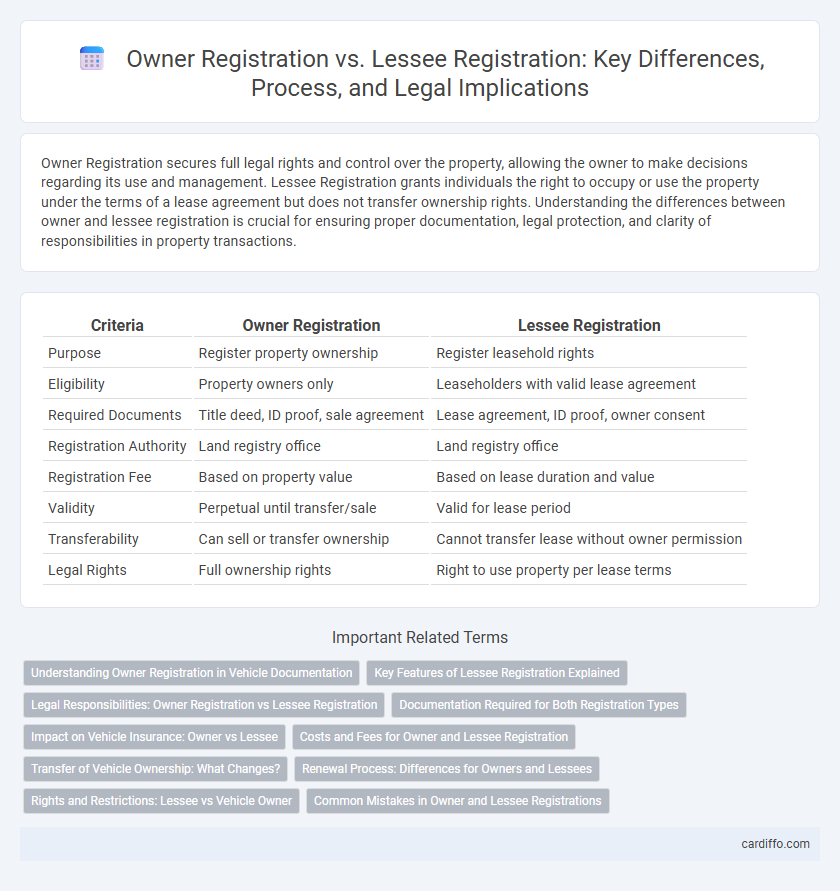
Owner Registration secures full legal rights and control over the property, allowing the owner to make decisions regarding its use and management. Lessee Registration grants individuals the right to occupy or use the property under the terms of a lease agreement but does not transfer ownership rights. Understanding the differences between owner and lessee registration is crucial for ensuring proper documentation, legal protection, and clarity of responsibilities in property transactions.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Owner Registration | Lessee Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Register property ownership | Register leasehold rights |
| Eligibility | Property owners only | Leaseholders with valid lease agreement |
| Required Documents | Title deed, ID proof, sale agreement | Lease agreement, ID proof, owner consent |
| Registration Authority | Land registry office | Land registry office |
| Registration Fee | Based on property value | Based on lease duration and value |
| Validity | Perpetual until transfer/sale | Valid for lease period |
| Transferability | Can sell or transfer ownership | Cannot transfer lease without owner permission |
| Legal Rights | Full ownership rights | Right to use property per lease terms |
Understanding Owner Registration in Vehicle Documentation
Owner registration in vehicle documentation legally establishes the individual or entity holding the title and primary rights to the vehicle, ensuring accountability for taxes, insurance, and compliance with regulations. Unlike lessee registration, which lists the person leasing the vehicle without transferring ownership rights, owner registration includes the authority to sell or transfer the vehicle. Accurate owner registration is crucial for clear legal responsibility and facilitates proper record-keeping with motor vehicle departments.
Key Features of Lessee Registration Explained
Lessee registration grants tenants official recognition for lease agreements, ensuring legal rights and protection under property laws. Key features include documented lease duration, lease payment records, and easy transferability or renewal rights, providing transparency and security for both lessees and property owners. Unlike owner registration, lessee registration does not confer ownership rights but establishes a clear, enforceable occupancy record.
Legal Responsibilities: Owner Registration vs Lessee Registration
Owner registration establishes the legal responsibility for the property, making the owner accountable for taxes, liabilities, and compliance with local regulations. Lessee registration primarily assigns responsibilities related to the use and maintenance of the property during the lease term, while ownership rights and long-term legal obligations remain with the owner. Understanding the distinction in legal responsibilities between owner and lessee registration is crucial for defining accountability in property management and dispute resolution.
Documentation Required for Both Registration Types
Owner registration requires documents such as proof of ownership, vehicle invoice, valid insurance, and a government-issued identification card, ensuring the registrant holds legal title. Lessee registration demands a valid lease agreement, a no-objection certificate (NOC) from the owner, valid insurance, and identification, verifying the lessee's permission to use the vehicle. Both processes mandate emission test certificates and address proof to comply with regulatory standards.
Impact on Vehicle Insurance: Owner vs Lessee
Owner registration typically provides the vehicle owner with direct control over insurance policies, often resulting in lower premiums due to ownership verification and risk assessment based on the owner's history. Lessee registration can complicate insurance claims and may require additional coverage or endorsements, increasing overall costs since the insurance company assesses risk based on the lessee's driving profile and contractual obligations. Understanding the distinctions between owner and lessee registration is essential for optimizing vehicle insurance liability, coverage limits, and premium rates.
Costs and Fees for Owner and Lessee Registration
Owner registration typically involves higher initial costs due to property valuation fees, title deed processing, and registration taxes. Lessee registration fees are generally lower, often limited to lease agreement notarization and administrative charges. Both processes may include service fees, but owner registration entails more substantial government and legal expenses reflecting property ownership transfer.
Transfer of Vehicle Ownership: What Changes?
Owner registration involves the vehicle being officially registered under the name of the person who holds legal ownership, granting full authority to transfer ownership, modify registration details, or sell the vehicle. Lessee registration assigns the vehicle registration to the lessee for the lease term, but the original owner retains ultimate ownership rights, limiting the lessee's authority to transfer ownership without owner consent. Transfer of vehicle ownership requires notarized documentation and approval from the regional transport office, with owner registration simplifying the process, whereas lessee registration necessitates additional legal clearances from the leasing company.
Renewal Process: Differences for Owners and Lessees
Owner registration renewal typically requires proof of ownership and updated identification documents, ensuring the property title remains accurate in public records. Lessee registration renewal emphasizes leasing contract validation and lessor's consent, focusing on tenancy verification rather than ownership. Both processes necessitate timely submission, but owners face stricter title-based scrutiny, while lessees deal primarily with lease agreement continuity.
Rights and Restrictions: Lessee vs Vehicle Owner
Owner registration grants full legal rights over the vehicle, including transfer, sale, and modification permissions, while lessee registration provides limited rights bound by the lease agreement. Lessees face restrictions on altering the vehicle or selling it, as ownership remains with the registered vehicle owner until the lease term concludes. Vehicle owners retain ultimate control and responsibility, ensuring compliance with regulatory obligations and enabling full utilization of ownership privileges.
Common Mistakes in Owner and Lessee Registrations
Common mistakes in owner registration include providing incorrect property details and failing to update ownership after property transfer, leading to legal disputes and delayed transactions. Lessee registration errors often involve incomplete lease agreements and neglecting to register the lease within required timeframes, which can affect tenant rights and eviction processes. Accurate and timely submission of both owner and lessee documents is crucial to ensure legal protection and compliance with property registration laws.
Owner Registration vs Lessee Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com