Winter diesel contains additives that prevent gelling and improve flow in cold temperatures, ensuring better engine performance and reliability. Summer diesel is formulated with a higher energy content and fewer additives, optimizing combustion efficiency and reducing emissions under warmer conditions. Selecting the appropriate diesel type maximizes fuel efficiency and protects engine components throughout seasonal temperature changes.
Table of Comparison
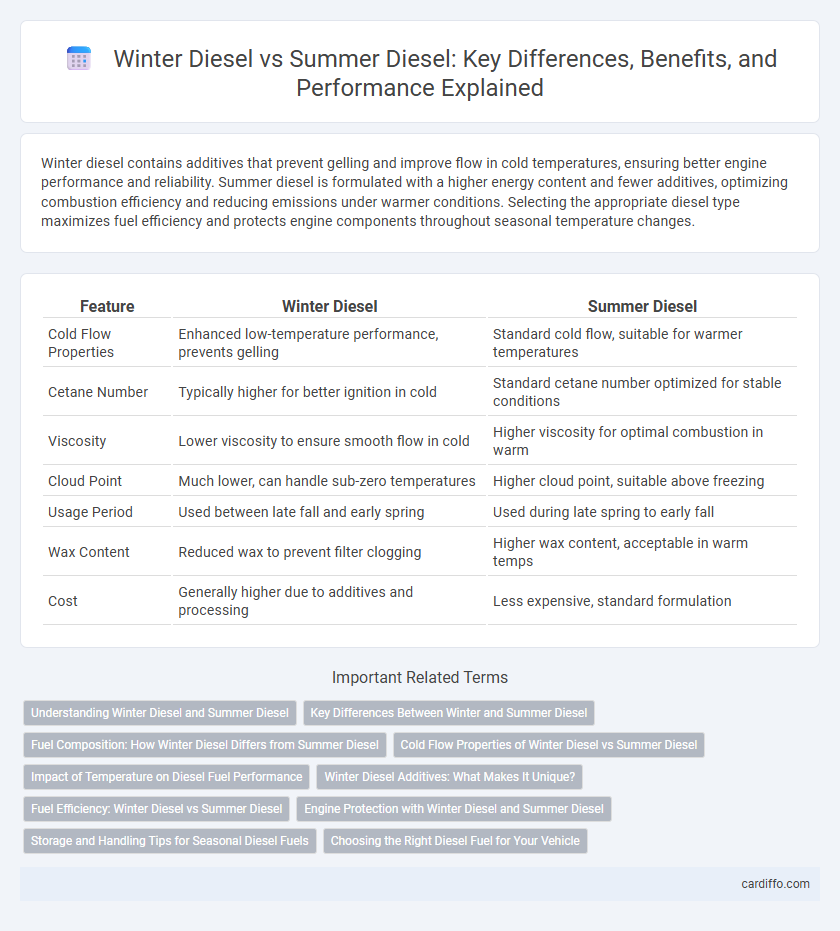
| Feature | Winter Diesel | Summer Diesel |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Flow Properties | Enhanced low-temperature performance, prevents gelling | Standard cold flow, suitable for warmer temperatures |
| Cetane Number | Typically higher for better ignition in cold | Standard cetane number optimized for stable conditions |
| Viscosity | Lower viscosity to ensure smooth flow in cold | Higher viscosity for optimal combustion in warm |
| Cloud Point | Much lower, can handle sub-zero temperatures | Higher cloud point, suitable above freezing |
| Usage Period | Used between late fall and early spring | Used during late spring to early fall |
| Wax Content | Reduced wax to prevent filter clogging | Higher wax content, acceptable in warm temps |
| Cost | Generally higher due to additives and processing | Less expensive, standard formulation |
Understanding Winter Diesel and Summer Diesel
Winter diesel contains additives and a lower pour point to prevent gelling and ensure better flow in subzero temperatures, making it ideal for cold climates. Summer diesel lacks these cold-flow improvers but has higher energy content and stability for use in warmer conditions. Choosing the appropriate diesel type enhances engine performance and reduces fuel line blockages during seasonal temperature fluctuations.
Key Differences Between Winter and Summer Diesel
Winter diesel contains additives like anti-gel agents and lower cloud points to prevent fuel gelling in cold temperatures, ensuring reliable engine performance. Summer diesel has a higher energy content and fewer additives, optimized for warmer weather conditions to maximize engine efficiency and reduce emissions. The key difference lies in their formulation, which adapts to temperature variations to maintain fuel flow and combustion stability throughout the seasons.
Fuel Composition: How Winter Diesel Differs from Summer Diesel
Winter diesel contains specific additives such as anti-gel agents and flow improvers that prevent fuel from gelling or crystallizing at low temperatures, ensuring smooth engine operation in cold climates. Its composition features a higher proportion of lighter hydrocarbons and lower cloud point compared to summer diesel, reducing the risk of fuel line freezing. Summer diesel, in contrast, has fewer additives and a higher cloud point, optimized for warmer temperatures to maintain stability and combustion efficiency.
Cold Flow Properties of Winter Diesel vs Summer Diesel
Winter diesel features enhanced cold flow properties, including lower cloud points and pour points, enabling it to remain fluid at subzero temperatures and preventing gelling in cold climates. In contrast, summer diesel has higher cloud and pour points optimized for warmer conditions, which can cause waxing and fuel filter plugging when exposed to cold. These cold flow property differences ensure winter diesel maintains engine performance and reliability during harsh winter environments.
Impact of Temperature on Diesel Fuel Performance
Winter diesel is specially formulated with additives and lower cloud points to prevent gelling and improve flow in subfreezing temperatures, ensuring reliable engine start-up and operation. Summer diesel contains less paraffin wax and is optimized for higher temperatures, reducing vapor lock and maintaining combustion efficiency during warmer months. Temperature fluctuations directly influence diesel fuel viscosity, cold filter plugging point, and cetane number, impacting overall engine performance and emissions.
Winter Diesel Additives: What Makes It Unique?
Winter diesel contains specialized additives such as anti-gel agents and cold flow improvers that prevent fuel from thickening and clogging filters in low temperatures. These additives lower the fuel's pour point and cloud point, ensuring smooth engine starts and consistent combustion in harsh winter conditions. Enhanced lubrication properties in winter diesel additives also protect fuel injectors and pumps from wear during prolonged cold exposure.
Fuel Efficiency: Winter Diesel vs Summer Diesel
Winter diesel contains additives that lower its pour point and improve cold-flow properties, ensuring better combustion efficiency in low temperatures compared to summer diesel. Summer diesel, optimized for higher ambient temperatures, offers a higher energy content, which can slightly enhance fuel economy in warm conditions. Using season-specific diesel helps maintain optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency throughout the year by matching fuel formulations to temperature requirements.
Engine Protection with Winter Diesel and Summer Diesel
Winter diesel includes anti-gel additives that prevent fuel from thickening in cold temperatures, ensuring smooth engine starts and reliable combustion. Summer diesel has a higher cetane rating and lower volatility, reducing engine knocking and deposits under warmer conditions. Using the appropriate seasonal diesel enhances fuel flow and combustion efficiency, protecting engine components from wear and maintaining optimal performance year-round.
Storage and Handling Tips for Seasonal Diesel Fuels
Winter diesel contains additives that prevent gelling at low temperatures, enhancing flow and engine performance in cold climates, while summer diesel is formulated for higher temperatures to maintain stability and energy content. Store winter diesel in well-insulated, temperature-controlled tanks to avoid condensation and fuel degradation, and ensure tanks are tightly sealed to prevent moisture contamination year-round. Regularly rotate stock to use older fuel first, and consider adding cetane boosters or anti-gel additives during extreme cold to maintain optimal fuel viscosity and combustion quality.
Choosing the Right Diesel Fuel for Your Vehicle
Winter diesel contains additives that prevent gelling and improve cold flow properties, ensuring reliable engine performance in freezing temperatures. Summer diesel has a higher energy content and fewer additives, making it more efficient for warmer conditions and reducing emissions. Selecting the appropriate diesel based on seasonal temperature variations enhances fuel efficiency, engine longevity, and overall vehicle performance.
Winter Diesel vs Summer Diesel Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com