Carbureted engines rely on a mechanical system to mix air and fuel, often resulting in less precise fuel delivery and lower efficiency compared to fuel-injected engines. Fuel-injected systems use electronic controls to optimize the air-fuel mixture, improving combustion efficiency, performance, and emissions. Choosing between carbureted and fuel-injected depends on factors like maintenance preferences, fuel economy, and vehicle age.
Table of Comparison
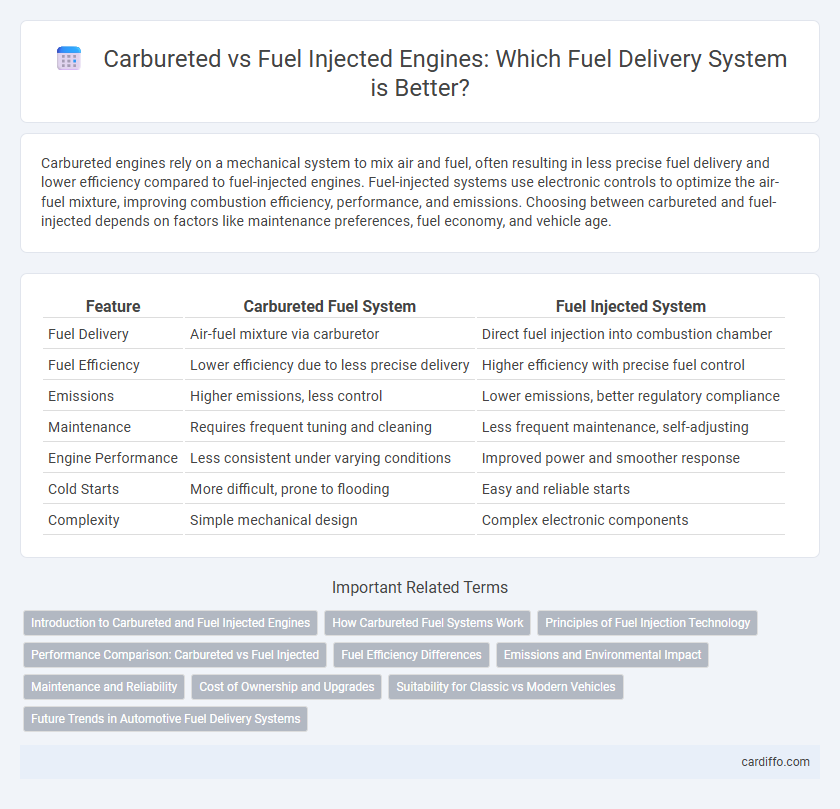
| Feature | Carbureted Fuel System | Fuel Injected System |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Delivery | Air-fuel mixture via carburetor | Direct fuel injection into combustion chamber |
| Fuel Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to less precise delivery | Higher efficiency with precise fuel control |
| Emissions | Higher emissions, less control | Lower emissions, better regulatory compliance |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent tuning and cleaning | Less frequent maintenance, self-adjusting |
| Engine Performance | Less consistent under varying conditions | Improved power and smoother response |
| Cold Starts | More difficult, prone to flooding | Easy and reliable starts |
| Complexity | Simple mechanical design | Complex electronic components |
Introduction to Carbureted and Fuel Injected Engines
Carbureted engines use a carburetor to mix air and fuel before delivering it to the engine cylinders, relying on vacuum to draw fuel into the intake stream. Fuel injected engines employ electronic fuel injectors that precisely spray fuel directly into the combustion chamber or intake manifold, improving efficiency and performance. The transition from carbureted to fuel injected systems has enhanced fuel economy, reduced emissions, and allowed for more precise engine management.
How Carbureted Fuel Systems Work
Carbureted fuel systems work by mixing air and fuel mechanically before delivering the mixture to the engine cylinders, using a venturi to create suction that draws fuel into the airflow. The carburetor adjusts the fuel-to-air ratio based on throttle position and engine demand, relying on jets and needles for precise fuel metering. This system operates without electronic controls, making it simpler but less efficient compared to fuel-injected systems.
Principles of Fuel Injection Technology
Fuel injection technology precisely delivers atomized fuel directly into the combustion chamber or intake manifold, optimizing air-fuel mixture for enhanced combustion efficiency and reduced emissions. Unlike carburetors, which rely on vacuum pressure to mix fuel and air, fuel injectors use electronically controlled pumps and sensors to maintain accurate fuel delivery based on engine load and speed. This system improves throttle response, fuel economy, and lowers carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emissions, making it a superior choice for modern engines.
Performance Comparison: Carbureted vs Fuel Injected
Fuel-injected engines deliver superior performance through precise fuel metering, resulting in improved throttle response, better fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions compared to carbureted systems. Carburetors tend to provide less consistent fuel delivery, leading to potential issues like engine hesitation and higher fuel consumption, especially under varying load conditions. Modern fuel injection systems adapt in real-time to engine demands, optimizing combustion for enhanced power output and smoother acceleration.
Fuel Efficiency Differences
Fuel-injected engines typically offer superior fuel efficiency compared to carbureted systems due to precise air-fuel mixture control and improved atomization. Carbureted engines often result in richer fuel mixtures, increasing consumption and emissions. Modern fuel injection technology optimizes combustion, reducing fuel waste and enhancing mileage by up to 15-20%.
Emissions and Environmental Impact
Fuel injection systems provide more precise control of air-fuel mixture, resulting in lower emissions of hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides compared to carbureted engines. Carburetors tend to produce higher levels of unburned fuel pollutants due to less efficient fuel atomization and delivery. Modern fuel injection technology significantly reduces environmental impact by enhancing combustion efficiency and meeting stricter emission regulations.
Maintenance and Reliability
Carbureted engines require frequent adjustments and cleaning to maintain optimal fuel-air mixture, making them more labor-intensive in terms of maintenance compared to fuel-injected systems. Fuel injection offers superior reliability due to precise electronic control and fewer mechanical parts prone to wear and clogging. Modern fuel-injected systems also improve engine performance and fuel efficiency while reducing the need for regular manual tuning.
Cost of Ownership and Upgrades
Carbureted engines often have lower initial repair costs due to simpler mechanical components but require more frequent maintenance, impacting long-term cost of ownership. Fuel injected systems provide improved fuel efficiency and engine performance with lower emissions, resulting in higher upfront costs but reduced fuel and maintenance expenses over time. Upgrades for carbureted systems are generally more affordable and easier to implement, while fuel injection upgrades demand advanced diagnostic tools and specialized knowledge.
Suitability for Classic vs Modern Vehicles
Carbureted systems are ideal for classic vehicles due to their simple mechanical design, ease of maintenance, and compatibility with vintage engine technology. Fuel injection provides superior fuel efficiency, precise air-fuel mixture control, and emissions reduction, making it more suitable for modern vehicles equipped with advanced electronic engine management systems. Classic cars benefit from the authenticity of carburetion, whereas modern vehicles require the performance and regulatory compliance that fuel injection offers.
Future Trends in Automotive Fuel Delivery Systems
Fuel injection systems are rapidly advancing due to their superior precision and efficiency compared to traditional carbureted setups, driving a shift toward electronic fuel delivery in automotive engines. Innovations such as direct injection and variable fuel-pressure technology enhance combustion control, reduce emissions, and improve fuel economy, aligning with stricter environmental regulations. Emerging trends include integration with hybrid and electric powertrains, highlighting a future where fuel injection remains pivotal in optimizing performance while supporting sustainability goals.
Carbureted vs Fuel Injected Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com