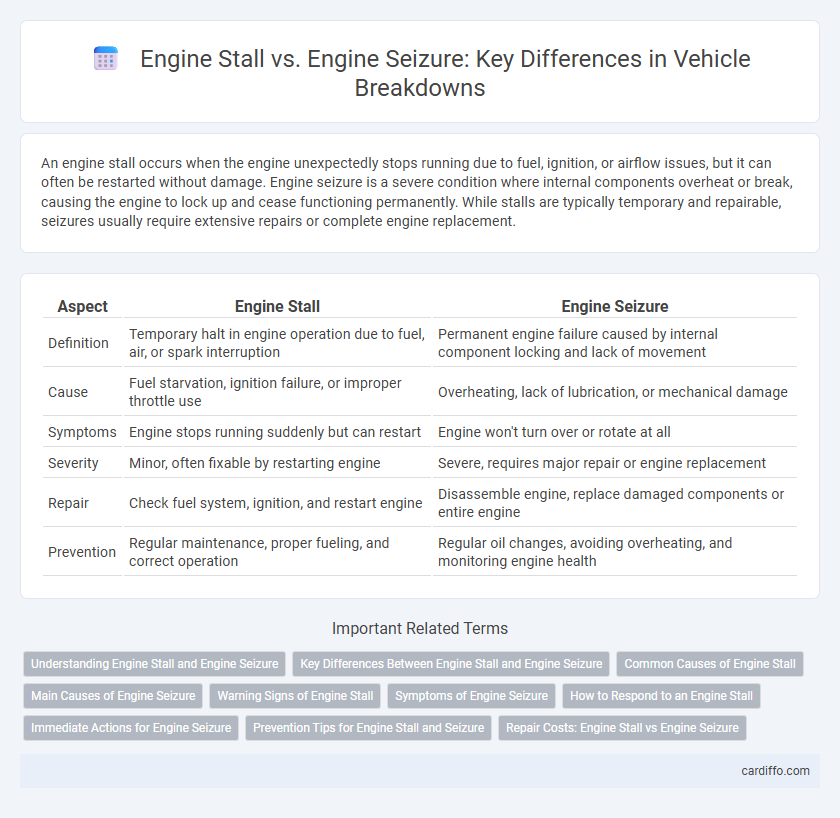
An engine stall occurs when the engine unexpectedly stops running due to fuel, ignition, or airflow issues, but it can often be restarted without damage. Engine seizure is a severe condition where internal components overheat or break, causing the engine to lock up and cease functioning permanently. While stalls are typically temporary and repairable, seizures usually require extensive repairs or complete engine replacement.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Engine Stall | Engine Seizure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary halt in engine operation due to fuel, air, or spark interruption | Permanent engine failure caused by internal component locking and lack of movement |
| Cause | Fuel starvation, ignition failure, or improper throttle use | Overheating, lack of lubrication, or mechanical damage |
| Symptoms | Engine stops running suddenly but can restart | Engine won't turn over or rotate at all |
| Severity | Minor, often fixable by restarting engine | Severe, requires major repair or engine replacement |
| Repair | Check fuel system, ignition, and restart engine | Disassemble engine, replace damaged components or entire engine |
| Prevention | Regular maintenance, proper fueling, and correct operation | Regular oil changes, avoiding overheating, and monitoring engine health |
Understanding Engine Stall and Engine Seizure
Engine stall occurs when the engine suddenly stops running due to fuel or ignition issues, often allowing for a quick restart without lasting damage. Engine seizure is a severe mechanical failure where internal components, such as pistons or bearings, overheat and lock, causing complete engine immobilization. Recognizing the symptoms of engine stall and seizure is crucial for timely diagnosis and preventing costly repairs.
Key Differences Between Engine Stall and Engine Seizure
Engine stall occurs when the engine suddenly stops running due to fuel, air, or ignition system issues, but it can usually be restarted without damage. Engine seizure involves a complete mechanical failure where the engine components lock up, often caused by severe overheating or lack of lubrication, requiring extensive repairs or replacement. Key differences include reversibility, cause, and severity: stalls are typically temporary and related to operational errors, while seizures indicate catastrophic engine damage.
Common Causes of Engine Stall
Engine stall commonly occurs due to fuel system issues such as clogged fuel filters or an empty fuel tank, leading to sudden loss of power. Ignition system malfunctions, including faulty spark plugs or ignition coils, also frequently trigger engine stall by disrupting combustion. Additionally, air intake obstructions, sensor failures, and electrical problems can interrupt engine operation and cause stalling without leading to a complete seizure.
Main Causes of Engine Seizure
Engine seizure primarily occurs due to a lack of lubrication, causing metal components to overheat and fuse together, leading to complete mechanical failure. Overheating from coolant loss or excessive engine load can also cause the engine's internal parts to expand beyond tolerances, resulting in seizure. Contaminated oil or foreign debris within the engine can further exacerbate wear and friction, increasing the risk of engine seizure compared to a typical engine stall.
Warning Signs of Engine Stall
Warning signs of engine stall include sudden loss of power, engine sputtering, and irregular RPM fluctuations. Drivers may notice a drop in engine sound or vibration, difficulty accelerating, or a warning light on the dashboard. Recognizing these symptoms early helps prevent further damage and ensures timely intervention to avoid a complete engine breakdown.
Symptoms of Engine Seizure
Engine seizure occurs when internal components excessively overheat or lack lubrication, causing the engine to abruptly stop functioning. Symptoms include sudden loss of power, inability to restart the engine, and unusual grinding or knocking noises from the engine bay. Visible signs may also include smoke or steam emissions due to extreme internal friction.
How to Respond to an Engine Stall
An engine stall occurs when the engine suddenly stops running but can often be restarted by quickly turning the ignition key or pressing the start button while ensuring the vehicle is in neutral or park. To respond effectively, immediately shift to neutral, apply the brakes firmly, and attempt to restart the engine, avoiding sudden movements that could cause accidents. Understanding the difference between engine stall and engine seizure is crucial, as a seizure indicates mechanical failure requiring professional repair, whereas a stall is generally temporary and recoverable.
Immediate Actions for Engine Seizure
During an engine seizure, immediately shut off the ignition to prevent further damage and stop fuel flow to the engine. Avoid attempting to restart or crank the engine to reduce the risk of catastrophic failure. Seek professional mechanical assistance promptly to assess and repair the seized engine components.
Prevention Tips for Engine Stall and Seizure
Regular engine maintenance, including timely oil changes and coolant checks, is crucial to prevent engine stall and seizure by ensuring optimal lubrication and temperature control. Monitoring and addressing warning signs such as engine overheating, unusual noises, or loss of power can significantly reduce the risk of engine failure. Using high-quality fuel and avoiding aggressive driving habits further contribute to sustained engine performance and prevention of mechanical breakdowns.
Repair Costs: Engine Stall vs Engine Seizure
Repair costs for an engine stall typically involve diagnosing electrical or fuel delivery issues, often resulting in expenses ranging from $300 to $1,200. In contrast, engine seizure repair demands more extensive work, such as rebuilding or replacing engine components, with costs soaring between $2,500 and $5,000 or more. Timely intervention in engine stall cases can prevent progression to seizure, significantly reducing overall repair expenditures.
Engine stall vs engine seizure Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com