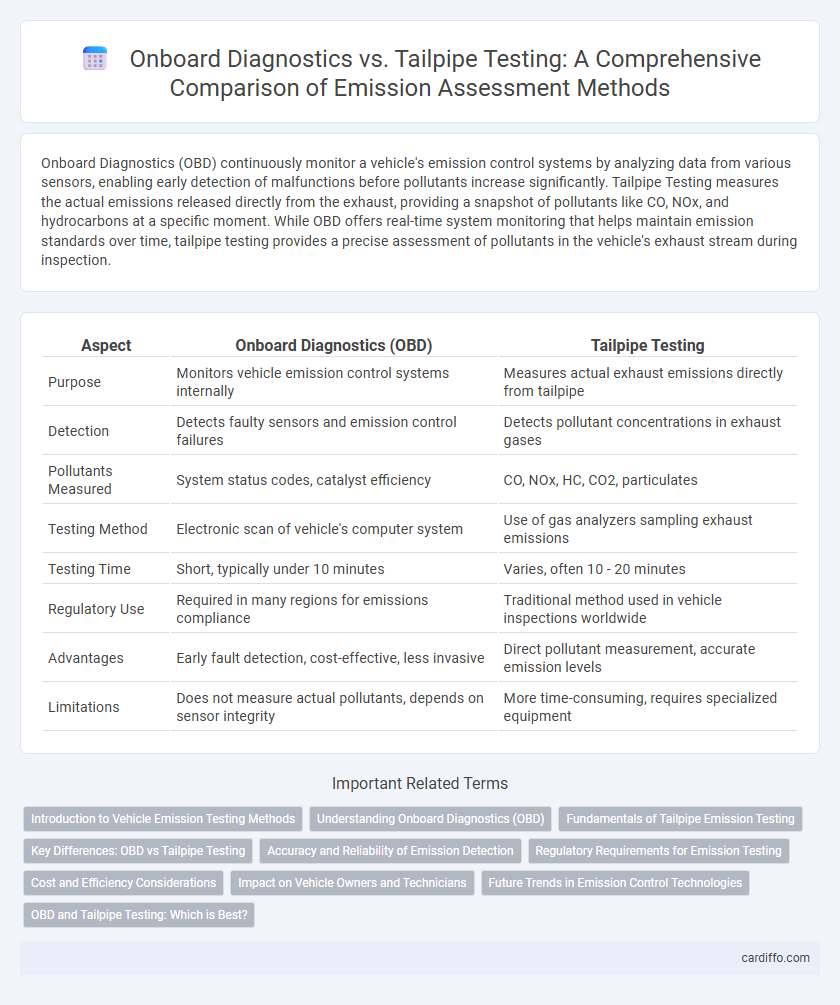
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) continuously monitor a vehicle's emission control systems by analyzing data from various sensors, enabling early detection of malfunctions before pollutants increase significantly. Tailpipe Testing measures the actual emissions released directly from the exhaust, providing a snapshot of pollutants like CO, NOx, and hydrocarbons at a specific moment. While OBD offers real-time system monitoring that helps maintain emission standards over time, tailpipe testing provides a precise assessment of pollutants in the vehicle's exhaust stream during inspection.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) | Tailpipe Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Monitors vehicle emission control systems internally | Measures actual exhaust emissions directly from tailpipe |
| Detection | Detects faulty sensors and emission control failures | Detects pollutant concentrations in exhaust gases |
| Pollutants Measured | System status codes, catalyst efficiency | CO, NOx, HC, CO2, particulates |
| Testing Method | Electronic scan of vehicle's computer system | Use of gas analyzers sampling exhaust emissions |
| Testing Time | Short, typically under 10 minutes | Varies, often 10 - 20 minutes |
| Regulatory Use | Required in many regions for emissions compliance | Traditional method used in vehicle inspections worldwide |
| Advantages | Early fault detection, cost-effective, less invasive | Direct pollutant measurement, accurate emission levels |
| Limitations | Does not measure actual pollutants, depends on sensor integrity | More time-consuming, requires specialized equipment |
Introduction to Vehicle Emission Testing Methods
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) and Tailpipe Testing represent two critical vehicle emission testing methods aimed at reducing air pollution. OBD continuously monitors the performance of engine components and emission control systems, detecting faults that contribute to increased emissions in real-time. Tailpipe Testing measures pollutants such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides directly from the vehicle's exhaust, providing a snapshot of emission levels during operation.
Understanding Onboard Diagnostics (OBD)
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) systems continuously monitor a vehicle's emission control components, detecting malfunctions and storing diagnostic trouble codes to ensure compliance with environmental standards. OBD provides real-time data on engine performance and emissions, enabling faster identification and repair of issues compared to traditional tailpipe testing. This advanced technology supports effective emission reductions by maintaining optimal vehicle operation throughout the vehicle's lifespan.
Fundamentals of Tailpipe Emission Testing
Tailpipe emission testing measures pollutants directly from the vehicle's exhaust, capturing real-time data on gases like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides. This method assesses the actual emissions released during engine operation, providing accurate insight into the vehicle's environmental impact. Unlike onboard diagnostics (OBD), which analyze engine system data, tailpipe testing evaluates the final pollutant output, ensuring compliance with emission standards.
Key Differences: OBD vs Tailpipe Testing
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) continuously monitors vehicle emissions systems through the car's computer, detecting malfunctions that affect pollutant levels in real time. Tailpipe testing directly measures the concentration of exhaust gases such as CO, NOx, and hydrocarbons emitted by the vehicle under specific operational conditions. Unlike tailpipe testing, which provides a snapshot of emissions performance, OBD offers ongoing diagnostics and alerts for emission-related faults, making it essential for early detection and compliance with emission standards.
Accuracy and Reliability of Emission Detection
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) systems provide real-time monitoring of vehicle emissions by detecting malfunctions through sensors, offering higher accuracy in identifying specific component failures compared to Tailpipe Testing. Tailpipe Testing measures actual emissions output directly from the exhaust but may be influenced by transient conditions and test environment, potentially affecting reliability. OBD's continuous data and early fault detection enhance emission control effectiveness, while Tailpipe Testing remains crucial for verifying overall pollutant levels under standardized conditions.
Regulatory Requirements for Emission Testing
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) systems are mandated by regulatory agencies such as the EPA and CARB to continuously monitor vehicle emissions and ensure compliance with emission standards throughout a vehicle's life. Tailpipe testing remains a regulatory requirement in many jurisdictions to measure actual exhaust gases and verify that emissions meet specific pollutant limits like CO, NOx, and particulate matter. Regulatory frameworks increasingly emphasize OBD due to its real-time diagnostic capabilities, but tailpipe testing persists as a complementary method for comprehensive emission control and enforcement.
Cost and Efficiency Considerations
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) systems provide continuous emissions monitoring with lower operational costs compared to Tailpipe Testing, which requires specialized equipment and labor for each inspection. OBD enables real-time detection of emission-related faults, improving maintenance efficiency and reducing overall testing time. Tailpipe Testing, while offering direct measurement of pollutants, is often more expensive and less efficient for large-scale emission compliance programs.
Impact on Vehicle Owners and Technicians
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) streamline emissions monitoring by providing real-time data, simplifying fault detection and reducing the need for frequent physical inspections, which benefits vehicle owners with quicker repairs and lower costs. Tailpipe Testing requires direct sampling of exhaust emissions, involving more time-consuming and sometimes costly visits to inspection centers, impacting both owners and technicians with increased labor and waiting times. Technicians benefit from OBD systems through precise diagnostic codes that enhance repair accuracy, while tailpipe tests rely more on interpretation and specialized equipment operation.
Future Trends in Emission Control Technologies
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) systems are evolving rapidly with advanced sensors and real-time data analytics to detect emissions-related malfunctions more accurately than traditional Tailpipe Testing. Future trends emphasize integration of machine learning algorithms to predict emission failures before they occur, enhancing proactive maintenance strategies. Emerging technologies aim to harmonize OBD with remote emissions monitoring to comply with stricter environmental regulations worldwide.
OBD and Tailpipe Testing: Which is Best?
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) systems continuously monitor vehicle emissions by detecting malfunctions in engine components, providing real-time data that helps prevent excessive pollution. Tailpipe testing measures the actual pollutants emitted during vehicle operation, offering a direct assessment of emission levels but only at the time of testing. OBD offers greater efficiency and early detection of issues, while tailpipe testing provides comprehensive emission data, making a combined approach ideal for stringent environmental compliance.
Onboard Diagnostics vs Tailpipe Testing Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com