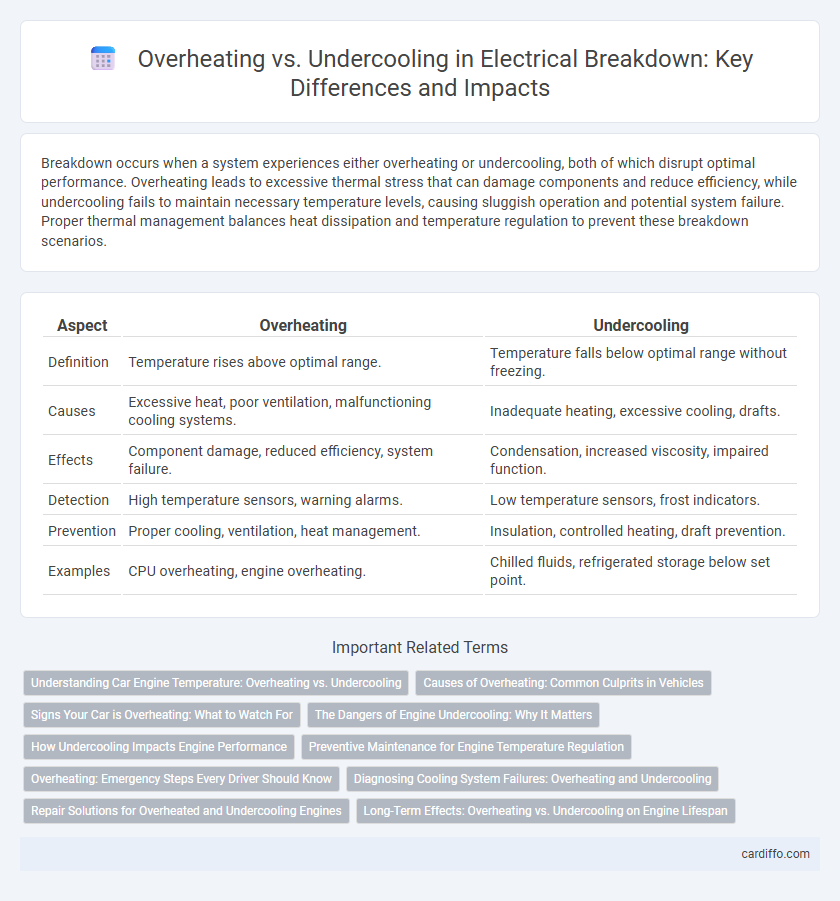
Breakdown occurs when a system experiences either overheating or undercooling, both of which disrupt optimal performance. Overheating leads to excessive thermal stress that can damage components and reduce efficiency, while undercooling fails to maintain necessary temperature levels, causing sluggish operation and potential system failure. Proper thermal management balances heat dissipation and temperature regulation to prevent these breakdown scenarios.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Overheating | Undercooling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature rises above optimal range. | Temperature falls below optimal range without freezing. |
| Causes | Excessive heat, poor ventilation, malfunctioning cooling systems. | Inadequate heating, excessive cooling, drafts. |
| Effects | Component damage, reduced efficiency, system failure. | Condensation, increased viscosity, impaired function. |
| Detection | High temperature sensors, warning alarms. | Low temperature sensors, frost indicators. |
| Prevention | Proper cooling, ventilation, heat management. | Insulation, controlled heating, draft prevention. |
| Examples | CPU overheating, engine overheating. | Chilled fluids, refrigerated storage below set point. |
Understanding Car Engine Temperature: Overheating vs. Undercooling
Car engine temperature regulation is crucial for optimal performance and longevity, with overheating causing severe engine damage due to excessive heat, while undercooling prevents the engine from reaching efficient operating temperature. Overheating often results from coolant leaks, thermostat failure, or radiator issues, leading to warped cylinder heads and gasket failures. Undercooling, typically caused by clogged thermostat or low coolant circulation, reduces fuel efficiency and increases engine wear due to incomplete combustion and improper lubrication.
Causes of Overheating: Common Culprits in Vehicles
Overheating in vehicles often results from coolant leaks, malfunctioning thermostats, or radiator issues that disrupt efficient engine temperature regulation. A failing water pump or clogged radiator can impede coolant circulation, causing the engine to retain excessive heat. Ignoring these common culprits leads to engine damage, reduced performance, and expensive repairs.
Signs Your Car is Overheating: What to Watch For
Signs your car is overheating include a rising temperature gauge, steam or smoke coming from under the hood, and a strong burning smell. You may also notice engine knocking, loss of power, or the coolant warning light illuminating on the dashboard. Early detection of these indicators is crucial to prevent severe engine damage and costly repairs.
The Dangers of Engine Undercooling: Why It Matters
Engine undercooling disrupts optimal operating temperature, leading to incomplete combustion and increased fuel consumption. Prolonged undercooling accelerates engine wear by causing sludge buildup and corrosion within critical components. Recognizing and resolving undercooling issues prevents performance loss and costly mechanical failures.
How Undercooling Impacts Engine Performance
Undercooling in an engine leads to inefficient combustion, causing incomplete fuel burn and increased emissions. The lower than optimal temperature prevents the engine from reaching its ideal operating range, resulting in reduced fuel economy and power output. Continuous undercooling can cause excessive engine wear and potential damage to critical components due to improper lubrication and thermal expansion.
Preventive Maintenance for Engine Temperature Regulation
Effective preventive maintenance for engine temperature regulation requires monitoring for signs of overheating, such as coolant leaks, worn-out radiator fans, and clogged hoses, to prevent engine damage. Undercooling, caused by thermostat malfunctions or low coolant levels, reduces engine efficiency and increases emissions, necessitating regular inspection and timely replacement of cooling system components. Maintaining optimal engine temperature through routine checks and timely repairs helps avoid costly breakdowns and ensures engine longevity.
Overheating: Emergency Steps Every Driver Should Know
Overheating in vehicles occurs when the engine temperature exceeds safe operating limits, potentially causing severe engine damage. Drivers must immediately turn off the air conditioning, turn on the heater to maximum, stop the vehicle safely, and allow the engine to cool before attempting to open the radiator cap. Checking coolant levels and seeking professional assistance promptly can prevent costly repairs and ensure vehicle safety.
Diagnosing Cooling System Failures: Overheating and Undercooling
Diagnosing cooling system failures requires identifying symptoms of both overheating and undercooling, as these conditions indicate distinct malfunctions. Overheating often results from coolant leaks, thermostat failures, or radiator blockages, while undercooling may stem from a stuck-open thermostat or low coolant levels. Accurate diagnosis leverages temperature gauge readings, pressure tests, and coolant inspections to prevent engine damage and ensure optimal performance.
Repair Solutions for Overheated and Undercooling Engines
Repair solutions for overheated engines include flushing the cooling system, replacing the thermostat, and checking for coolant leaks to restore optimal temperature regulation. Undercooling engines require inspection of the thermostat for malfunctions, cleaning or replacing clogged radiator passages, and ensuring proper coolant circulation to prevent inefficient engine performance. Timely diagnosis and maintenance of these components are crucial for preventing further engine damage and ensuring long-term reliability.
Long-Term Effects: Overheating vs. Undercooling on Engine Lifespan
Prolonged engine overheating leads to severe damage such as warped cylinder heads, degraded lubricants, and accelerated wear on critical components, significantly reducing engine lifespan. Undercooling, often caused by thermostat failure, results in insufficient operating temperature that increases fuel consumption, causes carbon buildup, and contributes to premature engine wear by preventing oil from reaching optimal viscosity. Maintaining precise temperature regulation is essential to minimize thermal stress and ensure maximum engine durability over time.
Overheating vs undercooling Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com