Engine seizure occurs when the engine components, such as pistons and cylinders, overheat or lose lubrication, causing them to lock up and stop moving entirely. Piston knock, on the other hand, is a distinct metallic knocking sound produced by improper combustion or worn piston components, indicating potential damage but not immediate engine stoppage. Both issues are critical engine problems requiring prompt diagnosis and repair to prevent extensive damage to the engine.
Table of Comparison
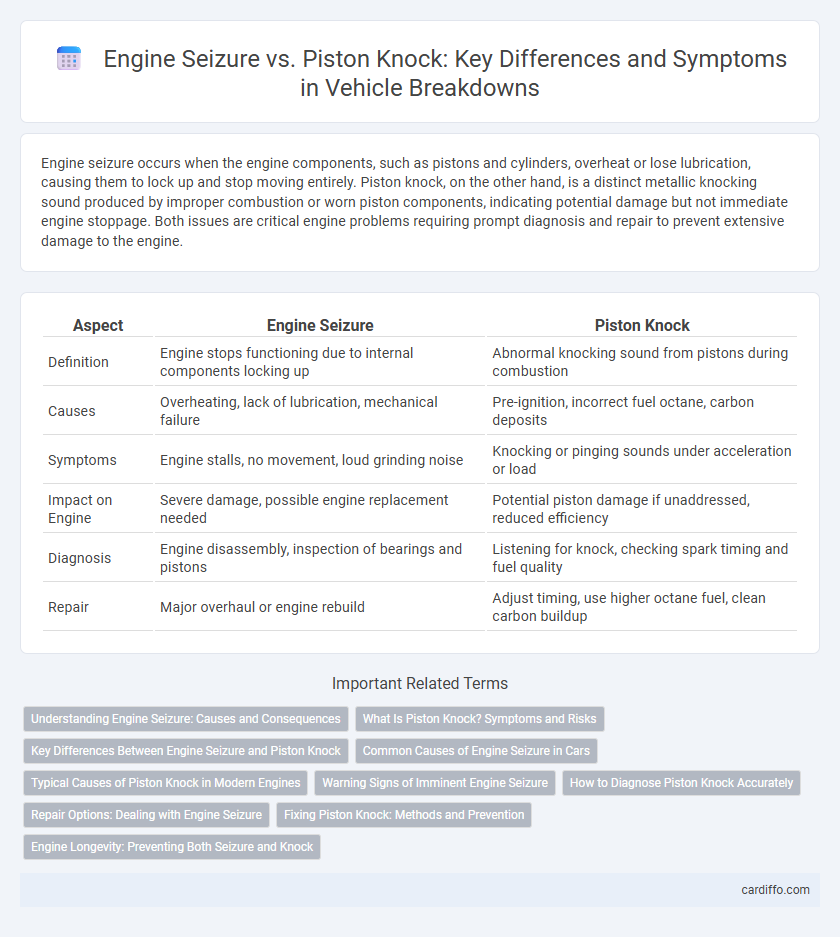
| Aspect | Engine Seizure | Piston Knock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engine stops functioning due to internal components locking up | Abnormal knocking sound from pistons during combustion |
| Causes | Overheating, lack of lubrication, mechanical failure | Pre-ignition, incorrect fuel octane, carbon deposits |
| Symptoms | Engine stalls, no movement, loud grinding noise | Knocking or pinging sounds under acceleration or load |
| Impact on Engine | Severe damage, possible engine replacement needed | Potential piston damage if unaddressed, reduced efficiency |
| Diagnosis | Engine disassembly, inspection of bearings and pistons | Listening for knock, checking spark timing and fuel quality |
| Repair | Major overhaul or engine rebuild | Adjust timing, use higher octane fuel, clean carbon buildup |
Understanding Engine Seizure: Causes and Consequences
Engine seizure occurs when the piston overheats and expands excessively, causing it to jam within the cylinder walls, often due to inadequate lubrication or overheating. This mechanical failure results in severe engine damage, rendering the vehicle inoperable until extensive repairs or replacement are undertaken. Unlike piston knock, which is an audible warning of pre-ignition or detonation, engine seizure indicates catastrophic internal engine failure requiring immediate attention.
What Is Piston Knock? Symptoms and Risks
Piston knock is a distinct engine noise caused by abnormal combustion or piston slapping against the cylinder walls, often resulting from improper fuel mixture or worn components. Symptoms include a metallic knocking sound during acceleration, reduced engine performance, and increased fuel consumption. Ignoring piston knock risks severe engine damage like scoring of the cylinder walls, overheating, and eventual engine seizure if not addressed promptly.
Key Differences Between Engine Seizure and Piston Knock
Engine seizure occurs when the engine's moving parts, primarily the piston and cylinder, stop moving due to extreme overheating or lack of lubrication, leading to metal fusion and complete engine failure. Piston knock, also known as detonation or engine knocking, is characterized by abnormal combustion causing a knocking noise without immediate engine stoppage, often resulting from incorrect fuel octane or timing issues. The key difference lies in severity: engine seizure results in total engine immobilization, while piston knock indicates combustion irregularities that can be addressed before catastrophic damage occurs.
Common Causes of Engine Seizure in Cars
Engine seizure in cars commonly occurs due to insufficient lubrication, causing excessive friction and overheating between the piston and cylinder walls. Overheating from coolant system failure or prolonged high engine temperatures also leads to metal expansion and eventual piston binding. Contaminated oil, lack of maintenance, or mechanical damage such as a broken timing belt can further increase the risk of engine components locking up.
Typical Causes of Piston Knock in Modern Engines
Piston knock in modern engines typically results from abnormal combustion events such as pre-ignition or detonation caused by low-octane fuel, incorrect ignition timing, or excessive engine temperature. Worn piston bearings and insufficient lubrication can also lead to piston slap, producing a knocking sound associated with piston knock. Detecting and addressing these issues promptly prevents severe engine damage like engine seizure.
Warning Signs of Imminent Engine Seizure
Warning signs of imminent engine seizure include sudden loss of engine power, unusual knocking noises from the piston area, and a rapid increase in engine temperature. Persistent piston knock, indicated by rhythmic metallic sounds, often signals insufficient lubrication or excessive friction, which can lead to engine seizure. Monitoring oil pressure and temperature gauges regularly helps detect these critical symptoms early to prevent catastrophic engine failure.
How to Diagnose Piston Knock Accurately
Diagnosing piston knock accurately involves using specialized diagnostic tools to detect abnormal engine vibrations and frequency patterns specific to piston slap or detonation. Visual inspection of spark plugs for signs of carbon buildup or uneven wear can help differentiate piston knock from engine seizure, which typically shows metal debris in the oil. Employing an engine analyzer or stethoscope to pinpoint the source of knocking noise ensures precise identification and timely intervention.
Repair Options: Dealing with Engine Seizure
Engine seizure repair options typically involve disassembling the engine to assess damage, which often includes replacing or machining the seized components such as pistons, cylinders, and bearings. In severe cases, a complete engine rebuild or replacement may be necessary to restore functionality and prevent further damage. Proper lubrication system inspection and addressing overheating causes are crucial steps during repair to avoid recurrent engine seizure.
Fixing Piston Knock: Methods and Prevention
Fixing piston knock involves identifying the root causes such as improper fuel octane, carbon buildup, or incorrect ignition timing and addressing them through dialed-in engine tuning and fuel upgrades. Preventive measures include regular maintenance, using recommended octane fuel, ensuring proper cooling system functionality, and employing periodic engine decarbonization treatments. Advanced diagnostics like knock sensors and ECU remapping further help in early detection and mitigation of piston knock to protect engine longevity.
Engine Longevity: Preventing Both Seizure and Knock
Engine longevity depends on preventing both engine seizure and piston knock, which damage critical components like pistons and cylinders. Proper lubrication with high-quality engine oil reduces friction and heat buildup, lowering the risk of seizure, while using the correct fuel octane minimizes pre-ignition and detonation that cause piston knock. Regular maintenance, including timely oil changes and fuel system checks, ensures optimal engine performance and extends the life of the engine.
Engine seizure vs piston knock Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com