Individual registration offers a streamlined process tailored for single users, providing quick access with minimal documentation requirements. Corporate registration involves a more comprehensive procedure, requiring detailed company information, multiple authorized signatories, and compliance verification to ensure legal and operational legitimacy. Choosing between individual and corporate registration depends on the intended use, scale of operations, and regulatory obligations.
Table of Comparison
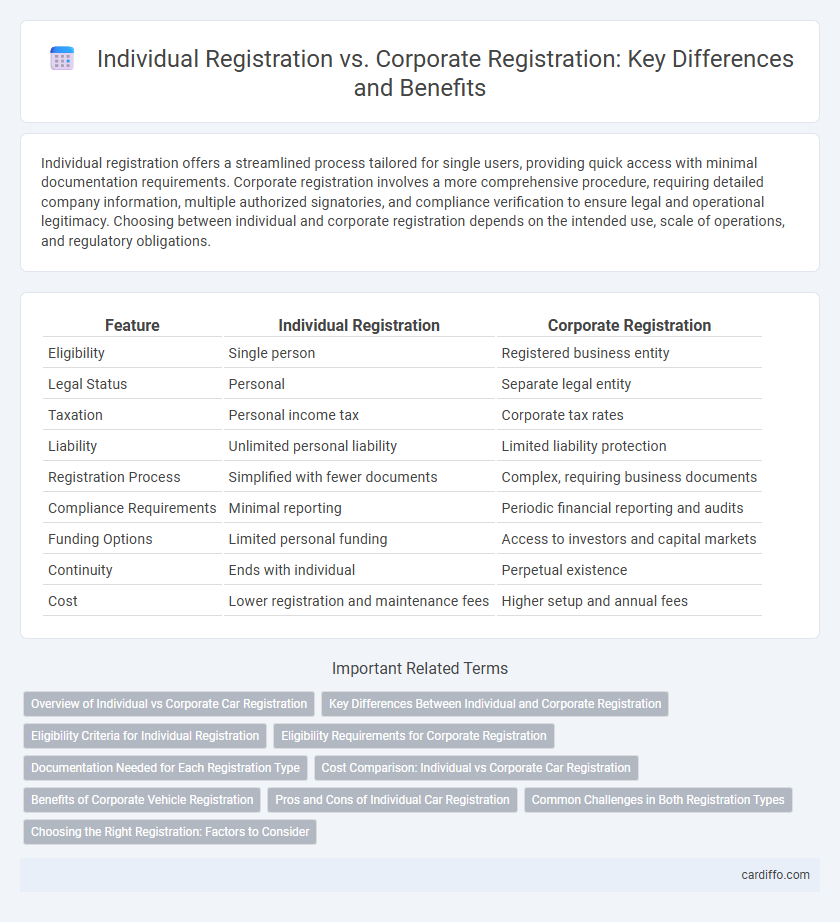
| Feature | Individual Registration | Corporate Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Single person | Registered business entity |
| Legal Status | Personal | Separate legal entity |
| Taxation | Personal income tax | Corporate tax rates |
| Liability | Unlimited personal liability | Limited liability protection |
| Registration Process | Simplified with fewer documents | Complex, requiring business documents |
| Compliance Requirements | Minimal reporting | Periodic financial reporting and audits |
| Funding Options | Limited personal funding | Access to investors and capital markets |
| Continuity | Ends with individual | Perpetual existence |
| Cost | Lower registration and maintenance fees | Higher setup and annual fees |
Overview of Individual vs Corporate Car Registration
Individual car registration assigns ownership to a single person, simplifying legal responsibility and ensuring personalized control over the vehicle. Corporate car registration designates a company or organization as the owner, facilitating fleet management, tax benefits, and liability structuring under business regulations. Choosing between individual and corporate registration depends on factors such as usage purpose, financial considerations, and legal accountability.
Key Differences Between Individual and Corporate Registration
Individual registration requires personal identification documents such as a passport or driver's license, while corporate registration mandates submission of business licenses, articles of incorporation, and tax identification numbers. Individual registration typically involves simpler processes and fewer regulatory requirements compared to corporate registration, which demands compliance with corporate governance, financial disclosures, and often higher registration fees. Tax obligations differ significantly, as individuals pay personal income tax, whereas corporations are subject to corporate tax rates and may need to report employee payroll taxes.
Eligibility Criteria for Individual Registration
Eligibility criteria for individual registration require applicants to be natural persons, typically aged 18 or older, possessing valid identification documents such as a government-issued ID or passport. The individual must meet residency requirements specified by the registering authority and provide proof of address. Unlike corporate registration, individual registration does not require business licenses or tax identification numbers but mandates personal information verification for identity and eligibility confirmation.
Eligibility Requirements for Corporate Registration
Corporate registration requires that the entity be legally recognized as a corporation, partnership, or LLC, with valid incorporation documents filed according to jurisdictional laws. Eligibility mandates submission of a Certificate of Incorporation, Articles of Association, and proof of business address along with authorized signatory details. Compliance with specific industry regulations and payment of applicable fees is essential for approval during the corporate registration process.
Documentation Needed for Each Registration Type
Individual registration requires personal identification documents such as a government-issued ID, proof of address, and sometimes a social security number or tax identification number. Corporate registration necessitates more comprehensive documentation, including articles of incorporation, business licenses, tax identification numbers, and proof of authorized representatives. Specific requirements vary by jurisdiction but always emphasize proof of identity, legal existence, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Cost Comparison: Individual vs Corporate Car Registration
Individual car registration typically incurs lower fees compared to corporate registration due to simplified processes and reduced administrative requirements. Corporate car registration often involves additional costs such as higher registration fees, insurance premiums, and compliance expenses related to business usage. Evaluating total ownership costs reveals that individual registration is more cost-effective for personal vehicles, while corporate registration suits fleet management but demands higher budgets.
Benefits of Corporate Vehicle Registration
Corporate vehicle registration offers significant benefits, including enhanced asset protection by separating personal and business liabilities, which reduces legal risks for individual owners. It enables streamlined fleet management and simplifies tax deductions related to business use, improving financial efficiency and regulatory compliance. Additionally, corporate registration can enhance the company's professional image and creditability with clients and partners, supporting business growth.
Pros and Cons of Individual Car Registration
Individual car registration offers personalized control over vehicle ownership and simpler documentation processes compared to corporate registration. It often results in lower fees and taxes but limits liability protection and may not provide business-related tax benefits available to corporations. The registration is straightforward for personal use but lacks advantages in asset management or fleet organization inherent in corporate registrations.
Common Challenges in Both Registration Types
Both individual registration and corporate registration face challenges such as verifying accurate identification, managing compliance with regulatory requirements, and ensuring data security. Complex documentation processes and the need for thorough validation can delay registration timelines and increase administrative costs. Furthermore, both types must address issues related to fraud prevention and maintaining up-to-date records to support ongoing legal obligations.
Choosing the Right Registration: Factors to Consider
When choosing between Individual Registration and Corporate Registration, evaluate factors such as liability protection, tax implications, and administrative requirements. Individual Registration suits sole proprietors seeking simplicity and direct control, while Corporate Registration benefits businesses needing limited liability and potential for growth. Consider long-term goals, regulatory compliance, and financial strategy to select the optimal registration type.
Individual Registration vs Corporate Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com