Turbocharged engines increase power and efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, resulting in better fuel economy and higher performance compared to naturally aspirated engines. Naturally aspirated engines rely solely on atmospheric pressure, providing a linear throttle response and simpler design but often at the cost of lower power output and fuel efficiency. Choosing between turbocharged and naturally aspirated depends on balancing performance needs and fuel consumption priorities.
Table of Comparison
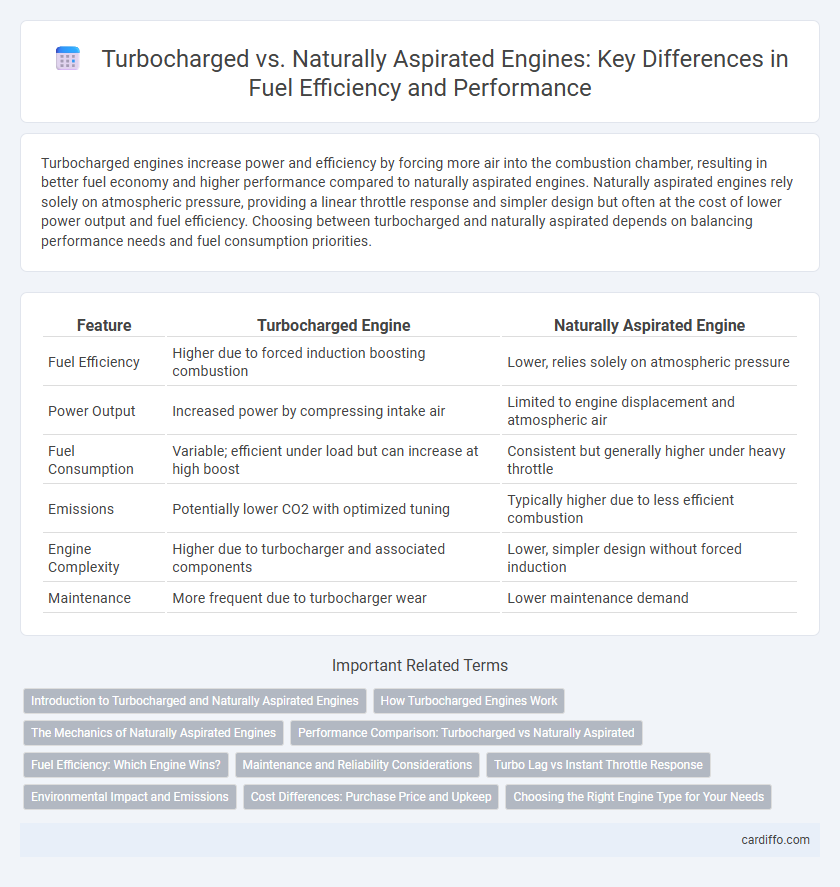
| Feature | Turbocharged Engine | Naturally Aspirated Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher due to forced induction boosting combustion | Lower, relies solely on atmospheric pressure |
| Power Output | Increased power by compressing intake air | Limited to engine displacement and atmospheric air |
| Fuel Consumption | Variable; efficient under load but can increase at high boost | Consistent but generally higher under heavy throttle |
| Emissions | Potentially lower CO2 with optimized tuning | Typically higher due to less efficient combustion |
| Engine Complexity | Higher due to turbocharger and associated components | Lower, simpler design without forced induction |
| Maintenance | More frequent due to turbocharger wear | Lower maintenance demand |
Introduction to Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
Turbocharged engines utilize forced induction by compressing air through a turbine powered by exhaust gases, significantly increasing engine efficiency and power output. Naturally aspirated engines rely on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber, resulting in a simpler design with more linear throttle response. The choice between turbocharged and naturally aspirated systems impacts fuel consumption, emissions, and overall vehicle performance.
How Turbocharged Engines Work
Turbocharged engines utilize exhaust gas to spin a turbine connected to a compressor, forcing more air into the combustion chamber for increased oxygen supply. This process enhances fuel combustion efficiency, resulting in higher power output and better fuel economy compared to naturally aspirated engines. The compressed air allows the engine to burn more fuel while maintaining optimal air-fuel ratios, improving overall performance and responsiveness.
The Mechanics of Naturally Aspirated Engines
Naturally aspirated engines rely on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber without external forced induction, resulting in a simpler intake system and predictable throttle response. These engines use a carefully designed intake manifold and camshaft timing to optimize airflow and fuel mixture, maximizing efficiency and power within the limits of ambient air pressure. Unlike turbocharged engines, naturally aspirated engines do not require intercoolers or turbochargers, reducing mechanical complexity and potential maintenance issues.
Performance Comparison: Turbocharged vs Naturally Aspirated
Turbocharged engines deliver higher power and torque output by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance compared to naturally aspirated engines. Naturally aspirated engines offer linear throttle response and simplicity, but generally produce less peak power and reduced efficiency at higher altitudes. Turbocharged systems enhance fuel efficiency and power density, making them ideal for performance-driven applications despite added complexity and potential lag.
Fuel Efficiency: Which Engine Wins?
Turbocharged engines typically deliver better fuel efficiency compared to naturally aspirated engines by extracting more power from the same amount of fuel through forced induction. This increased efficiency results from higher air intake pressure, allowing for more complete combustion and improved engine performance. While naturally aspirated engines offer simplicity and reliability, turbocharged technology continues to lead in optimizing fuel consumption and reducing emissions.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
Turbocharged engines require more frequent maintenance due to higher operating temperatures and increased stress on components, including regular oil changes and inspection of turbo seals. Naturally aspirated engines generally offer greater reliability with simpler designs and fewer parts prone to failure, resulting in lower maintenance costs over time. Proper upkeep of turbocharged systems is essential to prevent turbo lag and premature wear, while naturally aspirated engines benefit from consistent, straightforward maintenance routines.
Turbo Lag vs Instant Throttle Response
Turbocharged engines often experience turbo lag, a delay in power delivery caused by the time needed for the turbocharger to spool up and increase boost pressure. Naturally aspirated engines provide instant throttle response since they rely solely on atmospheric pressure, delivering power immediately without any forced induction delay. This immediate responsiveness makes naturally aspirated engines preferable for drivers seeking consistent and predictable acceleration.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Turbocharged engines improve fuel efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, resulting in better fuel atomization and reduced fuel consumption compared to naturally aspirated engines. Lower fuel consumption directly correlates with reduced CO2 emissions, making turbocharged engines more environmentally friendly in terms of greenhouse gas output. However, turbocharged engines may produce higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) due to increased combustion temperatures, necessitating advanced emission control technologies to meet stringent environmental regulations.
Cost Differences: Purchase Price and Upkeep
Turbocharged engines generally have a higher purchase price compared to naturally aspirated engines due to their complex design and additional components like turbochargers and intercoolers. Maintenance costs for turbocharged engines tend to be higher because of more frequent oil changes, specialized parts, and potential turbocharger repairs or replacements. Naturally aspirated engines usually offer lower upfront costs and simpler upkeep, making them more budget-friendly for everyday driving.
Choosing the Right Engine Type for Your Needs
Turbocharged engines deliver increased power and improved fuel efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, making them ideal for performance-oriented drivers or those needing better fuel economy in varying conditions. Naturally aspirated engines provide linear power delivery and simpler mechanics, resulting in lower maintenance costs and greater reliability for everyday driving and long-term durability. Selecting the right engine type depends on your priorities for power output, fuel efficiency, maintenance, and driving habits.
Turbocharged vs Naturally Aspirated Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com