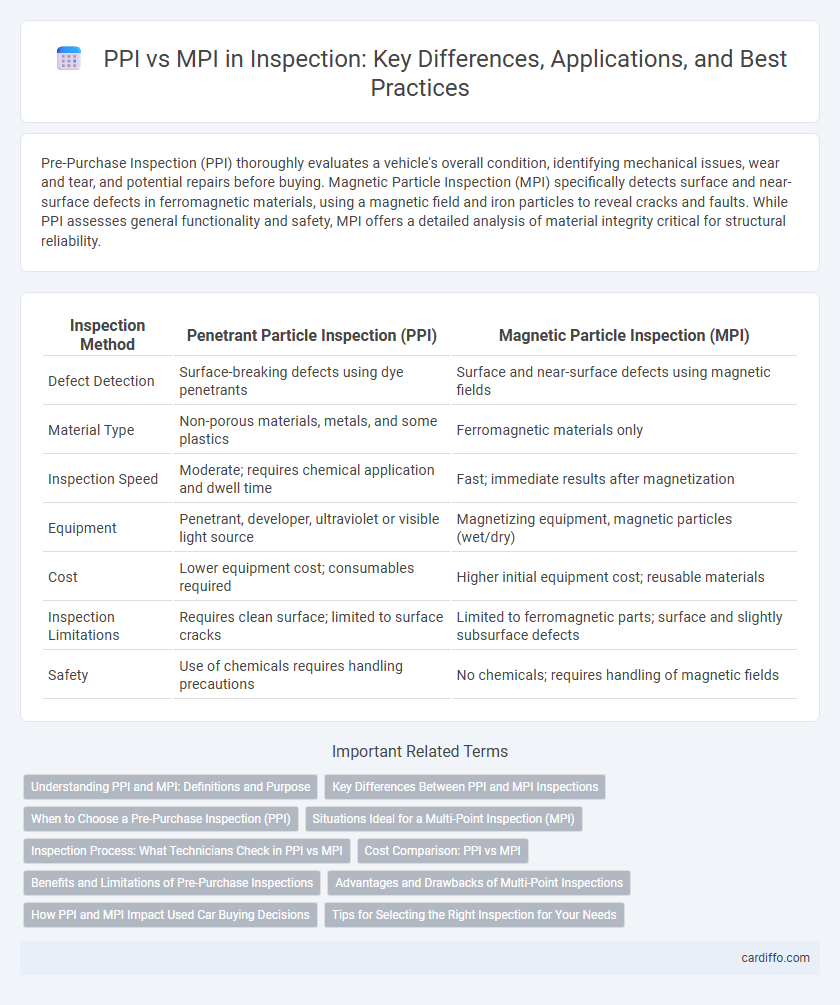
Pre-Purchase Inspection (PPI) thoroughly evaluates a vehicle's overall condition, identifying mechanical issues, wear and tear, and potential repairs before buying. Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI) specifically detects surface and near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials, using a magnetic field and iron particles to reveal cracks and faults. While PPI assesses general functionality and safety, MPI offers a detailed analysis of material integrity critical for structural reliability.
Table of Comparison
| Inspection Method | Penetrant Particle Inspection (PPI) | Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI) |
|---|---|---|
| Defect Detection | Surface-breaking defects using dye penetrants | Surface and near-surface defects using magnetic fields |
| Material Type | Non-porous materials, metals, and some plastics | Ferromagnetic materials only |
| Inspection Speed | Moderate; requires chemical application and dwell time | Fast; immediate results after magnetization |
| Equipment | Penetrant, developer, ultraviolet or visible light source | Magnetizing equipment, magnetic particles (wet/dry) |
| Cost | Lower equipment cost; consumables required | Higher initial equipment cost; reusable materials |
| Inspection Limitations | Requires clean surface; limited to surface cracks | Limited to ferromagnetic parts; surface and slightly subsurface defects |
| Safety | Use of chemicals requires handling precautions | No chemicals; requires handling of magnetic fields |
Understanding PPI and MPI: Definitions and Purpose
PPI (Positive Material Identification) uses X-ray fluorescence or optical emission spectroscopy to verify material composition, ensuring the correct alloy or metal grade before manufacturing or assembly. MPI (Magnetic Particle Inspection) detects surface and near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials by applying magnetic fields and iron particles, revealing cracks or discontinuities invisible to the naked eye. Both methods play critical roles in quality control, with PPI confirming material identity and MPI ensuring structural integrity.
Key Differences Between PPI and MPI Inspections
PPI (Pre-Painted Inspection) primarily evaluates coating integrity, surface defects, and adhesion on pre-painted materials, ensuring aesthetic and protective quality before final use. MPI (Magnetic Particle Inspection) detects surface and subsurface cracks or discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials by applying magnetic fields and magnetic particles, focusing on structural integrity rather than surface appearance. The key difference lies in PPI's emphasis on coating quality versus MPI's role in identifying material flaws critical to safety and durability.
When to Choose a Pre-Purchase Inspection (PPI)
A Pre-Purchase Inspection (PPI) should be chosen when buyers need a thorough evaluation of a vehicle's overall condition before finalizing a purchase, ensuring no hidden mechanical or structural issues exist. It is essential for identifying potential costly repairs and verifying the seller's claims, especially for used cars or private sales. Selecting a PPI helps buyers make informed decisions, avoid unexpected expenses, and negotiate better prices based on the inspection report.
Situations Ideal for a Multi-Point Inspection (MPI)
Multi-Point Inspection (MPI) is ideal for comprehensive evaluations of complex machinery where multiple components require simultaneous assessment to ensure overall system reliability. Situations involving routine maintenance, pre-purchase vehicle checks, and preventive safety audits benefit significantly from MPI due to its ability to identify interconnected issues across various systems. MPI's systematic approach facilitates early detection of wear and tear, minimizing downtime and costly repairs.
Inspection Process: What Technicians Check in PPI vs MPI
Technicians performing Penetrant Penetrant Inspection (PPI) focus on detecting surface-breaking defects by applying a visible or fluorescent dye, ensuring cracks, porosity, and laps are clearly visible under proper lighting conditions. Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI) technicians examine ferromagnetic materials using magnetic fields to identify surface and subsurface discontinuities such as cracks or inclusions by observing the accumulation of magnetic particles at defect sites. Both inspection processes prioritize accurate defect detection but differ in material applicability and indicative techniques, with PPI suited for non-porous materials and MPI for magnetic metals.
Cost Comparison: PPI vs MPI
Pre-Paint Inspection (PPI) typically incurs lower costs compared to Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI) due to less specialized equipment and simpler procedural requirements. MPI demands expensive magnetization devices and consumables, increasing both initial investment and operational expenses. Choosing PPI or MPI depends on balancing cost efficiency against inspection sensitivity and defect detection precision.
Benefits and Limitations of Pre-Purchase Inspections
Pre-Purchase Inspections (PPI) provide crucial benefits by identifying potential defects and hidden damages in a vehicle before purchase, reducing the risk of costly repairs and ensuring informed decision-making. However, PPIs have limitations as they may not detect all mechanical issues, especially intermittent problems or those arising after the inspection, and they rely heavily on the inspector's expertise and the thoroughness of the inspection process. Balancing these benefits and limitations helps buyers safeguard their investment and negotiate better terms based on the vehicle's true condition.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Multi-Point Inspections
Multi-point inspections (MPI) offer comprehensive coverage by evaluating multiple components simultaneously, enabling early detection of diverse issues and reducing downtime. However, the extensive nature of MPI can lead to longer inspection times and higher costs compared to pre-purchase inspections (PPI), which are more focused and quicker. While MPI benefits preventive maintenance with thorough diagnostics, it may result in unnecessary replacements or repairs if not prioritized correctly.
How PPI and MPI Impact Used Car Buying Decisions
PPI (Pre-Purchase Inspection) and MPI (Multi-Point Inspection) significantly influence used car buying decisions by providing detailed insights into vehicle condition and potential repair costs. PPI offers a comprehensive evaluation tailored to specific buyer concerns, while MPI covers a standardized range of components for overall vehicle health assessment. Understanding these inspections helps buyers avoid hidden issues, negotiate better prices, and make informed investment choices in the used car market.
Tips for Selecting the Right Inspection for Your Needs
Choosing between Pre-Paint Inspection (PPI) and Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI) depends on the material type and defect sensitivity required; PPI is ideal for surface cleanliness and coating adherence, while MPI excels at detecting surface and subsurface cracks in ferromagnetic materials. Consider factors like component geometry, defect criticality, and inspection environment to ensure accuracy and efficiency. Consulting ASTM standards and leveraging expert guidance can optimize inspection outcomes and resource allocation.
PPI vs MPI Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com