealers benefit from streamlined tax processes and enhanced credibility with suppliers and customers, fostering business growth opportunities. This registration also provides eligibility for exclusive incentives and manufacturer support programs unavailable to individual registrants.
Benefits of Individual Car Registration
Individual car registration offers personalized ownership, enabling direct control over vehicle records and legal responsibilities. It simplifies the transfer of ownership and ensures clear liability in case of accidents or violations. Unlike dealer registration, individual registration supports long-term asset management and potential resale value enhancement.
Common Challenges in Dealer and Individual Registration
Common challenges in dealer and individual registration include verifying identity documents, ensuring accuracy of submitted information, and navigating complex compliance requirements. Dealers often face additional scrutiny due to bulk data submissions and business verification, while individuals struggle with limited digital literacy and fewer supporting documents. Both registration types require robust user support systems to address technical issues and streamline the approval process.
Choosing the Right Registration Type for Your Needs
Choosing the right registration type depends on your business structure and goals; dealer registration is ideal for businesses planning to buy and sell vehicles or products in bulk, offering benefits like tax advantages and access to manufacturer incentives. Individual registration suits personal use or sole proprietorships, focusing on simpler compliance and minimal documentation. Assess your operational scale and legal requirements to select the most efficient and cost-effective registration option.
Dealer Registration vs Individual Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com