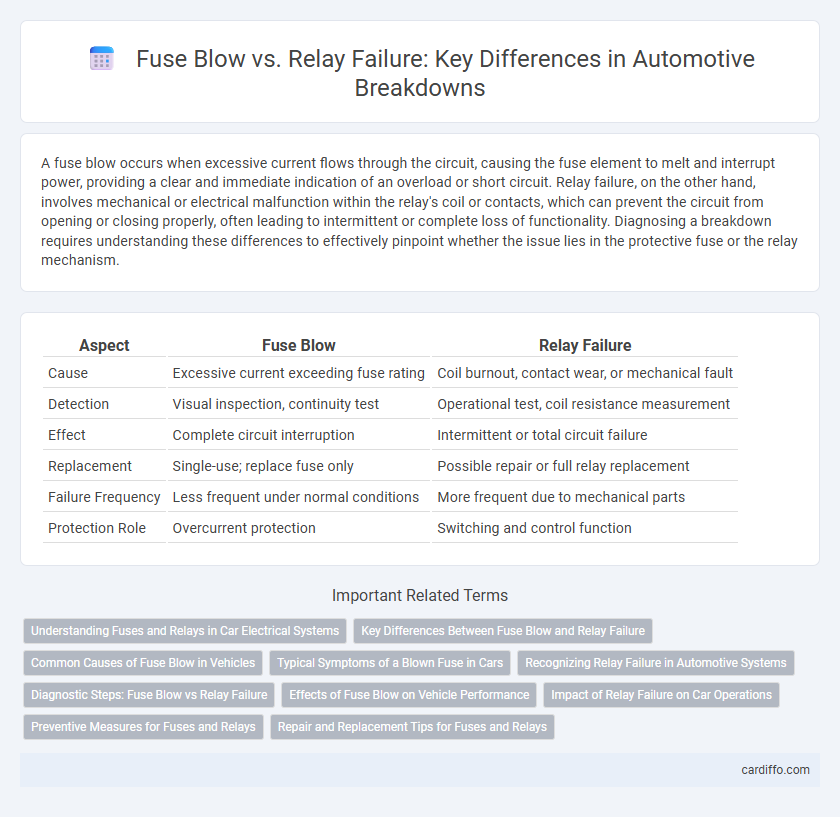
A fuse blow occurs when excessive current flows through the circuit, causing the fuse element to melt and interrupt power, providing a clear and immediate indication of an overload or short circuit. Relay failure, on the other hand, involves mechanical or electrical malfunction within the relay's coil or contacts, which can prevent the circuit from opening or closing properly, often leading to intermittent or complete loss of functionality. Diagnosing a breakdown requires understanding these differences to effectively pinpoint whether the issue lies in the protective fuse or the relay mechanism.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fuse Blow | Relay Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Excessive current exceeding fuse rating | Coil burnout, contact wear, or mechanical fault |
| Detection | Visual inspection, continuity test | Operational test, coil resistance measurement |
| Effect | Complete circuit interruption | Intermittent or total circuit failure |
| Replacement | Single-use; replace fuse only | Possible repair or full relay replacement |
| Failure Frequency | Less frequent under normal conditions | More frequent due to mechanical parts |
| Protection Role | Overcurrent protection | Switching and control function |
Understanding Fuses and Relays in Car Electrical Systems
Fuses protect car electrical systems by breaking the circuit when current exceeds safe levels, preventing damage to wiring and components. Relays act as electrically operated switches that control high-current circuits with low-current signals, ensuring reliable operation of devices like headlights and fuel pumps. While a blown fuse indicates an overload or short circuit, relay failure often results from mechanical wear or coil defects, affecting circuit functionality without necessarily causing a complete power loss.
Key Differences Between Fuse Blow and Relay Failure
Fuse blow occurs when excessive current causes the fuse element to melt, interrupting the electrical circuit and preventing damage to other components. Relay failure involves mechanical or coil malfunctions that prevent proper switching actions, disrupting the control of electrical circuits. Key differences include that fuse blow is a protective response to overcurrent, while relay failure is a fault in the switching mechanism itself, often requiring diagnostic testing for coil continuity or contact integrity.
Common Causes of Fuse Blow in Vehicles
Common causes of fuse blow in vehicles include short circuits, overloaded electrical circuits, and faulty wiring connections. Exposure to moisture or corrosion can also increase the risk of fuse failure by compromising the fuse's integrity. Regular inspection of the vehicle's electrical system and prompt replacement of damaged components help prevent frequent fuse blows.
Typical Symptoms of a Blown Fuse in Cars
A blown fuse in cars typically results in electrical components such as headlights, radio, or interior lights suddenly ceasing to function. Drivers may notice intermittent power loss or complete failure of specific circuits, often accompanied by a burnt odor near the fuse box. Unlike relay failure, which can cause erratic or delayed responses, a blown fuse causes immediate and consistent shutdown of the affected system.
Recognizing Relay Failure in Automotive Systems
Recognizing relay failure in automotive systems involves identifying symptoms such as intermittent electrical component operation, unusual clicking noises, or complete failure of functions like headlights, fuel pumps, or cooling fans. Unlike fuse blowouts that result from overcurrent and are typically indicated by a visible break or discoloration, relay failure can manifest through internal contact wear or coil malfunction, which prevents proper circuit activation. Diagnostic methods include measuring relay coil resistance and performing voltage tests to ensure consistent relay switching and functionality in critical vehicle systems.
Diagnostic Steps: Fuse Blow vs Relay Failure
Diagnosing a fuse blow versus a relay failure requires inspecting the electrical circuit for signs of short circuits or overloads that typically cause fuse damage, whereas relay failure often stems from coil malfunction or contact wear. Testing involves measuring voltage continuity across the fuse and relay terminals and checking for abnormal resistance levels that indicate faults. Using a multimeter to perform these checks helps isolate whether the issue lies with the fuse or the relay component.
Effects of Fuse Blow on Vehicle Performance
A fuse blow in a vehicle primarily disrupts the electrical circuit it protects, leading to immediate loss of functionality in the associated system, such as lighting, ignition, or fuel pumps. This interruption causes engine stalling, failure to start, or loss of vital safety features, directly impacting vehicle performance and reliability. Unlike relay failure, which may cause intermittent or delayed operation, a fuse blow results in a complete shutdown of the affected electrical component.
Impact of Relay Failure on Car Operations
Relay failure in vehicles often leads to critical disruptions in electrical circuits, causing malfunction or complete shutdown of essential systems such as the fuel pump, ignition, or headlights. Unlike a fuse blow, which isolates a short circuit by breaking the connection, a relay failure can result in intermittent or unpredictable behavior, complicating diagnosis and repair. This can severely affect engine starting, safety features, and overall vehicle reliability, increasing downtime and maintenance costs.
Preventive Measures for Fuses and Relays
Regular inspection and testing of fuses and relays eliminate faults before failure occurs, ensuring continuous circuit protection. Utilizing appropriate fuse ratings and relay specifications tailored to the equipment's electrical load prevents premature damage and enhances system reliability. Implementing thermal monitoring and surge protection devices further mitigates the risk of fuse blowouts and relay malfunctions during transient electrical events.
Repair and Replacement Tips for Fuses and Relays
When repairing fuse blow or relay failure, always start by identifying the root cause to prevent repeated issues. Use a multimeter to test continuity in fuses and check coil resistance in relays before replacement. Select replacement fuses and relays matching the exact amperage and voltage ratings specified by the equipment manufacturer to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Fuse blow vs relay failure Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com