An ECU malfunction typically disrupts the entire engine control system, causing inconsistent performance or complete shutdown, whereas a sensor fault usually affects specific functions like temperature or oxygen levels, leading to targeted error codes. Diagnosing an ECU issue often requires specialized tools and software, while sensor faults can sometimes be identified through visual inspection or simple testing. Proper differentiation between these faults ensures accurate repairs and prevents unnecessary part replacements.
Table of Comparison
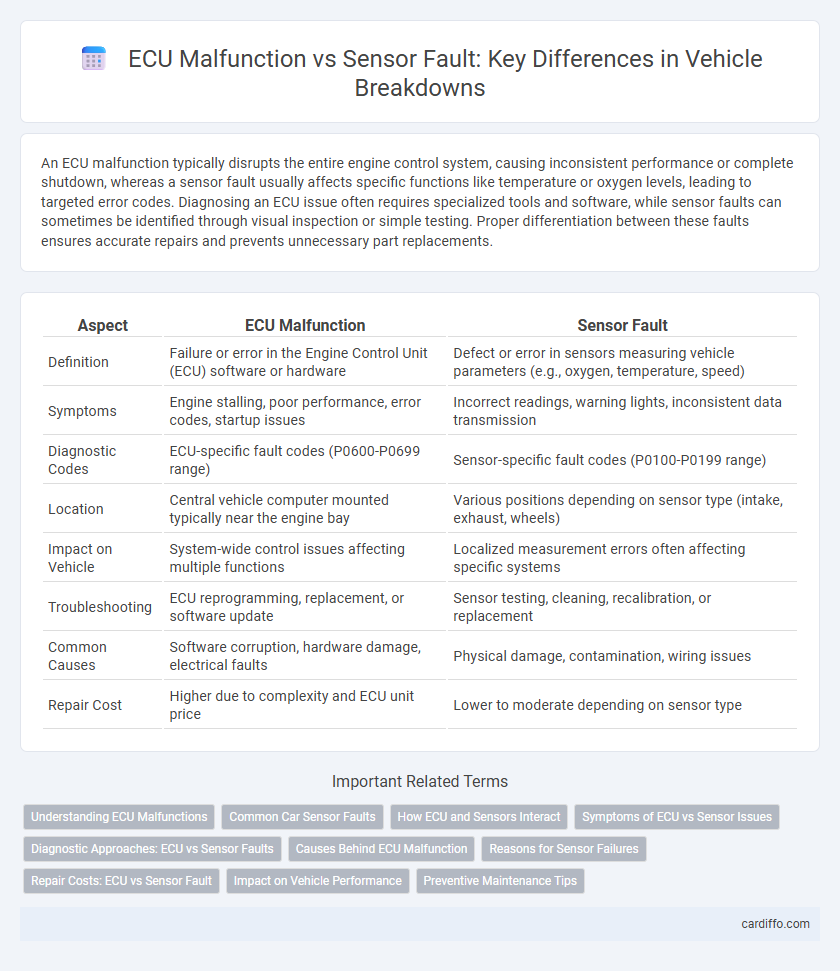
| Aspect | ECU Malfunction | Sensor Fault |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Failure or error in the Engine Control Unit (ECU) software or hardware | Defect or error in sensors measuring vehicle parameters (e.g., oxygen, temperature, speed) |
| Symptoms | Engine stalling, poor performance, error codes, startup issues | Incorrect readings, warning lights, inconsistent data transmission |
| Diagnostic Codes | ECU-specific fault codes (P0600-P0699 range) | Sensor-specific fault codes (P0100-P0199 range) |
| Location | Central vehicle computer mounted typically near the engine bay | Various positions depending on sensor type (intake, exhaust, wheels) |
| Impact on Vehicle | System-wide control issues affecting multiple functions | Localized measurement errors often affecting specific systems |
| Troubleshooting | ECU reprogramming, replacement, or software update | Sensor testing, cleaning, recalibration, or replacement |
| Common Causes | Software corruption, hardware damage, electrical faults | Physical damage, contamination, wiring issues |
| Repair Cost | Higher due to complexity and ECU unit price | Lower to moderate depending on sensor type |
Understanding ECU Malfunctions
ECU malfunctions often stem from software errors, wiring issues, or power supply problems that disrupt the control unit's ability to process sensor data accurately. Unlike sensor faults, which result in incorrect or missing inputs, ECU failures affect the entire vehicle management system, leading to inconsistent engine performance and diagnostic trouble codes. Proper diagnosis requires specialized scan tools to differentiate between ECU errors and faulty sensors for targeted repairs.
Common Car Sensor Faults
Common car sensor faults that lead to ECU malfunctions include oxygen sensor failure, mass airflow sensor errors, and crankshaft position sensor issues. These sensor problems disrupt accurate data transmission to the ECU, causing engine misfires, poor fuel economy, and stalling. Diagnosing sensor faults early prevents costly ECU damage and ensures optimal vehicle performance.
How ECU and Sensors Interact
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) continuously monitors sensor inputs such as oxygen, temperature, and throttle position to optimize engine performance and emissions. When sensors send faulty data, the ECU may misinterpret signals, leading to incorrect adjustments or triggering a malfunction indicator. Understanding the interactive feedback loop between the ECU and sensors is essential for accurately diagnosing whether a breakdown is due to ECU malfunction or sensor fault.
Symptoms of ECU vs Sensor Issues
ECU malfunction symptoms often include erratic engine behavior, inconsistent power delivery, and frequent warning lights on the dashboard, while sensor faults typically cause inaccurate data readings, delayed system responses, or specific component malfunctions like faulty oxygen sensors triggering poor fuel economy. Diagnosing ECU issues requires comprehensive scanning for error codes and system-wide testing, whereas sensor faults can often be isolated by testing the individual sensors for voltage and signal output irregularities. Distinguishing between ECU and sensor problems is critical for accurate repairs, as ECU failures affect multiple systems, whereas sensor faults generally impact targeted functions.
Diagnostic Approaches: ECU vs Sensor Faults
Diagnostic approaches for ECU malfunction versus sensor faults involve distinct strategies targeting the root causes. ECU malfunctions often require comprehensive software diagnostics, including error code retrieval and system reprogramming, to identify firmware or internal hardware issues. Sensor faults are typically diagnosed through signal testing, continuity checks, and verifying sensor outputs against expected parameters to isolate faulty components.
Causes Behind ECU Malfunction
ECU malfunction often stems from electrical issues such as voltage spikes, wiring shorts, or damaged connectors, disrupting its communication with vehicle sensors. Heat exposure and water ingress can degrade the ECU's internal circuitry, leading to erratic behavior or failure. Unlike sensor faults that involve inaccurate data input, ECU malfunctions primarily arise from hardware defects or software corruption within the control unit itself.
Reasons for Sensor Failures
Sensor failures often result from environmental factors like extreme temperatures, moisture intrusion, and physical damage caused by debris or vibrations. Corrosion of electrical contacts and wiring issues such as short circuits or disconnections contribute significantly to sensor malfunction. Contamination from oil, dirt, or road salt can also interfere with sensor accuracy, leading to erroneous data sent to the ECU and subsequent breakdowns.
Repair Costs: ECU vs Sensor Fault
Repair costs for ECU malfunctions are significantly higher than those for sensor faults due to the complexity and central role of the ECU in vehicle operations. Replacing or reprogramming an ECU can range from $400 to over $1,200, while sensor repairs typically cost between $50 and $300. Diagnosing ECU issues often requires specialized equipment and expertise, contributing to increased labor expenses compared to sensor fault repairs.
Impact on Vehicle Performance
ECU malfunction often causes erratic engine behavior, including misfires, poor fuel efficiency, and stalling, leading to a significant decline in overall vehicle performance. Sensor faults typically trigger incorrect data signals to the ECU, resulting in improper adjustments to engine parameters and reduced operational accuracy. Both issues compromise drivability but ECU malfunctions generally have a more severe impact on system stability and responsiveness.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Regular diagnostics on the ECU using OBD-II scanners can identify early signs of malfunction, preventing unexpected breakdowns. Inspecting sensor connections and cleaning or replacing faulty sensors ensures accurate data transmission to the ECU, maintaining optimal engine performance. Scheduling routine preventive maintenance with certified technicians reduces the risk of ECU and sensor failures, enhancing vehicle reliability.
ECU malfunction vs sensor fault Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com