Buyer inspections prioritize identifying potential defects and verifying property conditions before finalizing a purchase, ensuring due diligence and informed decision-making. Seller inspections are conducted to preemptively uncover issues, allowing sellers to address repairs and avoid surprises during negotiations. Both inspections aim to enhance transparency and protect the interests of their respective parties in real estate transactions.
Table of Comparison
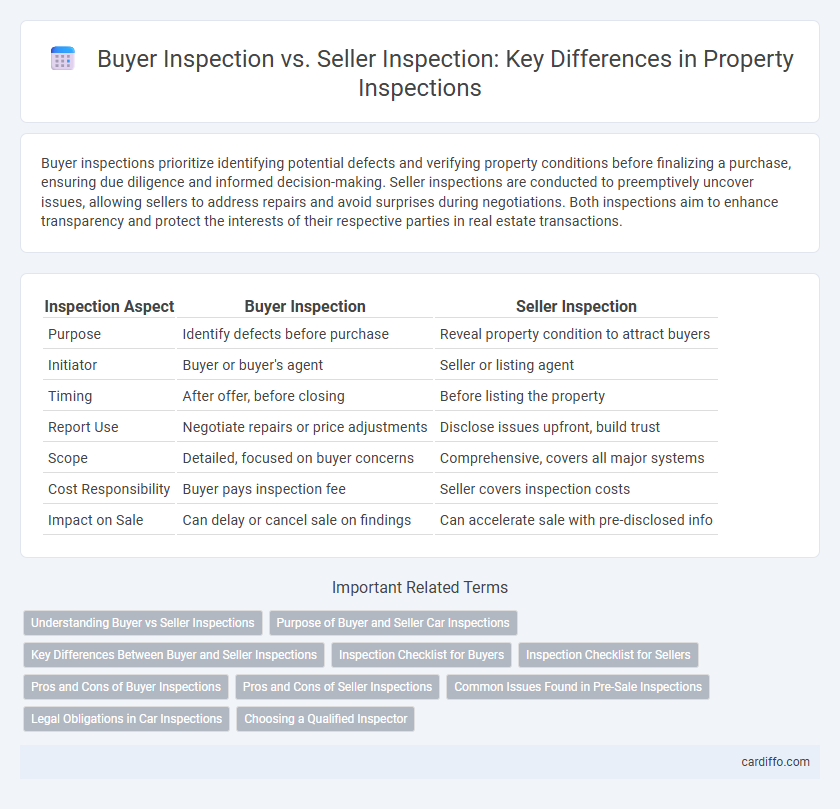
| Inspection Aspect | Buyer Inspection | Seller Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify defects before purchase | Reveal property condition to attract buyers |
| Initiator | Buyer or buyer's agent | Seller or listing agent |
| Timing | After offer, before closing | Before listing the property |
| Report Use | Negotiate repairs or price adjustments | Disclose issues upfront, build trust |
| Scope | Detailed, focused on buyer concerns | Comprehensive, covers all major systems |
| Cost Responsibility | Buyer pays inspection fee | Seller covers inspection costs |
| Impact on Sale | Can delay or cancel sale on findings | Can accelerate sale with pre-disclosed info |
Understanding Buyer vs Seller Inspections
Buyer inspections primarily focus on identifying potential issues or defects in the property before purchase, ensuring informed decision-making and negotiation power. Seller inspections aim to uncover and address problems proactively, enhancing property value and transparency to attract buyers. Understanding the distinct purposes and benefits of buyer vs seller inspections helps streamline the transaction process and reduces the risk of post-sale disputes.
Purpose of Buyer and Seller Car Inspections
Buyer inspections prioritize identifying potential issues and assessing the overall condition of the vehicle to ensure a fair purchase decision. Seller inspections focus on verifying the car's current state and addressing any defects to enhance buyer confidence and justify the asking price. Both inspection types aim to provide transparency, but the buyer's purpose centers on risk assessment, while the seller's goal emphasizes disclosure and trust-building.
Key Differences Between Buyer and Seller Inspections
Buyer inspections primarily assess a property's condition to identify defects before purchase, focusing on potential repair costs and safety issues. Seller inspections aim to preemptively uncover and address problems to facilitate smoother transactions and improve property value disclosures. The key difference lies in buyer inspections being condition-focused for negotiation leverage, while seller inspections are proactive to enhance marketability and transparency.
Inspection Checklist for Buyers
Buyers conducting inspections should use a detailed inspection checklist covering structural elements, HVAC systems, plumbing, electrical components, and potential safety hazards to ensure comprehensive property evaluation. This checklist helps buyers identify costly repairs and negotiate better terms, contrasting with seller inspections typically aimed at pre-emptive issue resolution for smoother transactions. Prioritizing thorough buyer inspections reduces unforeseen expenses and supports informed purchasing decisions in real estate deals.
Inspection Checklist for Sellers
An effective inspection checklist for sellers includes verifying the condition of major systems such as HVAC, plumbing, and electrical to reduce surprises during the buyer inspection. Sellers should also address visible issues like roof damage, leaks, and structural concerns to increase property value and buyer confidence. Completing pre-inspections and repairs beforehand streamlines negotiations and can lead to faster, smoother transactions compared to waiting for the buyer's inspection findings.
Pros and Cons of Buyer Inspections
Buyer inspections offer the advantage of providing a comprehensive evaluation of the property's condition before purchase, helping buyers identify potential repairs and negotiate better terms. However, these inspections can reveal issues that might lead to increased costs or the need for renegotiation, potentially complicating or delaying the transaction. While buyer inspections empower purchasers with critical information, they may also result in the buyer assuming responsibility for repair risks if issues are discovered late in the process.
Pros and Cons of Seller Inspections
Seller inspections provide transparency by identifying property issues before listing, potentially reducing negotiation delays and increasing buyer confidence. However, these inspections may reveal costly repairs sellers are reluctant to address, risking lower offers or deal cancellations. Unlike buyer inspections, seller inspections rely on the seller's choice of inspector, which could lead to biased or incomplete reports.
Common Issues Found in Pre-Sale Inspections
Buyer inspections often reveal issues such as structural damage, faulty electrical systems, and plumbing leaks, which are critical for negotiating repairs or price adjustments. Seller inspections typically identify cosmetic problems and maintenance needs like worn-out roofing, HVAC inefficiencies, and outdated appliances to proactively address concerns before listing. Common issues in pre-sale inspections emphasize the importance of thorough evaluations to prevent surprises during property transactions.
Legal Obligations in Car Inspections
Buyer inspection typically involves a comprehensive evaluation conducted by the purchaser or an appointed expert to identify defects and ensure the vehicle meets agreed standards before finalizing the sale. Seller inspection, while often less detailed, may legally require disclosure of known issues to avoid claims of misrepresentation or fraud under consumer protection laws. Legal obligations vary by jurisdiction, but failure to adhere to mandatory inspections or disclose significant vehicle defects can result in penalties, contract nullification, or litigation.
Choosing a Qualified Inspector
Selecting a qualified inspector ensures accurate assessments during both buyer and seller inspections, safeguarding transaction integrity. Buyer inspections require thorough evaluation of the property's condition to identify potential repairs, while seller inspections focus on uncovering issues to address before listing. Certified inspectors with industry experience and proper credentials provide reliable reports that facilitate informed decision-making.
Buyer inspection vs seller inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com