Undercoating creates a thick protective barrier on the vehicle's underside, shielding it from moisture, salt, and debris that cause rust and corrosion. Rustproofing involves applying a chemical treatment to metal surfaces, sealing small crevices and preventing oxidation at the molecular level. Choosing between undercoating and rustproofing depends on the vehicle's exposure to harsh conditions and desired longevity of protection.
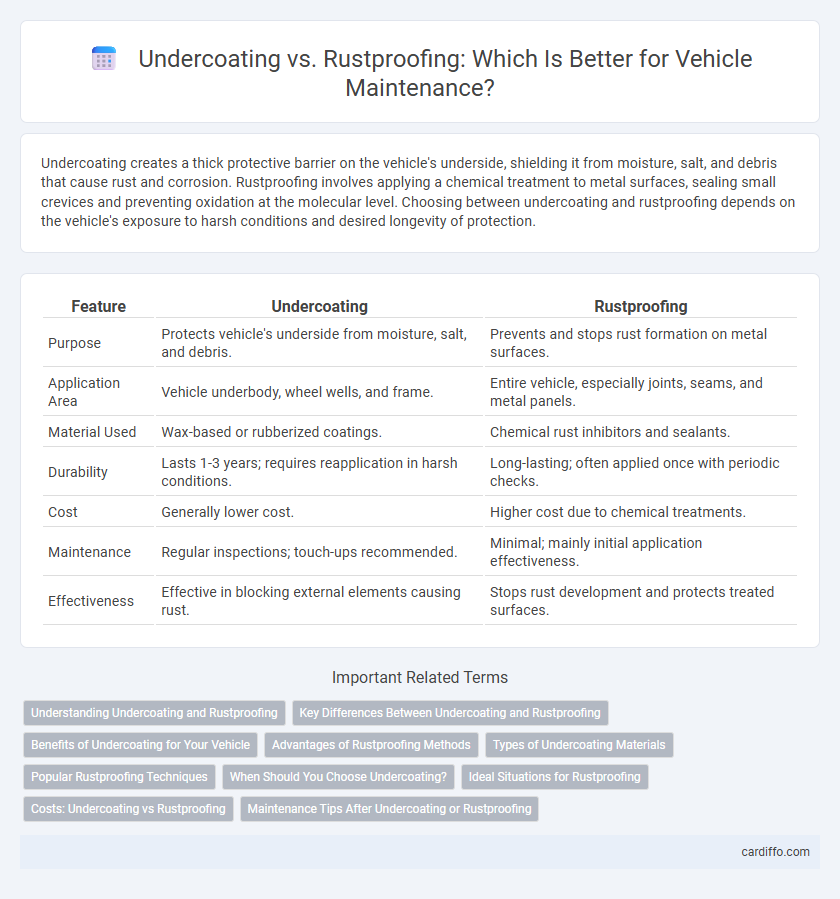
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Undercoating | Rustproofing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects vehicle's underside from moisture, salt, and debris. | Prevents and stops rust formation on metal surfaces. |
| Application Area | Vehicle underbody, wheel wells, and frame. | Entire vehicle, especially joints, seams, and metal panels. |
| Material Used | Wax-based or rubberized coatings. | Chemical rust inhibitors and sealants. |
| Durability | Lasts 1-3 years; requires reapplication in harsh conditions. | Long-lasting; often applied once with periodic checks. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost. | Higher cost due to chemical treatments. |
| Maintenance | Regular inspections; touch-ups recommended. | Minimal; mainly initial application effectiveness. |
| Effectiveness | Effective in blocking external elements causing rust. | Stops rust development and protects treated surfaces. |
Understanding Undercoating and Rustproofing
Undercoating involves applying a protective layer, often rubberized or asphalt-based, to the underbody of a vehicle to shield it from moisture, salt, and debris, effectively preventing rust formation. Rustproofing is a broader treatment that includes chemical applications designed to penetrate seams and crevices, offering corrosion resistance beyond surface protection. Understanding the differences helps vehicle owners choose the appropriate method based on exposure conditions and long-term maintenance goals.
Key Differences Between Undercoating and Rustproofing
Undercoating primarily involves applying a thick, protective layer of material to the vehicle's underbody to shield it from physical damage and moisture, while rustproofing focuses on penetrating treatments that prevent corrosion from forming on metal surfaces. Undercoating uses tar or rubberized compounds to create a barrier against stones, salt, and road debris, whereas rustproofing usually employs chemical sprays or wax-based products to inhibit oxidation at a molecular level. The key difference lies in undercoating serving as a physical shield, whereas rustproofing is a chemical process aimed at preventing rust development internally and externally.
Benefits of Undercoating for Your Vehicle
Undercoating provides a durable protective layer that shields your vehicle's undercarriage from moisture, salt, and road debris, significantly reducing the risk of rust and corrosion. This treatment enhances the longevity of critical components such as the frame, brake lines, and fuel tanks, preserving structural integrity and maintaining vehicle safety. Regular undercoating can also help maintain resale value by preventing costly rust damage over time.
Advantages of Rustproofing Methods
Rustproofing methods provide superior protection by creating a chemical barrier that prevents oxidation and corrosion more effectively than traditional undercoating. These advanced treatments penetrate metal surfaces to seal pores and cracks, significantly extending the lifespan of vehicle components and reducing maintenance costs. Modern rustproofing products often include corrosion inhibitors and waterproof agents that enhance durability and resist environmental damage.
Types of Undercoating Materials
Undercoating materials primarily include rubberized asphalt, wax-based, and petroleum-based compounds, each offering different levels of protection against moisture, salt, and road debris. Rubberized asphalt is the most common type, providing a durable, flexible barrier that reduces road noise and prevents corrosion effectively. Wax-based undercoatings offer excellent water resistance but may degrade faster under high temperatures, while petroleum-based options create a strong seal but can harden and crack over time.
Popular Rustproofing Techniques
Popular rustproofing techniques include applying oil-based sprays, wax coatings, and electronic rust inhibitors that form protective barriers against moisture and salt. Undercoating typically involves a thick rubberized material applied to the vehicle's undercarriage to shield against corrosion and physical damage from debris. Both methods enhance vehicle longevity but differ in application, with rustproofing focusing more on chemical deterrents and undercoating providing a durable physical layer.
When Should You Choose Undercoating?
Choose undercoating when your vehicle is frequently exposed to harsh conditions such as salted roads, snow, and off-road terrains that accelerate rust formation. This protective layer, typically made of rubberized asphalt, provides durable shield against moisture, salt, and gravel impact, prolonging the lifespan of the vehicle's undercarriage. Undercoating is ideal for older vehicles or those with visible rust or damage that requires enhanced corrosion protection.
Ideal Situations for Rustproofing
Rustproofing is ideal for vehicles frequently exposed to wet, salty, or humid environments where metal corrosion risk is highest. It provides a long-lasting protective barrier against rust, making it suitable for cars driven in coastal areas or regions with heavy winter road salt use. Regular rustproofing helps preserve structural integrity and prevent costly repairs over time in these challenging conditions.
Costs: Undercoating vs Rustproofing
Undercoating typically costs between $100 and $200, offering a thick protective layer against moisture and road salt, while rustproofing ranges from $150 to $300 with chemical treatments designed to prevent internal corrosion. Both services vary by vehicle size and application method, but rustproofing often requires periodic reapplication for sustained effectiveness. Choosing between the two depends on budget considerations and long-term maintenance goals, with undercoating providing a more durable barrier and rustproofing offering comprehensive corrosion prevention.
Maintenance Tips After Undercoating or Rustproofing
Maintaining your vehicle after undercoating or rustproofing involves regular inspections for chips or cracks in the protective layer to prevent moisture penetration and corrosion. Washing the undercarriage thoroughly, especially after exposure to salt or mud, helps preserve the coating's integrity and extends its lifespan. Promptly addressing any damage or peeling by reapplying rustproofing or touch-up undercoating ensures continuous protection against rust development.
Undercoating vs Rustproofing Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com