Fuel injection delivers precise amounts of fuel directly into the combustion chamber or intake manifold, enhancing engine efficiency, improving fuel economy, and reducing emissions compared to carburetion. Carburetors rely on vacuum pressure to mix air and fuel, often resulting in less accurate fuel delivery and higher pollutant levels. Modern engines favor fuel injection systems for their superior performance, reliability, and adaptability to various operating conditions.
Table of Comparison
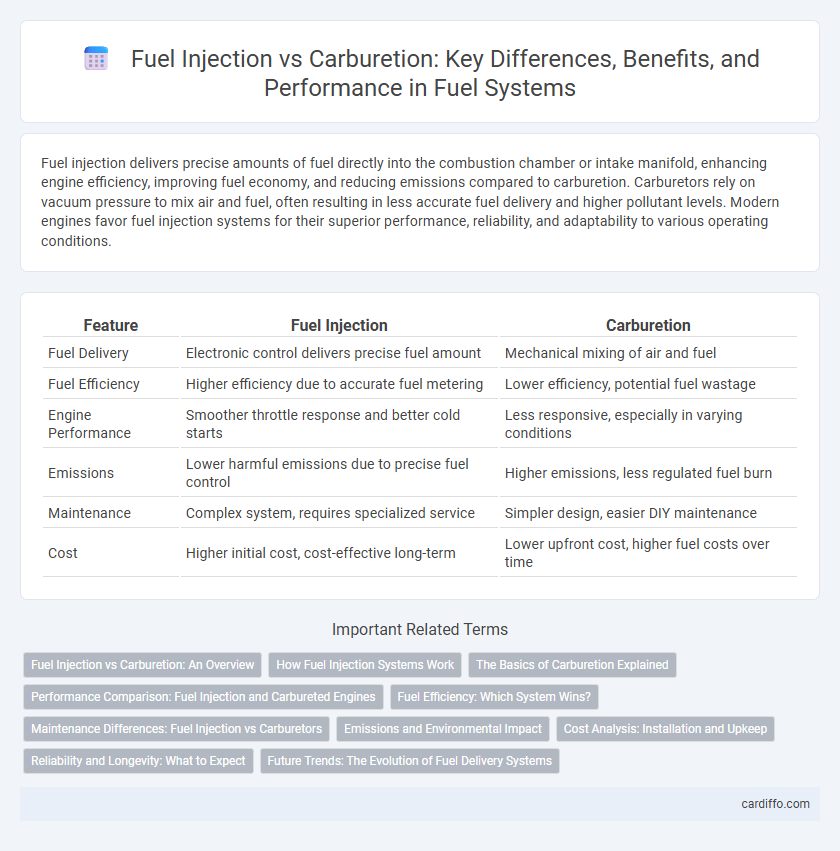
| Feature | Fuel Injection | Carburetion |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Delivery | Electronic control delivers precise fuel amount | Mechanical mixing of air and fuel |
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher efficiency due to accurate fuel metering | Lower efficiency, potential fuel wastage |
| Engine Performance | Smoother throttle response and better cold starts | Less responsive, especially in varying conditions |
| Emissions | Lower harmful emissions due to precise fuel control | Higher emissions, less regulated fuel burn |
| Maintenance | Complex system, requires specialized service | Simpler design, easier DIY maintenance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, cost-effective long-term | Lower upfront cost, higher fuel costs over time |
Fuel Injection vs Carburetion: An Overview
Fuel injection delivers precise amounts of fuel directly into the combustion chamber or intake manifold, enhancing engine efficiency and reducing emissions compared to carburetion, which mixes fuel and air mechanically before entering the engine. Modern fuel injection systems use electronic controls and sensors to optimize fuel delivery based on real-time engine parameters, while carburetors rely on vacuum pressure and mechanical jets, leading to less accurate fuel metering. The shift to fuel injection in automotive engines has improved fuel economy, throttle response, and overall performance while meeting stringent emission standards.
How Fuel Injection Systems Work
Fuel injection systems deliver precise amounts of fuel directly into the combustion chamber or intake manifold using electronically controlled injectors, optimizing air-fuel mixture for improved combustion efficiency. Sensors monitor engine parameters such as air intake, temperature, and throttle position to adjust fuel delivery in real-time, enhancing fuel economy and reducing emissions. Compared to carburetors, fuel injection provides smoother throttle response, better cold starts, and more consistent engine performance under varying conditions.
The Basics of Carburetion Explained
Carburetion involves mixing air and fuel in the correct ratio to ensure efficient combustion in an internal combustion engine. A carburetor uses venturi tubes to create a pressure difference that draws fuel into the airflow, relying on mechanical components for fuel regulation. Unlike fuel injection systems, carburetors lack electronic control, which can result in less precise fuel delivery and reduced engine efficiency.
Performance Comparison: Fuel Injection and Carbureted Engines
Fuel injection systems deliver precise amounts of fuel directly into the combustion chamber, resulting in improved throttle response, better fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions compared to carbureted engines. Carburetors rely on air pressure differences to mix fuel and air, which can lead to less accurate fuel delivery and decreased performance, especially under varied driving conditions. Modern fuel injection technology enhances engine power output and adaptability, contributing to superior overall engine performance relative to traditional carburetion methods.
Fuel Efficiency: Which System Wins?
Fuel injection systems deliver precise amounts of fuel directly into the combustion chamber or intake manifold, optimizing air-fuel mixture for maximum efficiency and reducing waste. Carburetors, relying on mechanical methods to blend fuel and air, often result in less accurate fuel delivery, leading to higher consumption and emissions. Modern fuel injection technology generally wins the fuel efficiency race by enhancing combustion control and adapting to operating conditions in real time.
Maintenance Differences: Fuel Injection vs Carburetors
Fuel injection systems require less frequent maintenance compared to carburetors due to their electronic control, resulting in fewer adjustments and cleaning needs. Carburetors demand regular tuning, cleaning of jets, and manual adjustment to maintain optimal performance and fuel efficiency. Modern fuel injection also improves reliability by minimizing issues related to fuel delivery inconsistencies common in carbureted engines.
Emissions and Environmental Impact
Fuel injection systems deliver precise amounts of fuel directly into the combustion chamber, resulting in more efficient combustion and significantly lower emissions of hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides compared to carburetion. Carburetors tend to mix fuel and air less accurately, leading to incomplete combustion and higher pollutant output. Modern fuel injection technologies contribute to reduced environmental impact through improved fuel atomization and optimized air-fuel ratios, supporting stricter emission regulations.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Upkeep
Fuel injection systems feature higher initial installation costs due to advanced electronic components and sensors, but they offer improved fuel efficiency and lower maintenance expenses over time. Carburetors generally have lower upfront expenses and simpler mechanical designs, resulting in easier and cheaper repairs, but they often require more frequent upkeep and tuning to maintain optimal performance. Evaluating lifetime costs, fuel injection tends to be more cost-effective despite higher starting costs, especially for long-term vehicle operation.
Reliability and Longevity: What to Expect
Fuel injection systems offer greater reliability and longevity due to precise fuel delivery and fewer mechanical parts prone to wear compared to carburetors. Carburetors often require frequent adjustments and maintenance to maintain optimal performance, leading to increased wear over time. Modern fuel injection enhances engine efficiency and reduces the risk of component failure, ensuring a longer lifespan for fuel system components.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Fuel Delivery Systems
Fuel injection systems are advancing rapidly with the integration of electronic control units (ECUs) and real-time data analytics, enabling precise fuel atomization and improved combustion efficiency. Emerging technologies such as direct injection and gasoline particulate filters are reducing emissions and enhancing fuel economy, aligning with stringent environmental regulations. The future of fuel delivery is moving towards adaptive, AI-driven systems that optimize fuel flow based on driving conditions, vehicle performance, and emission standards.
fuel injection vs carburetion Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com