Preventive maintenance involves regularly scheduled inspections and servicing to prevent equipment failure and extend machinery lifespan. Corrective maintenance occurs after a breakdown, addressing repairs to restore functionality and minimize downtime. Implementing preventive strategies can reduce the frequency and cost of corrective interventions while improving overall operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
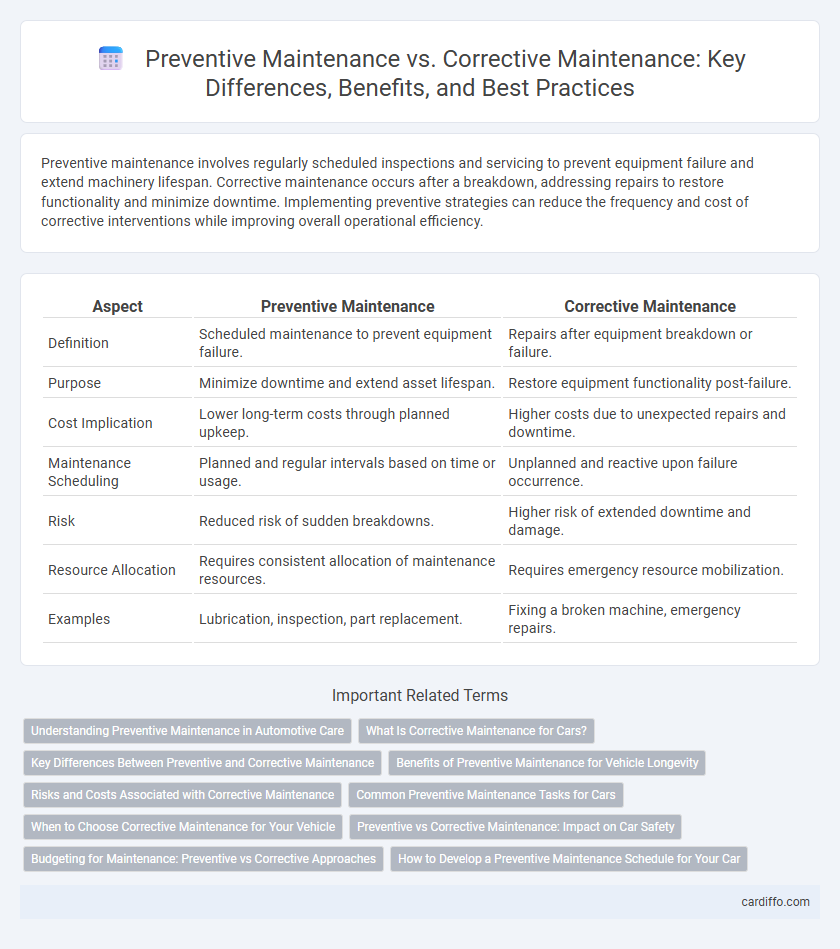
| Aspect | Preventive Maintenance | Corrective Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled maintenance to prevent equipment failure. | Repairs after equipment breakdown or failure. |
| Purpose | Minimize downtime and extend asset lifespan. | Restore equipment functionality post-failure. |
| Cost Implication | Lower long-term costs through planned upkeep. | Higher costs due to unexpected repairs and downtime. |
| Maintenance Scheduling | Planned and regular intervals based on time or usage. | Unplanned and reactive upon failure occurrence. |
| Risk | Reduced risk of sudden breakdowns. | Higher risk of extended downtime and damage. |
| Resource Allocation | Requires consistent allocation of maintenance resources. | Requires emergency resource mobilization. |
| Examples | Lubrication, inspection, part replacement. | Fixing a broken machine, emergency repairs. |
Understanding Preventive Maintenance in Automotive Care
Preventive maintenance in automotive care involves scheduled inspections and servicing to detect and resolve potential issues before they cause significant damage or failure. Regular activities such as oil changes, brake checks, and tire rotations extend vehicle lifespan and improve safety by maintaining optimal performance. This proactive approach reduces overall repair costs and downtime compared to corrective maintenance, which addresses problems only after breakdowns occur.
What Is Corrective Maintenance for Cars?
Corrective maintenance for cars involves repairing or replacing components after a malfunction or failure occurs, restoring the vehicle to its proper working condition. It addresses issues such as engine breakdowns, brake failures, or electrical problems that impact safety and performance. This maintenance type is essential for resolving unexpected repairs that were not identified during routine inspections.
Key Differences Between Preventive and Corrective Maintenance
Preventive maintenance involves regular, scheduled inspections and servicing to detect and address potential issues before equipment failure occurs, reducing downtime and extending asset lifespan. Corrective maintenance, on the other hand, is reactive, performed after equipment failure to restore functionality, often resulting in higher costs and longer operational interruptions. Key differences include timing, cost implications, and impact on equipment reliability, with preventive maintenance focusing on proactive care and corrective maintenance addressing breakdowns post-failure.
Benefits of Preventive Maintenance for Vehicle Longevity
Preventive maintenance extends vehicle longevity by ensuring regular inspections, timely oil changes, and replacement of worn parts before failure occurs. This proactive approach reduces the risk of costly breakdowns, improves fuel efficiency, and maintains optimal engine performance. Routine preventive care enhances overall vehicle reliability and safety, significantly minimizing long-term repair expenses.
Risks and Costs Associated with Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance often leads to higher costs due to unplanned downtime, emergency repairs, and potential damage to surrounding equipment. The risks associated with corrective maintenance include increased safety hazards, reduced equipment lifespan, and operational disruptions that can affect productivity. Implementing preventive maintenance reduces the likelihood of these costly interruptions and minimizes the financial impact caused by unexpected breakdowns.
Common Preventive Maintenance Tasks for Cars
Common preventive maintenance tasks for cars include regular oil changes, tire rotations, brake inspections, and fluid level checks to ensure optimal engine performance and safety. Scheduling timely replacement of air filters, spark plugs, and timing belts prevents unexpected breakdowns and extends vehicle lifespan. Consistent preventive care reduces repair costs by addressing potential issues before they require corrective maintenance.
When to Choose Corrective Maintenance for Your Vehicle
Corrective maintenance should be chosen when unexpected mechanical failures occur that cannot be predicted or avoided through regular inspections. It is ideal for addressing immediate repair needs in emergency situations to restore vehicle functionality quickly. Opting for corrective maintenance is cost-effective when the repair is isolated and does not justify the expense of preventive procedures.
Preventive vs Corrective Maintenance: Impact on Car Safety
Preventive maintenance significantly enhances car safety by regularly addressing potential issues before they lead to failures, reducing the risk of accidents caused by brake failures, tire blowouts, or engine malfunctions. Corrective maintenance, performed after a fault occurs, may increase safety hazards due to unexpected breakdowns or unsafe driving conditions during failure. Consistent preventive maintenance ensures optimal vehicle performance and compliance with safety standards, thereby minimizing the likelihood of dangerous incidents on the road.
Budgeting for Maintenance: Preventive vs Corrective Approaches
Budgeting for preventive maintenance often leads to lower long-term costs by reducing equipment downtime and avoiding expensive repairs through regular inspections and timely part replacements. Corrective maintenance budgeting tends to be more unpredictable, as expenses arise from unexpected breakdowns requiring immediate repairs, which can disrupt financial planning. Allocating resources toward preventive maintenance enhances cost efficiency by minimizing emergency repair costs and extending asset lifecycle.
How to Develop a Preventive Maintenance Schedule for Your Car
Developing a preventive maintenance schedule for your car involves tracking manufacturer-recommended service intervals and proactively replacing parts such as oil filters, brake pads, and timing belts before failure occurs. Utilizing digital tools or maintenance logs helps monitor mileage and service dates, ensuring timely inspections and fluid changes to prevent costly breakdowns. Prioritizing preventive maintenance reduces the frequency of corrective repairs and extends vehicle lifespan by maintaining optimal engine performance and safety.
Preventive Maintenance vs Corrective Maintenance Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com