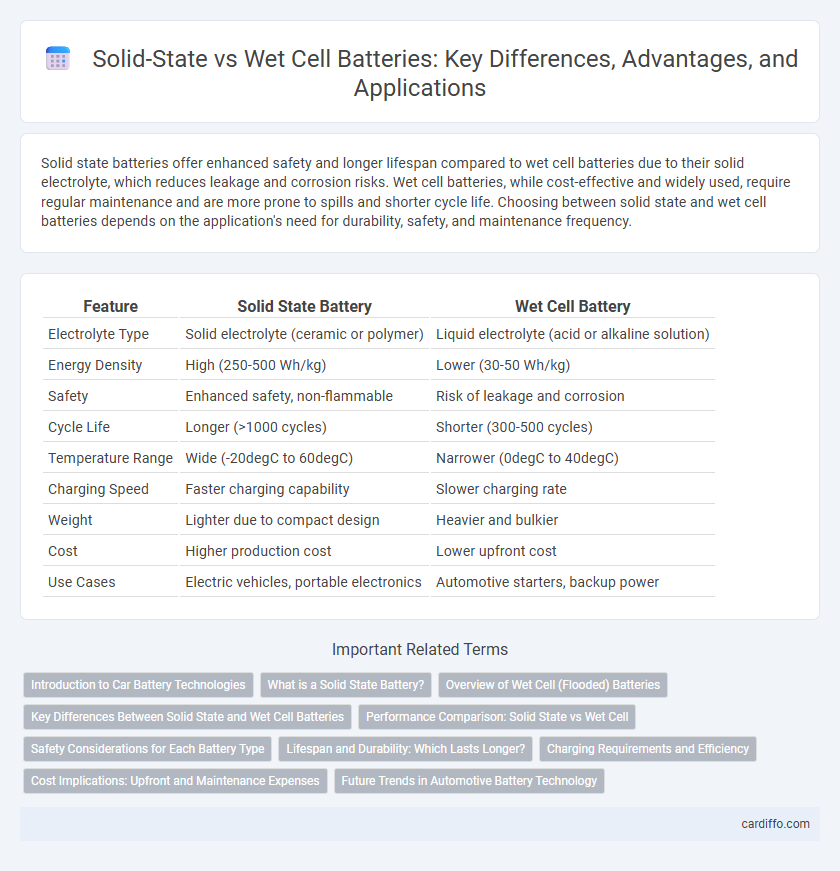
Solid state batteries offer enhanced safety and longer lifespan compared to wet cell batteries due to their solid electrolyte, which reduces leakage and corrosion risks. Wet cell batteries, while cost-effective and widely used, require regular maintenance and are more prone to spills and shorter cycle life. Choosing between solid state and wet cell batteries depends on the application's need for durability, safety, and maintenance frequency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solid State Battery | Wet Cell Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Type | Solid electrolyte (ceramic or polymer) | Liquid electrolyte (acid or alkaline solution) |
| Energy Density | High (250-500 Wh/kg) | Lower (30-50 Wh/kg) |
| Safety | Enhanced safety, non-flammable | Risk of leakage and corrosion |
| Cycle Life | Longer (>1000 cycles) | Shorter (300-500 cycles) |
| Temperature Range | Wide (-20degC to 60degC) | Narrower (0degC to 40degC) |
| Charging Speed | Faster charging capability | Slower charging rate |
| Weight | Lighter due to compact design | Heavier and bulkier |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Use Cases | Electric vehicles, portable electronics | Automotive starters, backup power |
Introduction to Car Battery Technologies
Solid state car batteries offer enhanced safety and higher energy density compared to traditional wet cell batteries, using solid electrolytes instead of liquid or gel-based ones. Wet cell batteries, commonly found in conventional vehicles, rely on liquid sulfuric acid to facilitate chemical reactions but are prone to leakage and corrosion. Advancements in solid state battery technology aim to improve vehicle range, reduce charging times, and increase lifespan, positioning them as a promising alternative in automotive energy storage.
What is a Solid State Battery?
A solid state battery uses a solid electrolyte instead of the liquid or gel electrolytes found in wet cell batteries, enhancing safety and energy density. These batteries offer higher voltage capacity, longer lifespan, and reduced risk of leakage or combustion compared to traditional wet cell batteries. Solid state technology is pivotal for electric vehicles and portable electronics, promising faster charging and improved overall performance.
Overview of Wet Cell (Flooded) Batteries
Wet cell batteries, also known as flooded batteries, contain a liquid electrolyte solution that submerges the battery's lead plates, facilitating efficient chemical reactions. These batteries are widely used in automotive and industrial applications due to their cost-effectiveness, durability, and ease of maintenance through periodic electrolyte refilling. Their design allows for high surge currents, making them ideal for starting engines, although they require ventilation to manage gas emissions during charging.
Key Differences Between Solid State and Wet Cell Batteries
Solid state batteries use a solid electrolyte, offering higher energy density, improved safety, and longer lifespan compared to wet cell batteries, which utilize liquid electrolytes prone to leakage and corrosion. Wet cell batteries, including lead-acid types, typically provide lower cost and proven reliability but suffer from limited cycle life and slower charging rates. The key distinctions lie in electrolyte state, energy efficiency, safety profile, and durability across various applications like electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
Performance Comparison: Solid State vs Wet Cell
Solid state batteries exhibit higher energy density and faster charging capabilities compared to traditional wet cell batteries, enabling longer device runtimes and reduced charging times. The solid electrolyte in solid state designs offers improved thermal stability and safety, minimizing the risk of leaks and fires common in wet cell counterparts with liquid electrolytes. Despite higher production costs, solid state batteries provide superior performance in durability and lifespan, making them ideal for advanced applications in electric vehicles and portable electronics.
Safety Considerations for Each Battery Type
Solid state batteries offer enhanced safety by utilizing a non-flammable solid electrolyte, significantly reducing the risk of leakage, thermal runaway, and combustion compared to wet cell batteries. Wet cell batteries contain liquid electrolytes which pose hazards such as acid spills, corrosion, and potential gas release under overcharge or physical damage conditions. Proper handling and protective casing are critical for wet cell batteries to mitigate safety risks, whereas solid state batteries inherently provide greater stability and safer operation in high-temperature or impact scenarios.
Lifespan and Durability: Which Lasts Longer?
Solid-state batteries offer significantly longer lifespans and enhanced durability compared to traditional wet cell batteries due to their solid electrolytes, which resist leakage and degradation over time. Wet cell batteries, relying on liquid electrolytes, are prone to corrosion and evaporation, resulting in shorter operational life and frequent maintenance. Advances in solid-state technology position these batteries as superior for long-term, reliable energy storage solutions.
Charging Requirements and Efficiency
Solid-state batteries require lower charging voltages and offer higher energy efficiency due to their solid electrolytes, which reduce internal resistance and minimize energy loss during charging. Wet cell batteries typically need more controlled charging voltages and longer charge times to prevent electrolyte degradation and sulfation, impacting overall efficiency. The improved thermal stability and faster ion transport in solid-state batteries contribute to more efficient and faster charging cycles compared to traditional wet cell designs.
Cost Implications: Upfront and Maintenance Expenses
Solid state batteries generally have higher upfront costs due to advanced materials and manufacturing processes but offer lower long-term maintenance expenses because of increased durability and safety. Wet cell batteries are typically more affordable initially, but their maintenance costs can accumulate over time due to electrolyte leakage, corrosion, and shorter lifespans. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors solid state technology for applications requiring longevity and reliability despite the initial investment.
Future Trends in Automotive Battery Technology
Solid-state batteries offer higher energy density and improved safety compared to traditional wet cell batteries, making them a promising solution for future electric vehicles. Advances in solid electrolyte materials are accelerating commercialization by enhancing charging speed and lifespan while reducing thermal risks. Automakers increasingly invest in solid-state technology to meet growing demands for longer driving ranges and faster charging, signaling a shift towards widespread adoption in next-generation automotive batteries.
Solid State vs Wet Cell Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com