Transmission slip occurs when the transmission's internal components fail to properly engage, causing a loss of power transfer and potential overheating, which can lead to further damage if not addressed promptly. Clutch burnout, on the other hand, results from excessive slippage of the clutch disc against the flywheel, generating heat and wear that degrade clutch performance. Recognizing the difference between these issues helps in diagnosing drivetrain problems and applying the correct repair strategy.
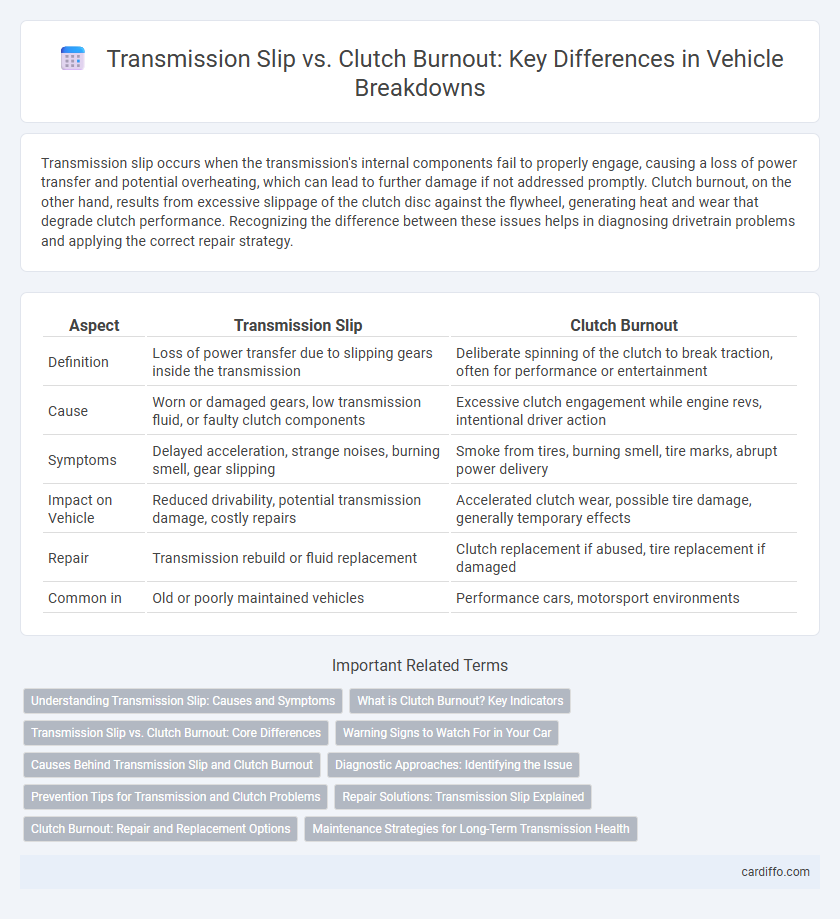
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Transmission Slip | Clutch Burnout |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loss of power transfer due to slipping gears inside the transmission | Deliberate spinning of the clutch to break traction, often for performance or entertainment |
| Cause | Worn or damaged gears, low transmission fluid, or faulty clutch components | Excessive clutch engagement while engine revs, intentional driver action |
| Symptoms | Delayed acceleration, strange noises, burning smell, gear slipping | Smoke from tires, burning smell, tire marks, abrupt power delivery |
| Impact on Vehicle | Reduced drivability, potential transmission damage, costly repairs | Accelerated clutch wear, possible tire damage, generally temporary effects |
| Repair | Transmission rebuild or fluid replacement | Clutch replacement if abused, tire replacement if damaged |
| Common in | Old or poorly maintained vehicles | Performance cars, motorsport environments |
Understanding Transmission Slip: Causes and Symptoms
Transmission slip occurs when the transmission fails to engage properly, causing a loss of power transfer between the engine and the wheels, often due to worn-out clutch plates, low transmission fluid, or damaged gears. Symptoms of transmission slip include delayed acceleration, engine revving without an increase in vehicle speed, and unusual noises such as whining or grinding. Identifying transmission slip early through these signs is crucial to prevent further damage and costly repairs.
What is Clutch Burnout? Key Indicators
Clutch burnout occurs when the clutch system experiences excessive friction and heat, causing the clutch disc to wear prematurely or even fail. Key indicators include a burning smell, slipping gears, delayed acceleration, and a noticeable loss of power transfer from the engine to the transmission. Early detection is crucial to prevent costly repairs and maintain optimal vehicle performance.
Transmission Slip vs. Clutch Burnout: Core Differences
Transmission slip happens when gear engagement fails to fully transfer engine power, causing delayed acceleration and potential gear grinding. Clutch burnout occurs from excessive friction heat due to prolonged clutch slipping, leading to a burnt clutch plate and loss of power transmission. Unlike clutch burnout, which primarily damages the clutch assembly, transmission slip indicates issues within the gearbox or torque converter, affecting overall drivability.
Warning Signs to Watch For in Your Car
Transmission slip often manifests as delayed acceleration, noisy gear shifts, or a burning smell, indicating worn gears or low transmission fluid levels. Clutch burnout typically presents with a distinct burning odor, difficulty engaging gears, and a spongy or slipping clutch pedal that fails to transfer power effectively. Early detection of these warning signs is crucial to prevent costly repairs and ensure vehicle safety and performance.
Causes Behind Transmission Slip and Clutch Burnout
Transmission slip occurs primarily due to worn or damaged transmission bands, low transmission fluid levels, or malfunctioning solenoids, which prevent proper gear engagement and lead to power loss. Clutch burnout results from excessive friction caused by riding the clutch pedal, aggressive driving, or a failing pressure plate, generating excessive heat that damages clutch components. Both issues stem from improper maintenance and driving habits, but transmission slip is typically linked to hydraulic or mechanical faults, while clutch burnout is driven by user-induced overheating and wear.
Diagnostic Approaches: Identifying the Issue
Transmission slip and clutch burnout can be diagnosed by analyzing vehicle response, such as changes in acceleration, RPM behavior, and unusual noises during gear shifts. Utilizing diagnostic tools like OBD-II scanners helps detect transmission error codes, while physical inspection of the clutch plate for wear and burn marks confirms clutch burnout. Test driving under controlled conditions and monitoring for slippage or delayed engagement aids in pinpointing the exact cause.
Prevention Tips for Transmission and Clutch Problems
Regularly checking and maintaining proper transmission fluid levels prevents transmission slip by ensuring smooth gear engagement and reducing wear. Avoid riding the clutch and limit excessive slipping to prevent clutch burnout and extend its lifespan. Timely inspections and using manufacturer-recommended fluids optimize performance and reduce the risk of costly transmission and clutch repairs.
Repair Solutions: Transmission Slip Explained
Transmission slip occurs when the transmission fails to properly engage gears, causing power loss and erratic vehicle movement; repairing this often involves replacing worn clutch packs, bands, or solenoids within the transmission system. Clutch burnout differs as it results from excessive friction causing clutch disc wear or damage, typically fixed by clutch replacement or resurfacing the flywheel. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for targeted repair, preventing further transmission damage and restoring optimal vehicle performance.
Clutch Burnout: Repair and Replacement Options
Clutch burnout occurs when excessive friction material wears down the clutch disc, causing slipping and loss of power transfer between the engine and transmission. Repair options include resurfacing the flywheel and replacing the clutch disc, pressure plate, and release bearing, which restores proper engagement and prevents further damage. Replacement is recommended when the clutch assembly components show severe wear or damage, ensuring reliable vehicle performance and preventing transmission issues.
Maintenance Strategies for Long-Term Transmission Health
Transmission slip often signals worn clutch plates or insufficient hydraulic pressure, requiring timely inspection and fluid replacement to prevent severe damage. Clutch burnout generates excessive heat and friction, leading to accelerated wear; regular clutch cable adjustment and avoiding excessive slipping are essential maintenance practices. Consistent monitoring, proper fluid levels, and adherence to manufacturer-recommended service intervals ensure long-term transmission health and optimal performance.
Transmission slip vs clutch burnout Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com