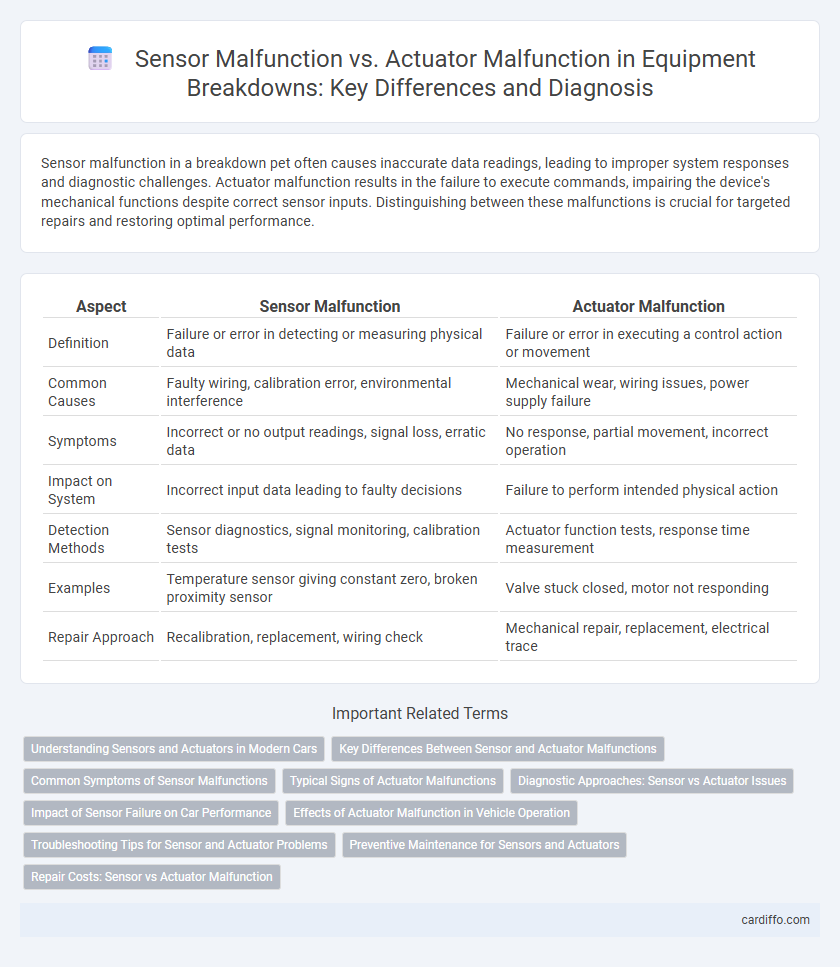
Sensor malfunction in a breakdown pet often causes inaccurate data readings, leading to improper system responses and diagnostic challenges. Actuator malfunction results in the failure to execute commands, impairing the device's mechanical functions despite correct sensor inputs. Distinguishing between these malfunctions is crucial for targeted repairs and restoring optimal performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sensor Malfunction | Actuator Malfunction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Failure or error in detecting or measuring physical data | Failure or error in executing a control action or movement |
| Common Causes | Faulty wiring, calibration error, environmental interference | Mechanical wear, wiring issues, power supply failure |
| Symptoms | Incorrect or no output readings, signal loss, erratic data | No response, partial movement, incorrect operation |
| Impact on System | Incorrect input data leading to faulty decisions | Failure to perform intended physical action |
| Detection Methods | Sensor diagnostics, signal monitoring, calibration tests | Actuator function tests, response time measurement |
| Examples | Temperature sensor giving constant zero, broken proximity sensor | Valve stuck closed, motor not responding |
| Repair Approach | Recalibration, replacement, wiring check | Mechanical repair, replacement, electrical trace |
Understanding Sensors and Actuators in Modern Cars
Sensors in modern cars detect parameters like temperature, pressure, and speed to provide real-time data essential for engine management and safety systems. Actuators receive electronic signals to perform physical actions such as adjusting throttle position or brake pressure, directly impacting vehicle performance. Identifying sensor malfunctions involves monitoring inaccurate or absent data transmission, while actuator malfunctions manifest as improper or failed mechanical responses.
Key Differences Between Sensor and Actuator Malfunctions
Sensor malfunctions typically involve inaccurate or no data transmission, leading to false readings or complete signal loss, whereas actuator malfunctions result in improper or failed physical actions despite correct sensor inputs. Key differences include root causes--sensor issues often stem from calibration errors, wiring problems, or environmental interference, while actuator faults commonly arise from mechanical wear, electrical failures, or hydraulic leakage. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for diagnosing breakdowns effectively and ensuring targeted maintenance of control systems.
Common Symptoms of Sensor Malfunctions
Sensor malfunctions commonly manifest as erratic data readings, intermittent signal loss, or complete failure to detect environmental changes. These issues often lead to incorrect system responses or trigger fault codes in diagnostic systems. Identifying these symptoms early is crucial for preventing further damage and ensuring reliable sensor operation.
Typical Signs of Actuator Malfunctions
Typical signs of actuator malfunctions include irregular or sluggish movement, unresponsive or erratic behavior, and unusual noises such as grinding or clicking. These symptoms often indicate mechanical wear, electrical faults, or hydraulic issues within the actuator system. Prompt diagnosis and repair are crucial to prevent further damage and ensure optimal performance.
Diagnostic Approaches: Sensor vs Actuator Issues
Diagnostic approaches for sensor malfunctions prioritize signal integrity analysis and real-time data validation to detect inconsistencies or erroneous readings, often using sensor-specific calibration checks and output monitoring. Actuator malfunction diagnostics emphasize functional performance testing, including response time evaluation and command execution verification, integrating feedback mechanisms to confirm mechanical or electrical operation. Advanced diagnostic tools combine sensor data fusion with actuator feedback loops to isolate faults and ensure accurate system troubleshooting.
Impact of Sensor Failure on Car Performance
Sensor failure in vehicles can disrupt real-time data acquisition, leading to inaccurate readings that impair engine control systems and compromise fuel efficiency. Malfunctioning sensors such as oxygen sensors or throttle position sensors often cause engine misfires, reduced acceleration, and erratic idling. In contrast to actuator malfunctions, sensor failures primarily affect diagnostic accuracy and system responsiveness, resulting in degraded overall car performance and increased emissions.
Effects of Actuator Malfunction in Vehicle Operation
Actuator malfunction in vehicle operation often leads to impaired control of essential systems such as braking, steering, and throttle response, significantly compromising safety and performance. This disruption can cause delayed or unresponsive vehicle actions, increasing the risk of accidents and mechanical failure. Unlike sensor malfunctions that primarily affect data input, actuator issues directly impact the execution of commands and vehicle dynamics.
Troubleshooting Tips for Sensor and Actuator Problems
Sensor malfunction often causes inaccurate readings or no signal output, making it essential to verify sensor wiring, check for physical damage, and use diagnostic tools to test sensor response. Actuator malfunction typically results in failure to execute commands, so inspecting power supply, control signals, and mechanical components helps identify issues. Calibrating sensors regularly and ensuring actuators receive proper voltage can prevent common breakdowns and improve system reliability.
Preventive Maintenance for Sensors and Actuators
Sensor malfunctions often arise from contamination, wiring issues, or calibration drift, while actuator malfunctions typically stem from mechanical wear, electrical faults, or signal failures. Preventive maintenance for sensors includes regular cleaning, calibration checks, and wiring inspections to ensure accurate data transmission. For actuators, scheduled lubrication, operational testing, and electrical continuity assessments help prevent unexpected breakdowns and extend component lifespan.
Repair Costs: Sensor vs Actuator Malfunction
Repair costs for sensor malfunctions typically range from $100 to $400, driven by the complexity of electronic diagnostics and part replacement. Actuator malfunctions, however, often incur higher expenses between $300 and $900 due to mechanical repairs or complete actuator assembly replacement. Labor intensity and part availability significantly influence the overall cost disparity between sensor and actuator repairs.
Sensor malfunction vs actuator malfunction Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com