Fuel pump failure causes the engine to stall or not start due to lack of fuel delivery, while ignition coil failure results in misfires and poor engine performance because of weak or no spark. Diagnosing these issues requires checking fuel pressure for pump problems and testing coil resistance or spark output for ignition coil faults. Timely identification ensures proper repairs, preventing further engine damage or breakdowns.
Table of Comparison
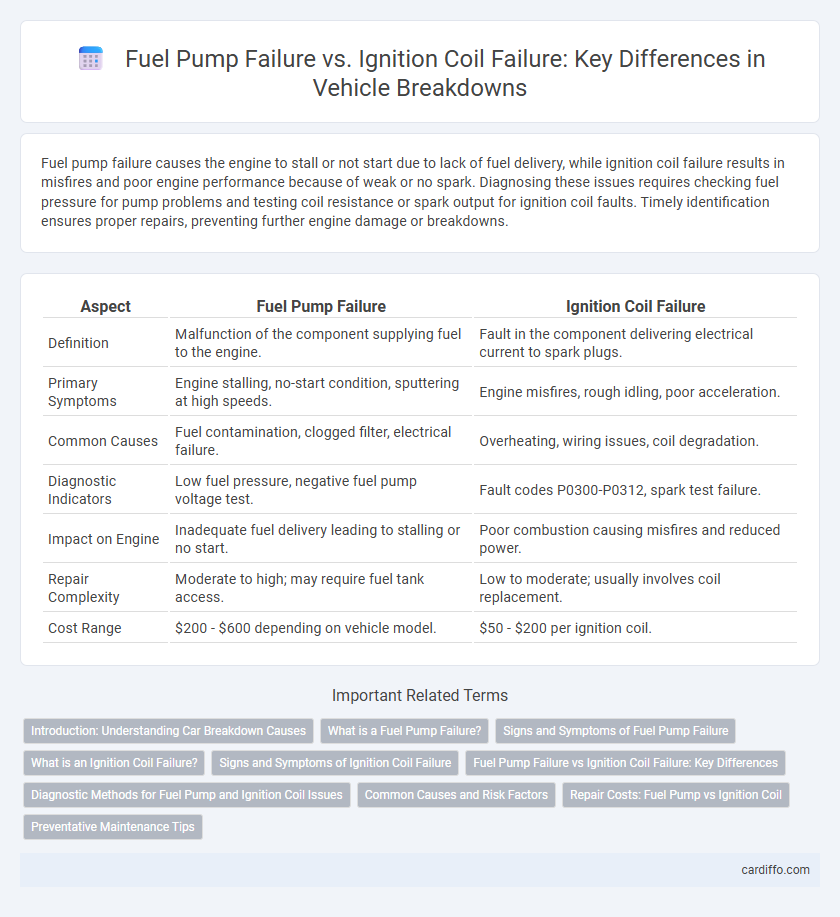
| Aspect | Fuel Pump Failure | Ignition Coil Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Malfunction of the component supplying fuel to the engine. | Fault in the component delivering electrical current to spark plugs. |
| Primary Symptoms | Engine stalling, no-start condition, sputtering at high speeds. | Engine misfires, rough idling, poor acceleration. |
| Common Causes | Fuel contamination, clogged filter, electrical failure. | Overheating, wiring issues, coil degradation. |
| Diagnostic Indicators | Low fuel pressure, negative fuel pump voltage test. | Fault codes P0300-P0312, spark test failure. |
| Impact on Engine | Inadequate fuel delivery leading to stalling or no start. | Poor combustion causing misfires and reduced power. |
| Repair Complexity | Moderate to high; may require fuel tank access. | Low to moderate; usually involves coil replacement. |
| Cost Range | $200 - $600 depending on vehicle model. | $50 - $200 per ignition coil. |
Introduction: Understanding Car Breakdown Causes
Fuel pump failure disrupts the engine's fuel supply, causing the car to stall or not start at all, while ignition coil failure prevents the spark plugs from igniting the fuel-air mixture, leading to misfires and rough engine performance. Diagnosing these issues involves checking fuel pressure for pump problems and testing ignition coils with a multimeter to ensure proper electrical output. Recognizing these distinct symptoms helps prevent prolonged breakdowns and costly repairs by directing accurate maintenance efforts.
What is a Fuel Pump Failure?
Fuel pump failure occurs when the fuel pump, responsible for delivering gasoline from the tank to the engine, malfunctions or stops working completely, causing the engine to stall or fail to start. Symptoms of fuel pump failure include engine sputtering, loss of power under load, and unusual whining noises from the fuel tank area. Unlike ignition coil failure, which disrupts the spark needed for combustion, a faulty fuel pump cuts off the necessary fuel supply, leading to breakdowns and potential engine damage.
Signs and Symptoms of Fuel Pump Failure
Signs of fuel pump failure include engine sputtering at high speeds, difficulty starting the vehicle, and a sudden loss of power during acceleration. A failing fuel pump often causes inconsistent fuel delivery, resulting in engine stalling or misfires. Low fuel pressure detected by a mechanic can confirm fuel pump malfunction as the root cause of breakdown issues.
What is an Ignition Coil Failure?
Ignition coil failure occurs when the coil, responsible for converting the battery's voltage into the high voltage needed to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine, malfunctions or breaks down. Symptoms include engine misfires, difficulty starting, rough idle, and reduced fuel efficiency, which differ from those of fuel pump failure such as loss of power and stalling. Diagnosing ignition coil failure involves checking for error codes, inspecting for physical damage, and testing coil resistance with a multimeter.
Signs and Symptoms of Ignition Coil Failure
Ignition coil failure commonly manifests through engine misfires, rough idling, and difficulty starting the vehicle. Other symptoms include poor fuel economy, decreased power during acceleration, and the illumination of the check engine light. Diagnosing ignition coil issues often involves scanning for error codes such as P0351 to P0354, which indicate coil circuit malfunctions.
Fuel Pump Failure vs Ignition Coil Failure: Key Differences
Fuel pump failure prevents fuel from reaching the engine, causing symptoms like engine sputtering, stalling, or complete no-start conditions, while ignition coil failure disrupts the spark necessary for combustion, leading to misfires, rough idling, or reduced engine power. Fuel pump issues often manifest with a loud whining noise from the fuel tank and poor acceleration, whereas ignition coil problems typically trigger the check engine light and error codes related to ignition timing. Diagnosing these failures involves checking fuel pressure for pump issues and testing coil resistance or spark output for coil faults.
Diagnostic Methods for Fuel Pump and Ignition Coil Issues
Diagnostic methods for fuel pump failure typically include measuring fuel pressure with a fuel pressure gauge to detect insufficient or inconsistent pressure, and listening for the pump's operational sound when the ignition is turned on. Ignition coil issues are often identified by scanning for error codes related to misfires using an OBD-II scanner, inspecting spark plugs for fouling, and testing coil resistance with a multimeter to verify proper electrical output. Accurate diagnostics rely on comparing sensor readings and electrical tests against manufacturer specifications to differentiate between fuel delivery problems and ignition system faults efficiently.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Fuel pump failure often results from contaminated fuel, worn-out components, and prolonged exposure to overheating, with risk factors including low fuel levels and poor maintenance. Ignition coil failure is commonly caused by electrical faults, heat damage, and aging insulation, with increased risk linked to frequent engine starts and ignition system stress. Both failures can lead to engine breakdowns, emphasizing the importance of regular inspection and quality fuel usage.
Repair Costs: Fuel Pump vs Ignition Coil
Fuel pump repair costs typically range from $400 to $800 due to the complexity and labor involved in accessing fuel system components, whereas ignition coil replacement generally costs between $150 and $300, reflecting the simpler installation process. The fuel pump is a more critical and expensive component because it delivers pressurized fuel to the engine, while the ignition coil's primary function is to provide the spark for combustion, making its replacement less costly. Understanding the substantial price difference helps vehicle owners prioritize repairs and budget accordingly when diagnosing breakdowns.
Preventative Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection and replacement of fuel filters can prevent fuel pump failure by ensuring clean fuel reaches the engine, while checking ignition coils for cracks or corrosion helps avoid ignition coil failure. Using high-quality fuel and maintaining a consistent engine tune-up schedule enhances the longevity of both components. Early detection of voltage irregularities and fuel pressure drops during diagnostic testing supports effective preventative maintenance strategies.
Fuel pump failure vs ignition coil failure Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com