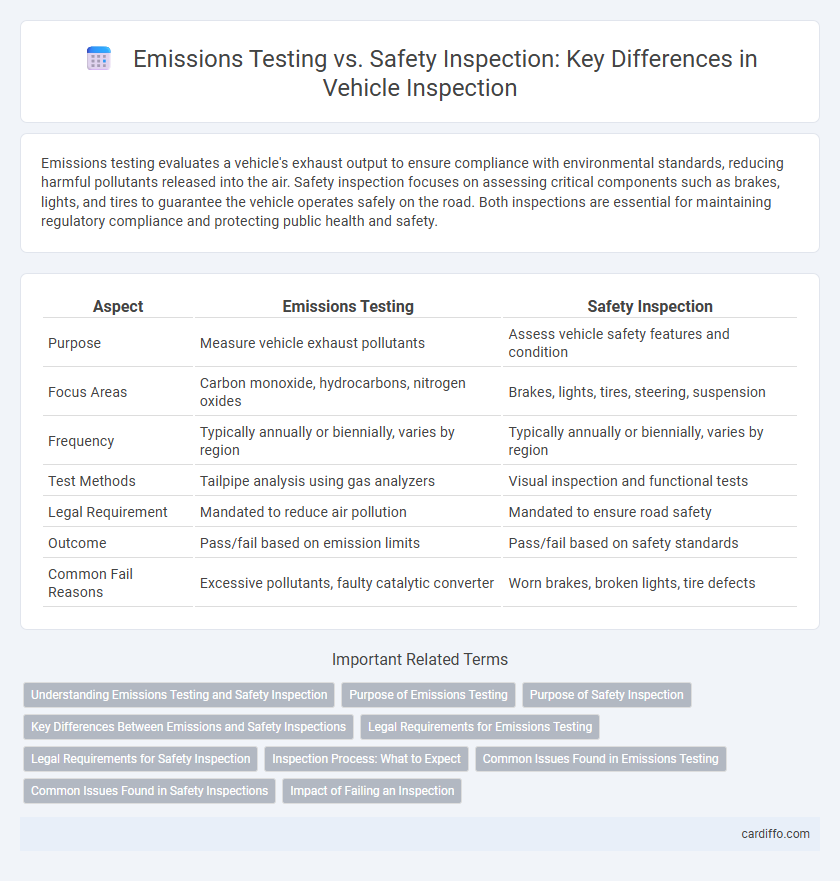
Emissions testing evaluates a vehicle's exhaust output to ensure compliance with environmental standards, reducing harmful pollutants released into the air. Safety inspection focuses on assessing critical components such as brakes, lights, and tires to guarantee the vehicle operates safely on the road. Both inspections are essential for maintaining regulatory compliance and protecting public health and safety.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Emissions Testing | Safety Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measure vehicle exhaust pollutants | Assess vehicle safety features and condition |
| Focus Areas | Carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxides | Brakes, lights, tires, steering, suspension |
| Frequency | Typically annually or biennially, varies by region | Typically annually or biennially, varies by region |
| Test Methods | Tailpipe analysis using gas analyzers | Visual inspection and functional tests |
| Legal Requirement | Mandated to reduce air pollution | Mandated to ensure road safety |
| Outcome | Pass/fail based on emission limits | Pass/fail based on safety standards |
| Common Fail Reasons | Excessive pollutants, faulty catalytic converter | Worn brakes, broken lights, tire defects |
Understanding Emissions Testing and Safety Inspection
Emissions testing evaluates a vehicle's exhaust to ensure pollutants meet environmental standards, reducing air pollution and promoting public health. Safety inspections assess critical components such as brakes, tires, lights, and steering systems to confirm the vehicle's operational safety on roads. Both inspections are regulatory requirements designed to enhance environmental protection and driver safety.
Purpose of Emissions Testing
Emissions testing aims to measure the amount of pollutants released by a vehicle's exhaust system to ensure compliance with environmental standards and reduce air pollution. This process identifies excessive emissions that contribute to smog, acid rain, and other harmful environmental effects. By enforcing limits on hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides, emissions testing protects public health and supports clean air initiatives.
Purpose of Safety Inspection
Safety inspections primarily aim to identify and address potential hazards in vehicles to ensure they meet essential operational and safety standards. These inspections evaluate critical components such as brakes, tires, lights, steering, and suspension to confirm the vehicle is safe for road use. Unlike emissions testing, which focuses on environmental impact, safety inspections prioritize preventing accidents and protecting occupants and other road users.
Key Differences Between Emissions and Safety Inspections
Emissions testing measures the level of pollutants emitted by a vehicle to ensure compliance with environmental standards, while safety inspection evaluates the mechanical condition and operational safety of critical components such as brakes, lights, and tires. Emissions tests focus primarily on reducing air pollution by monitoring exhaust gases like CO, NOx, and hydrocarbons, whereas safety inspections prioritize preventing accidents by identifying defects in steering, suspension, and seat belts. Both inspections are essential for vehicle certification but serve distinct regulatory objectives targeting environmental protection and occupant safety.
Legal Requirements for Emissions Testing
Emissions testing is mandated by environmental protection laws to ensure vehicles meet specific pollution control standards, reducing harmful exhaust pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons. These legal requirements vary by jurisdiction but commonly involve periodic testing intervals, typically annual or biennial, to comply with state or federal regulations such as the Clean Air Act in the United States. Failure to pass emissions tests can result in fines, vehicle registration holds, or mandatory repairs to bring the vehicle into compliance with air quality standards.
Legal Requirements for Safety Inspection
Safety inspections are legally mandated to ensure vehicle compliance with roadworthiness and safety standards, often governed by state or national automotive regulations. These inspections focus on critical components such as brakes, lights, tires, and steering systems to prevent accidents and enhance public safety. Emissions testing, while essential, primarily addresses environmental regulations separate from the statutory requirements of safety inspections.
Inspection Process: What to Expect
During emissions testing, inspectors measure vehicle exhaust pollutants using specialized analyzers to ensure compliance with environmental standards, targeting carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides. Safety inspections involve a comprehensive assessment of critical vehicle components, including brakes, tires, lights, steering, and suspension systems to guarantee roadworthiness. Both processes require the vehicle to be stationary or driven on a dynamometer, with results recorded electronically for certification or follow-up repairs.
Common Issues Found in Emissions Testing
Common issues found in emissions testing include high levels of carbon monoxide, excessive hydrocarbons, and elevated nitrogen oxide emissions, often caused by faulty oxygen sensors, malfunctioning catalytic converters, or poor engine maintenance. Vehicles may also fail due to dirty air filters, worn spark plugs, or issues with the fuel injection system. Addressing these problems helps ensure compliance with environmental regulations and improves overall engine performance.
Common Issues Found in Safety Inspections
Safety inspections commonly reveal issues such as worn brake pads, malfunctioning lights, and tire tread wear below legal limits. Defective seat belts and cracks in windshields also frequently cause vehicles to fail safety checks. These problems directly impact vehicle roadworthiness and occupant safety, necessitating timely repairs to pass inspection standards.
Impact of Failing an Inspection
Failing an emissions test typically results in mandatory repairs to reduce harmful pollutants, preventing vehicle registration renewal until compliance is achieved. In contrast, failing a safety inspection often requires immediate fixes to critical components like brakes or lights to ensure roadworthiness and avoid legal penalties. Both failures can lead to increased costs and downtime, but emissions failures primarily impact environmental regulations, while safety failures directly affect driver and public safety.
Emissions Testing vs Safety Inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com