Battery drain occurs gradually as energy is consumed by apps or background processes, leading to a reduced charge over time but still allowing the device to function temporarily. A battery dead condition means the power is fully depleted, preventing the device from turning on until recharged. Differentiating between battery drain and a dead battery helps determine whether a quick recharge or a battery replacement is necessary.
Table of Comparison
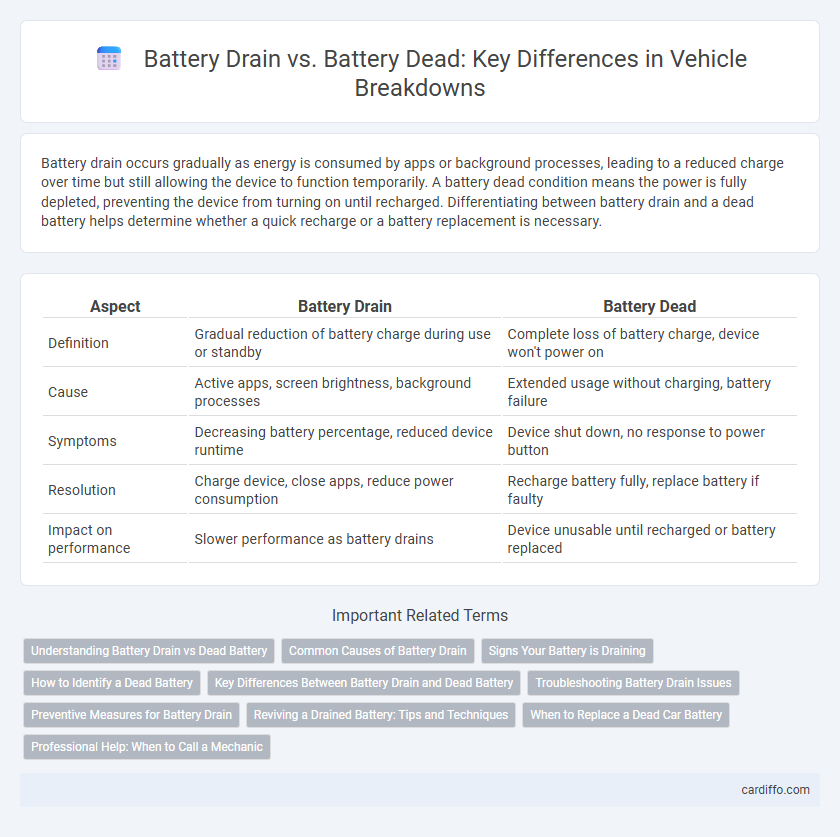
| Aspect | Battery Drain | Battery Dead |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual reduction of battery charge during use or standby | Complete loss of battery charge, device won't power on |
| Cause | Active apps, screen brightness, background processes | Extended usage without charging, battery failure |
| Symptoms | Decreasing battery percentage, reduced device runtime | Device shut down, no response to power button |
| Resolution | Charge device, close apps, reduce power consumption | Recharge battery fully, replace battery if faulty |
| Impact on performance | Slower performance as battery drains | Device unusable until recharged or battery replaced |
Understanding Battery Drain vs Dead Battery
Battery drain refers to the gradual loss of charge caused by apps running in the background or hardware components consuming power, whereas a dead battery means the battery can no longer hold any charge due to aging or damage. Understanding the difference helps in diagnosing issues accurately; battery drain can often be resolved by managing power settings and closing unnecessary apps, while a dead battery typically requires replacement. Monitoring battery health and usage patterns is essential for prolonging device performance and avoiding sudden shutdowns.
Common Causes of Battery Drain
Battery drain occurs gradually when background apps, screen brightness, and GPS continuously consume power, whereas a battery dead state happens when the device completely loses charge and cannot power on. Common causes of battery drain include high screen brightness, constant app refresh, outdated software, and poor signal strength forcing the device to work harder. Identifying and managing these factors can significantly extend overall battery life and device usability.
Signs Your Battery is Draining
Signs your battery is draining include rapid percentage drops, unexpected shutdowns, and noticeable sluggish performance in power-intensive apps. Frequent need for charging despite minimal usage and overheating during normal operation are also key indicators. Monitoring battery health through system diagnostics can help confirm if the issue is drain rather than complete battery failure.
How to Identify a Dead Battery
A dead battery in a vehicle is identified by the failure to start the engine despite multiple attempts, accompanied by dim or non-functional dashboard lights and electrical components. In contrast, battery drain occurs gradually, with symptoms like slow engine crank and intermittent electrical issues before complete failure. Using a multimeter to check the voltage, a reading below 12.4 volts typically indicates a weak or dead battery needing replacement.
Key Differences Between Battery Drain and Dead Battery
Battery drain refers to the gradual loss of battery power during regular device use, often caused by background apps or settings consuming energy, while a dead battery means the battery is completely discharged and unable to power the device. Battery drain can often be managed or slowed by adjusting device settings or closing apps, whereas a dead battery typically requires recharging or replacement to restore functionality. Understanding these key differences aids in diagnosing power issues and optimizing device performance effectively.
Troubleshooting Battery Drain Issues
Battery drain occurs when a device's battery depletes faster than expected without completely shutting down, while a battery dead state means the battery has lost all charge and the device won't power on. Troubleshooting battery drain involves identifying power-hungry apps, adjusting screen brightness, and disabling unnecessary background processes. Monitoring battery health and performing system updates can also help mitigate excessive battery consumption.
Preventive Measures for Battery Drain
Battery drain occurs when a device's power is slowly depleted due to background apps or inefficient settings, whereas a battery dead state means the battery is fully discharged and unresponsive. Preventive measures for battery drain include disabling unnecessary background app refresh, lowering screen brightness, and activating battery saver modes on smartphones. Regular software updates and avoiding extreme temperatures also help maintain optimal battery health and prolong device usage between charges.
Reviving a Drained Battery: Tips and Techniques
A drained battery shows reduced voltage and limited power, while a dead battery cannot hold a charge or start a device. To revive a drained battery, use techniques such as slow charging with a compatible charger, jump-starting with jumper cables, or applying a battery desulfator to break down sulfate crystals. Regular maintenance, including cleaning terminals and avoiding deep discharge, extends battery lifespan and improves reliability.
When to Replace a Dead Car Battery
A battery drain occurs when the car's electrical components slowly deplete the battery's charge, often resulting in a weak start or dim lights, but the battery can still be recharged. A dead car battery, however, is completely discharged or damaged beyond recovery, preventing the vehicle from starting altogether. Replace a dead car battery immediately if the battery fails to hold a charge after jump-starts or shows signs of swelling, corrosion, or age exceeding 3 to 5 years.
Professional Help: When to Call a Mechanic
Battery drain occurs when the battery loses charge gradually, often due to parasitic electrical loads or faulty alternators, while a battery dead means it cannot hold any charge and won't start the engine. Professional help is essential when repeated battery drains happen despite charging or when the battery shows signs of corrosion, swelling, or leakage. A mechanic can diagnose issues such as alternator failure, starter motor problems, or electrical shorts that require specialized tools and expertise.
Battery drain vs battery dead Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com