Mileage-based depreciation calculates a vehicle's value loss primarily on the number of miles driven, reflecting wear and tear related to usage. Age-based depreciation considers the vehicle's chronological age, emphasizing factors like technological obsolescence and overall aging regardless of mileage. Comparing both methods provides a more comprehensive understanding of a car's true depreciation, helping buyers and sellers make informed decisions.
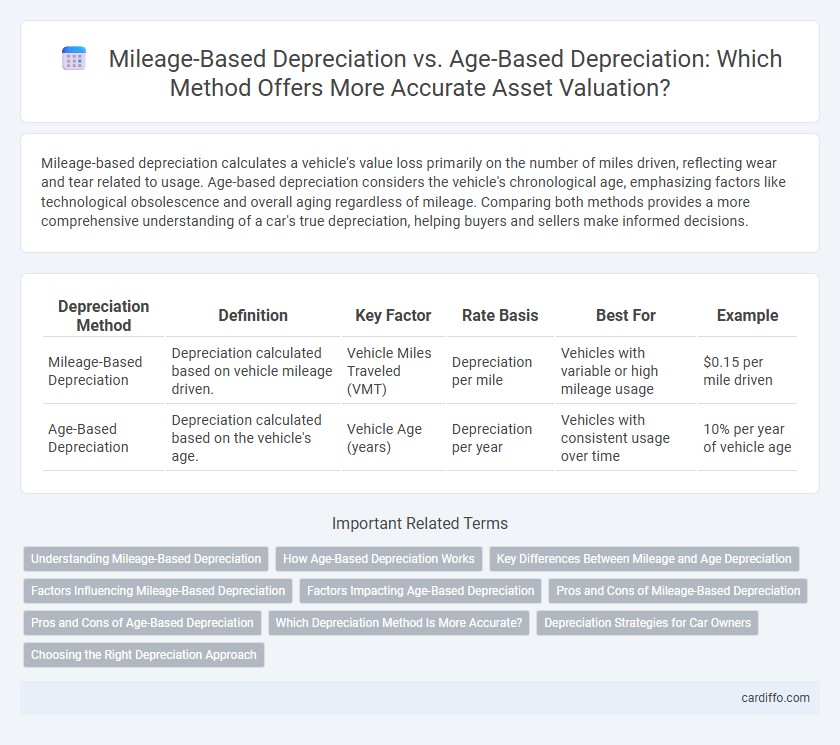
Table of Comparison
| Depreciation Method | Definition | Key Factor | Rate Basis | Best For | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mileage-Based Depreciation | Depreciation calculated based on vehicle mileage driven. | Vehicle Miles Traveled (VMT) | Depreciation per mile | Vehicles with variable or high mileage usage | $0.15 per mile driven |
| Age-Based Depreciation | Depreciation calculated based on the vehicle's age. | Vehicle Age (years) | Depreciation per year | Vehicles with consistent usage over time | 10% per year of vehicle age |
Understanding Mileage-Based Depreciation
Mileage-based depreciation calculates vehicle value loss primarily based on the total miles driven, reflecting wear and tear more accurately than age alone. This method considers that higher mileage typically leads to increased maintenance costs and faster component deterioration. Vehicles with low mileage retain higher resale value despite their model year, making mileage a critical factor in precise depreciation assessments.
How Age-Based Depreciation Works
Age-based depreciation calculates a vehicle's value loss using the car's chronological age, applying a fixed percentage or rate annually regardless of miles driven. This method simplifies accounting by assuming consistent wear and tear over time, often resulting in a steady decline in resale value. Commonly used for tax purposes and leasing agreements, age-based depreciation reflects depreciation schedules set by manufacturers or regulatory bodies.
Key Differences Between Mileage and Age Depreciation
Mileage-based depreciation measures a vehicle's value loss according to the number of miles driven, making it ideal for accurately reflecting wear and tear directly linked to usage. Age-based depreciation calculates value decline purely based on the vehicle's chronological age, regardless of how much it has been driven. Key differences lie in mileage depreciation's focus on actual usage impact, while age depreciation emphasizes time-related factors such as model obsolescence and mechanical aging.
Factors Influencing Mileage-Based Depreciation
Mileage-based depreciation is primarily influenced by the total miles driven, the type of driving conditions experienced, and the frequency of vehicle use, which directly affect wear and tear. Factors such as highway versus city driving, road quality, and maintenance routines significantly impact the rate at which a vehicle loses value based on mileage. Vehicles subjected to excessive or harsh driving conditions tend to depreciate faster compared to those with moderate, well-maintained usage.
Factors Impacting Age-Based Depreciation
Age-based depreciation is primarily influenced by the vehicle's chronological age, wear and tear, and maintenance history, which collectively determine its residual value over time. Environmental factors such as climate, exposure to sunlight, and road conditions accelerate the physical degradation of components, further affecting depreciation rates. Market trends, including consumer demand and advancements in automotive technology, also play critical roles in shaping how quickly a vehicle loses value as it ages.
Pros and Cons of Mileage-Based Depreciation
Mileage-based depreciation accurately reflects a vehicle's wear and tear by accounting for actual usage, making it highly precise for resale value assessments. It can incentivize lower mileage driving, potentially preserving vehicle condition, but may unfairly penalize drivers who use their cars more frequently for necessary travel. Unlike age-based depreciation, it doesn't consider time-related factors such as weathering or mechanical aging, which can also impact the vehicle's overall value.
Pros and Cons of Age-Based Depreciation
Age-based depreciation offers a straightforward method by reducing a vehicle's value consistently over time, simplifying accounting and tax calculations. This approach may not accurately reflect the actual wear and tear or usage, potentially undervaluing or overvaluing assets with unusual mileage patterns. Its primary advantage lies in predictability and ease of application, though it lacks sensitivity to intensive mileage, which can lead to discrepancies in assessing a vehicle's true market value.
Which Depreciation Method Is More Accurate?
Mileage-based depreciation typically offers a more accurate reflection of a vehicle's true wear and tear by accounting for actual usage, unlike age-based depreciation which assumes uniform deterioration over time regardless of driving habits. Vehicles with high mileage tend to experience faster declines in value, making mileage a critical factor for precise depreciation calculations. Age-based depreciation may oversimplify value loss, especially for low-mileage vehicles that remain in better condition despite their age.
Depreciation Strategies for Car Owners
Mileage-based depreciation accounts for the actual usage of a vehicle, reducing its value proportionally to the miles driven, which benefits owners who drive less frequently. Age-based depreciation calculates vehicle value loss solely based on the passage of time, regardless of usage, making it simpler but less precise for cars with lower mileage. Car owners can optimize depreciation strategies by combining mileage tracking with routine maintenance to retain resale value more effectively than relying on age alone.
Choosing the Right Depreciation Approach
Choosing the right depreciation approach depends on usage patterns and asset type; mileage-based depreciation accurately reflects wear for vehicles with high usage, while age-based depreciation suits assets that lose value primarily over time. Fleet managers often prefer mileage-based methods to align bookkeeping with actual usage and maintenance schedules. For businesses with varied vehicle utilization, combining both methods can optimize financial accuracy and tax reporting.
Mileage-Based Depreciation vs Age-Based Depreciation Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com