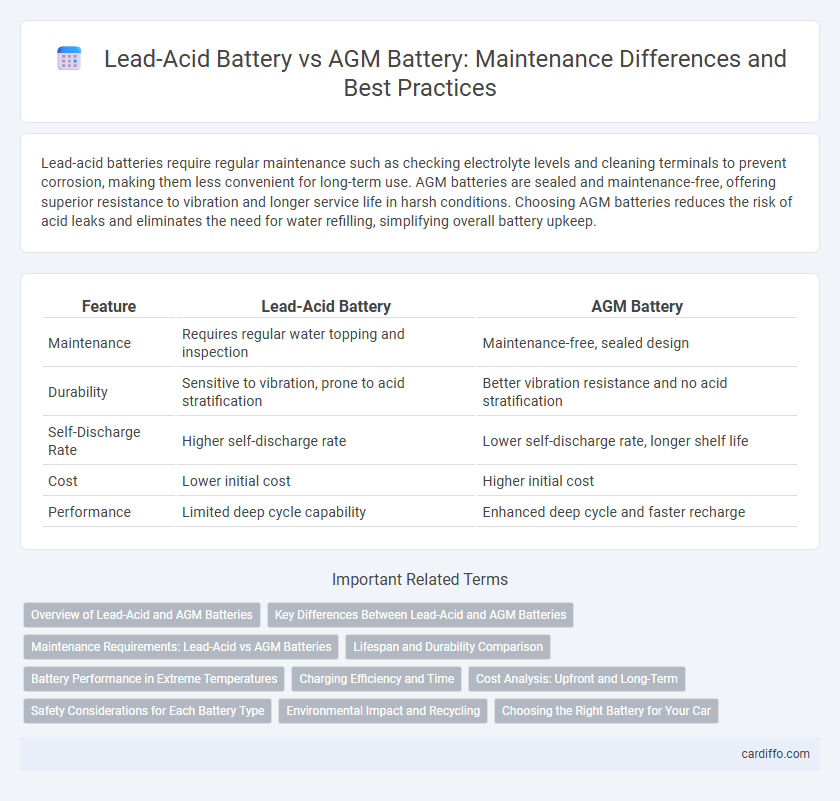
Lead-acid batteries require regular maintenance such as checking electrolyte levels and cleaning terminals to prevent corrosion, making them less convenient for long-term use. AGM batteries are sealed and maintenance-free, offering superior resistance to vibration and longer service life in harsh conditions. Choosing AGM batteries reduces the risk of acid leaks and eliminates the need for water refilling, simplifying overall battery upkeep.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lead-Acid Battery | AGM Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance | Requires regular water topping and inspection | Maintenance-free, sealed design |
| Durability | Sensitive to vibration, prone to acid stratification | Better vibration resistance and no acid stratification |
| Self-Discharge Rate | Higher self-discharge rate | Lower self-discharge rate, longer shelf life |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Performance | Limited deep cycle capability | Enhanced deep cycle and faster recharge |
Overview of Lead-Acid and AGM Batteries
Lead-acid batteries utilize a liquid electrolyte solution, making them heavier and more prone to acid spillage, while AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries employ a fiberglass mat separator that absorbs the electrolyte, providing enhanced vibration resistance and reduced maintenance requirements. AGM batteries exhibit lower self-discharge rates and better performance under deep-cycle conditions compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, extending overall battery lifespan. Both battery types are widely used in automotive and backup power applications, but AGM batteries offer improved durability and safety features suited for advanced energy storage needs.
Key Differences Between Lead-Acid and AGM Batteries
Lead-acid batteries feature liquid electrolyte that requires regular maintenance, including checking and refilling water levels, whereas AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries have a sealed design with immobilized electrolyte, eliminating the need for watering. AGM batteries offer superior vibration resistance and faster recharge times compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, enhancing durability and efficiency in high-demand applications. Temperature sensitivity varies, with AGM batteries performing better in cold conditions while lead-acid batteries may degrade faster under extreme heat.
Maintenance Requirements: Lead-Acid vs AGM Batteries
Lead-acid batteries require regular maintenance, including checking electrolyte levels and topping up distilled water, to ensure optimal performance and prevent sulfation. AGM batteries are maintenance-free, sealed units that eliminate the need for water refilling and reduce the risk of acid spills, making them ideal for low-maintenance applications. The low self-discharge rate of AGM batteries also enhances their longevity compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
Lifespan and Durability Comparison
Lead-acid batteries typically have a lifespan of 3 to 5 years, while AGM batteries can last between 4 to 7 years due to their enhanced design and sealed construction. AGM batteries offer superior durability by being more resistant to vibration, extreme temperatures, and deep discharges, making them ideal for demanding maintenance applications. Regular maintenance extends the longevity of lead-acid batteries, but AGMs require less frequent upkeep, contributing to a longer effective lifecycle.
Battery Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Lead-acid batteries experience significant voltage drop and reduced capacity in extreme cold, often below 0degC, due to slower chemical reactions. AGM batteries maintain better performance in low temperatures, offering higher cold-cranking amps and faster recharge times because of their sealed, fiberglass-mat construction. In high-temperature environments above 40degC, AGM batteries resist thermal degradation longer than traditional lead-acid batteries, extending operational life and reliability.
Charging Efficiency and Time
Lead-acid batteries typically require longer charging times due to their lower charge acceptance rates compared to Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) batteries, which feature advanced separators that enhance ion flow and reduce internal resistance. AGM batteries exhibit higher charging efficiency, often reaching full charge faster while minimizing energy loss and heat generation during the process. These characteristics make AGM batteries more suitable for applications demanding rapid recharge cycles and efficient maintenance.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Lead-Acid batteries have a lower upfront cost, making them more budget-friendly initially, but they require more frequent maintenance and replacements, which increases long-term expenses. AGM batteries come with a higher initial investment but offer longer lifespan, reduced maintenance, and better performance, leading to cost savings over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including replacement frequency, energy efficiency, and maintenance needs, is essential for informed decision-making in battery selection.
Safety Considerations for Each Battery Type
Lead-acid batteries require careful handling due to the risk of acid leaks and hydrogen gas buildup, which can cause corrosion or explosions if ventilation is inadequate. AGM batteries are sealed and maintenance-free, significantly reducing the risk of acid spills and offering enhanced safety in enclosed or mobile environments. Proper disposal and adherence to manufacturer safety guidelines remain critical for both battery types to prevent environmental hazards and ensure user safety.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Lead-acid batteries contain hazardous materials like sulfuric acid and lead that require specialized recycling processes to prevent environmental contamination. AGM batteries, while also containing lead, use absorbed glass mat technology which reduces acid spillage risks and improves safety during handling and recycling. Both battery types benefit from established recycling programs that recover valuable materials, reducing landfill waste and minimizing toxic pollution.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Car
When choosing the right battery for your car, consider that lead-acid batteries are typically more affordable and easier to recycle but require regular maintenance such as checking electrolyte levels and cleaning terminals. AGM batteries offer superior performance with enhanced vibration resistance, longer lifespan, and are maintenance-free, making them ideal for modern vehicles equipped with advanced electronics. Evaluating driving habits, climate conditions, and vehicle requirements ensures selecting the most efficient and reliable battery type.
Lead-Acid Battery vs AGM Battery Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com