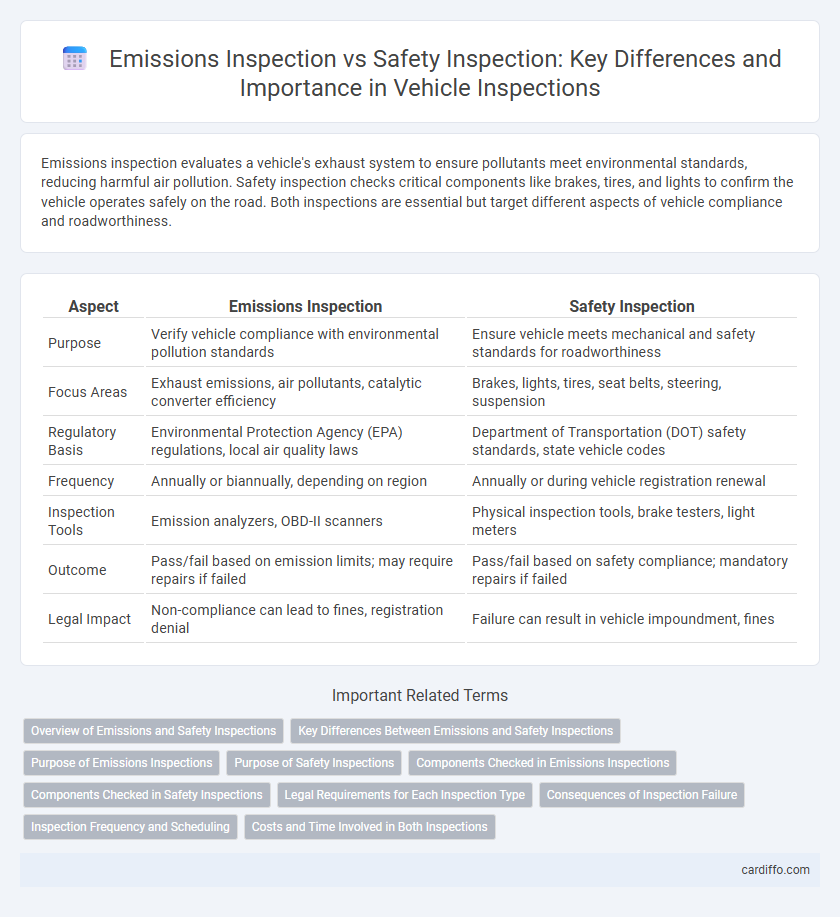
Emissions inspection evaluates a vehicle's exhaust system to ensure pollutants meet environmental standards, reducing harmful air pollution. Safety inspection checks critical components like brakes, tires, and lights to confirm the vehicle operates safely on the road. Both inspections are essential but target different aspects of vehicle compliance and roadworthiness.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Emissions Inspection | Safety Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify vehicle compliance with environmental pollution standards | Ensure vehicle meets mechanical and safety standards for roadworthiness |
| Focus Areas | Exhaust emissions, air pollutants, catalytic converter efficiency | Brakes, lights, tires, seat belts, steering, suspension |
| Regulatory Basis | Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations, local air quality laws | Department of Transportation (DOT) safety standards, state vehicle codes |
| Frequency | Annually or biannually, depending on region | Annually or during vehicle registration renewal |
| Inspection Tools | Emission analyzers, OBD-II scanners | Physical inspection tools, brake testers, light meters |
| Outcome | Pass/fail based on emission limits; may require repairs if failed | Pass/fail based on safety compliance; mandatory repairs if failed |
| Legal Impact | Non-compliance can lead to fines, registration denial | Failure can result in vehicle impoundment, fines |
Overview of Emissions and Safety Inspections
Emissions inspections primarily evaluate a vehicle's exhaust gases to ensure compliance with environmental regulations, focusing on pollutants such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides. Safety inspections assess key vehicle components including brakes, tires, lights, and suspension systems to confirm roadworthiness and prevent accidents. Both inspections serve distinct regulatory purposes, with emissions targeting pollution control and safety inspections emphasizing operational safety.
Key Differences Between Emissions and Safety Inspections
Emissions inspections focus on measuring a vehicle's exhaust pollutants to ensure compliance with environmental standards, while safety inspections evaluate critical mechanical components such as brakes, tires, and lights to confirm the vehicle's roadworthiness. Emissions tests primarily monitor air quality impact through the vehicle's tailpipe, whereas safety inspections address physical hazards that could cause accidents. Both inspections serve distinct regulatory purposes, with emissions protecting public health by reducing pollution and safety inspections maintaining driver and passenger security.
Purpose of Emissions Inspections
Emissions inspections primarily aim to measure the levels of pollutants released by a vehicle's exhaust system, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations designed to reduce air pollution. These inspections use specialized equipment to detect harmful gases such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides, which contribute to smog and respiratory problems. Unlike safety inspections that assess vehicle components like brakes and lights, emissions inspections focus strictly on the environmental impact and air quality standards compliance.
Purpose of Safety Inspections
Safety inspections primarily aim to identify and mitigate potential hazards in vehicles to ensure occupant and road user protection. Emissions inspections focus on measuring pollutants to comply with environmental standards, while safety inspections evaluate critical components like brakes, tires, lights, and steering systems. This process reduces accident risks and promotes overall vehicle reliability on the road.
Components Checked in Emissions Inspections
Emissions inspections primarily focus on components such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, exhaust system, and the vehicle's onboard diagnostics (OBD) system to ensure compliance with environmental standards. These inspections measure pollutants like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides to reduce air pollution and protect public health. Unlike safety inspections that assess brakes, tires, lights, and steering, emissions inspections specifically target the vehicle's impact on air quality.
Components Checked in Safety Inspections
Safety inspections primarily focus on critical vehicle components such as brakes, tires, steering systems, lights, windshield wipers, and seat belts to ensure proper function and roadworthiness. These components are evaluated for wear, damage, and compliance with safety regulations to prevent accidents and enhance driver safety. Unlike emissions inspections that measure pollutant output, safety inspections verify mechanical integrity and operational reliability of essential vehicle systems.
Legal Requirements for Each Inspection Type
Emissions inspections are mandated by environmental regulations to ensure vehicles meet specific air quality standards, reducing harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. Safety inspections focus on verifying the functional condition of critical vehicle components such as brakes, tires, lights, and steering to comply with traffic safety laws. Failure to meet legal requirements for either inspection type can result in fines, registration suspension, or vehicle impoundment, depending on jurisdictional enforcement policies.
Consequences of Inspection Failure
Failure in emissions inspection often results in fines, mandatory repairs, or vehicle registration denial due to non-compliance with environmental standards. In contrast, safety inspection failure can lead to immediate vehicle immobilization or prohibition from road use to prevent accidents caused by mechanical defects. Both types of inspection failures significantly impact vehicle legality and owner liability, emphasizing the necessity of regular maintenance and prompt compliance.
Inspection Frequency and Scheduling
Emissions inspections are typically mandated annually or biennially depending on regional environmental regulations, focusing on verifying vehicle compliance with air quality standards. Safety inspections, often required every six months to a year, emphasize the operational condition of critical vehicle systems such as brakes, lights, and tires to ensure driver and passenger safety. Scheduling for both types of inspections is usually dictated by state or local transportation authorities, with specific intervals designed to maximize environmental protection and road safety.
Costs and Time Involved in Both Inspections
Emissions inspections typically incur lower costs and require less time, averaging around $20 to $50 and lasting 15 to 30 minutes, focusing on measuring vehicle pollutants to ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Safety inspections often carry higher fees, ranging from $40 to $100, and take 30 to 60 minutes as they involve comprehensive checks of brakes, tires, lights, and other critical safety components. Both inspections vary by state, with emissions inspections sometimes mandatory annually, while safety inspections may occur biennially or during vehicle registration.
Emissions inspection vs safety inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com