Fuel starvation occurs when the engine does not receive enough fuel, often caused by clogged filters, faulty fuel pumps, or empty fuel tanks, leading to engine stalling or failure to start. Fuel contamination involves the presence of impurities such as water, dirt, or microbes in the fuel, which can damage engine components, reduce efficiency, and cause corrosion or clogging. Identifying the cause of the breakdown requires distinguishing between a lack of fuel supply and the degradation of fuel quality to ensure proper diagnosis and repair.
Table of Comparison
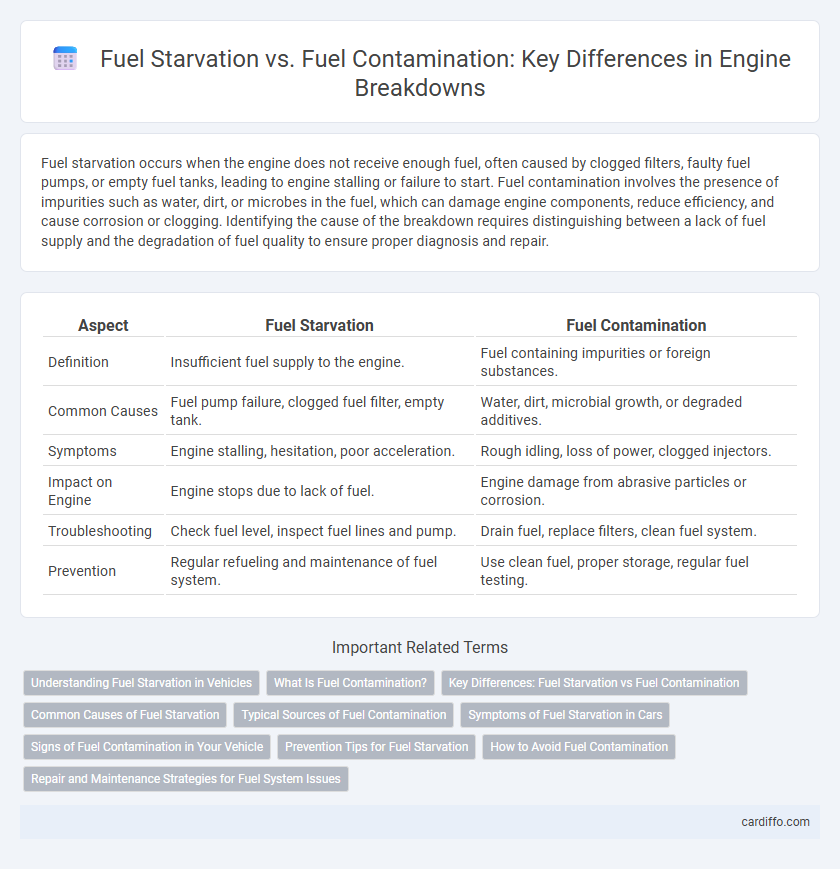
| Aspect | Fuel Starvation | Fuel Contamination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insufficient fuel supply to the engine. | Fuel containing impurities or foreign substances. |
| Common Causes | Fuel pump failure, clogged fuel filter, empty tank. | Water, dirt, microbial growth, or degraded additives. |
| Symptoms | Engine stalling, hesitation, poor acceleration. | Rough idling, loss of power, clogged injectors. |
| Impact on Engine | Engine stops due to lack of fuel. | Engine damage from abrasive particles or corrosion. |
| Troubleshooting | Check fuel level, inspect fuel lines and pump. | Drain fuel, replace filters, clean fuel system. |
| Prevention | Regular refueling and maintenance of fuel system. | Use clean fuel, proper storage, regular fuel testing. |
Understanding Fuel Starvation in Vehicles
Fuel starvation occurs when the engine does not receive an adequate supply of fuel, leading to stalling or a complete breakdown. It can be caused by clogged fuel filters, malfunctioning fuel pumps, or an empty fuel tank, disrupting the fuel flow essential for combustion. Unlike fuel contamination, which involves impurities affecting engine performance, fuel starvation primarily results from insufficient fuel delivery.
What Is Fuel Contamination?
Fuel contamination occurs when impurities like dirt, water, or microbial growth infiltrate the fuel system, reducing engine performance and causing potential damage. Unlike fuel starvation, which results from an inadequate fuel supply, contamination directly affects the quality and combustion process of the fuel. Common contaminants include sediments, rust particles, and biofilms that clog fuel filters and injectors, leading to engine misfires or stalling.
Key Differences: Fuel Starvation vs Fuel Contamination
Fuel starvation occurs when the engine is deprived of fuel due to blockages, empty tanks, or faulty fuel pumps, causing the vehicle to lose power or stall. Fuel contamination involves impurities like water, dirt, or debris mixed with fuel, leading to reduced engine efficiency, rough idling, and potential damage to fuel injectors. The key difference lies in fuel starvation being a shortage of fuel supply, while fuel contamination refers to compromised fuel quality affecting engine performance.
Common Causes of Fuel Starvation
Fuel starvation commonly results from clogged fuel filters, faulty fuel pumps, or empty fuel tanks, leading to insufficient fuel delivery to the engine. Airlocks within the fuel lines and damaged fuel injectors also contribute to interrupted fuel flow. Unlike fuel contamination, which involves impurities like dirt or water in the fuel, fuel starvation primarily stems from mechanical or supply issues that restrict fuel access.
Typical Sources of Fuel Contamination
Typical sources of fuel contamination include water, dirt, rust, and microbial growth within fuel tanks and supply lines. These contaminants can clog fuel filters and injectors, leading to poor engine performance or complete breakdown. Unlike fuel starvation, which is caused by insufficient fuel supply, contamination directly degrades fuel quality and disrupts combustion processes.
Symptoms of Fuel Starvation in Cars
Symptoms of fuel starvation in cars include engine sputtering, frequent stalling, and difficulty starting, often accompanied by a sudden loss of power during acceleration. Unlike fuel contamination, which may cause rough idling and inconsistent engine performance due to clogged fuel filters, fuel starvation results from insufficient fuel supply caused by clogged fuel lines or a failing fuel pump. Recognizing these symptoms early can prevent engine damage and improve vehicle reliability.
Signs of Fuel Contamination in Your Vehicle
Signs of fuel contamination in your vehicle include engine sputtering, rough idling, and a noticeable decrease in fuel efficiency. You may also experience difficulty starting the engine or unexpected stalling, often accompanied by unusual smells or visible particles in the fuel filter. Regular inspection of fuel lines and filters can help detect contamination before it leads to severe engine damage.
Prevention Tips for Fuel Starvation
Fuel starvation can be prevented by regularly inspecting fuel lines and filters for blockages or damage that restrict fuel flow. Using high-quality fuel and maintaining a clean fuel tank reduces the risk of contamination that might contribute to starvation. Ensuring the fuel pump operates correctly and checking for air leaks in the fuel system enhances consistent fuel delivery, minimizing breakdown risks.
How to Avoid Fuel Contamination
To avoid fuel contamination, regularly inspect and clean your fuel tank and replace fuel filters according to manufacturer guidelines. Use high-quality fuel from reputable sources and keep fuel storage containers sealed tightly to prevent water, dirt, and debris ingress. Implementing routine fuel system maintenance reduces the risk of clogs and engine breakdowns caused by contaminated fuel.
Repair and Maintenance Strategies for Fuel System Issues
Fuel starvation and fuel contamination require distinct repair and maintenance strategies to ensure optimal engine performance. Fuel starvation often necessitates inspecting and replacing clogged fuel filters, cleaning fuel lines, and checking fuel pump functionality, while fuel contamination demands thorough fuel tank cleaning, fuel system flushing, and the use of fuel additives to remove water and debris. Regular preventive maintenance, including fuel quality monitoring and scheduled inspection, minimizes the risk of both issues and enhances overall fuel system reliability.
Fuel starvation vs fuel contamination Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com