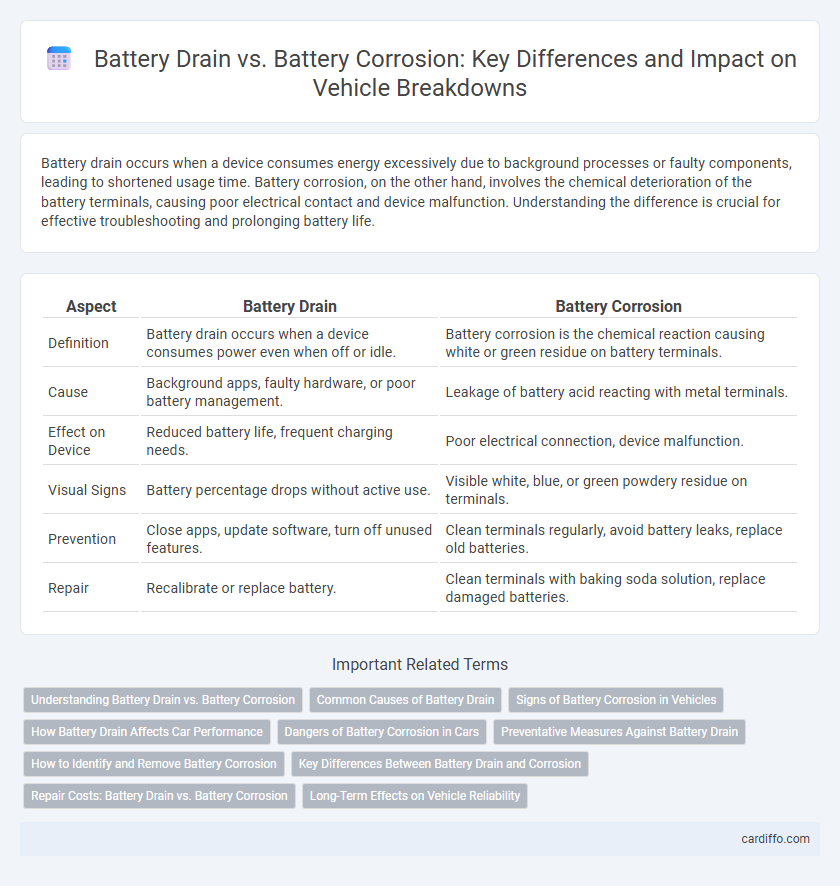
Battery drain occurs when a device consumes energy excessively due to background processes or faulty components, leading to shortened usage time. Battery corrosion, on the other hand, involves the chemical deterioration of the battery terminals, causing poor electrical contact and device malfunction. Understanding the difference is crucial for effective troubleshooting and prolonging battery life.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Battery Drain | Battery Corrosion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Battery drain occurs when a device consumes power even when off or idle. | Battery corrosion is the chemical reaction causing white or green residue on battery terminals. |
| Cause | Background apps, faulty hardware, or poor battery management. | Leakage of battery acid reacting with metal terminals. |
| Effect on Device | Reduced battery life, frequent charging needs. | Poor electrical connection, device malfunction. |
| Visual Signs | Battery percentage drops without active use. | Visible white, blue, or green powdery residue on terminals. |
| Prevention | Close apps, update software, turn off unused features. | Clean terminals regularly, avoid battery leaks, replace old batteries. |
| Repair | Recalibrate or replace battery. | Clean terminals with baking soda solution, replace damaged batteries. |
Understanding Battery Drain vs. Battery Corrosion
Battery drain refers to the loss of charge due to electrical device usage or faulty components, whereas battery corrosion involves the chemical degradation of battery terminals caused by leakage or exposure to moisture. Understanding the differences helps in accurately diagnosing power issues, as battery drain impacts performance over time while corrosion leads to poor electrical contact and potential device failure. Proper maintenance includes monitoring battery usage patterns and inspecting terminals regularly to prevent both drainage and corrosion-related problems.
Common Causes of Battery Drain
Common causes of battery drain include leaving lights or accessories on, poor charging system performance, and parasitic electrical draws from faulty wiring or malfunctioning components. Excessive use of electronic devices or extreme temperatures can accelerate the battery's energy depletion. Regular maintenance helps prevent corrosion, but battery drain primarily results from continuous electrical load and insufficient charging cycles.
Signs of Battery Corrosion in Vehicles
Signs of battery corrosion in vehicles include a white or bluish powdery substance accumulating around the battery terminals, causing poor electrical connections and difficulty starting the engine. Visible rust or leaking battery acid can indicate corrosion that may damage battery cables and reduce overall battery life. Inspecting for swelling, cracking, or an unusual odor near the battery can also help identify early stages of corrosion before it leads to complete battery failure.
How Battery Drain Affects Car Performance
Battery drain reduces the available electrical power in a vehicle, causing dim headlights, slow engine cranking, and malfunctioning electronic systems such as the ECU or infotainment. This diminished power supply can lead to inconsistent engine starting, increased fuel consumption, and potential stalling during operation. Unlike battery corrosion, which primarily affects terminal connection and can often be visually inspected, battery drain impacts the overall charge capacity and requires diagnostic testing to accurately assess.
Dangers of Battery Corrosion in Cars
Battery corrosion in cars poses significant dangers, including impaired electrical connections that can lead to starting failures and unreliable vehicle performance. Corroded terminals increase resistance, causing excessive heat buildup that may damage the battery and surrounding components. Ignoring corrosion risks worsens battery drain and can result in costly repairs or sudden breakdowns.
Preventative Measures Against Battery Drain
Battery drain can be minimized by regularly disconnecting electronic devices when not in use, as parasitic loads continuously consume power. Implementing smart charging systems that prevent overcharging helps maintain battery health and prolong lifespan. Temperature regulation and routine maintenance reduce the risk of corrosion, indirectly preserving battery capacity and performance.
How to Identify and Remove Battery Corrosion
Battery corrosion appears as a white, green, or blue powdery substance around the terminals, often causing poor electrical connection and accelerated battery drain. To identify corrosion, inspect the battery terminals for discoloration and a gritty texture; use a mixture of baking soda and water to safely neutralize and remove the buildup. Regular cleaning of the battery terminals with a wire brush followed by applying a protective terminal spray prevents further corrosion and maintains optimal battery performance.
Key Differences Between Battery Drain and Corrosion
Battery drain occurs when electrical components continuously consume power, leading to a gradual depletion of the battery's charge, whereas battery corrosion is the physical deterioration of battery terminals caused by chemical reactions, often involving leakage and buildup of acidic residue. Drain impacts performance by reducing available energy, while corrosion primarily affects the battery's ability to conduct electrical current by creating resistance. Effective maintenance involves preventing drain through proper usage and minimizing corrosion by cleaning terminals and applying protective coatings.
Repair Costs: Battery Drain vs. Battery Corrosion
Repair costs for battery drain typically involve software diagnostics and battery replacement, averaging $100 to $300 depending on the device. Battery corrosion repair expenses are higher as they require cleaning or replacing corroded terminals, often costing between $150 and $400. Corrosion damage may also lead to additional repairs on surrounding components, increasing overall maintenance expenses.
Long-Term Effects on Vehicle Reliability
Battery drain gradually reduces a vehicle's ability to start, causing repeated electrical failures that compromise reliability over time. Battery corrosion accelerates terminal degradation, leading to poor electrical connections and increased risk of electrical system faults. Long-term exposure to either issue can result in costly repairs and decreased overall vehicle performance and longevity.
Battery drain vs battery corrosion Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com