Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by indicating the maximum current available for 30 seconds at 0degF. Ampere Hour (Ah) rating defines the battery's total energy storage capacity, representing how long it can deliver a specific current before discharging. Understanding the difference between CCA and Ah is essential for selecting the right battery for both starting power and overall runtime.
Table of Comparison
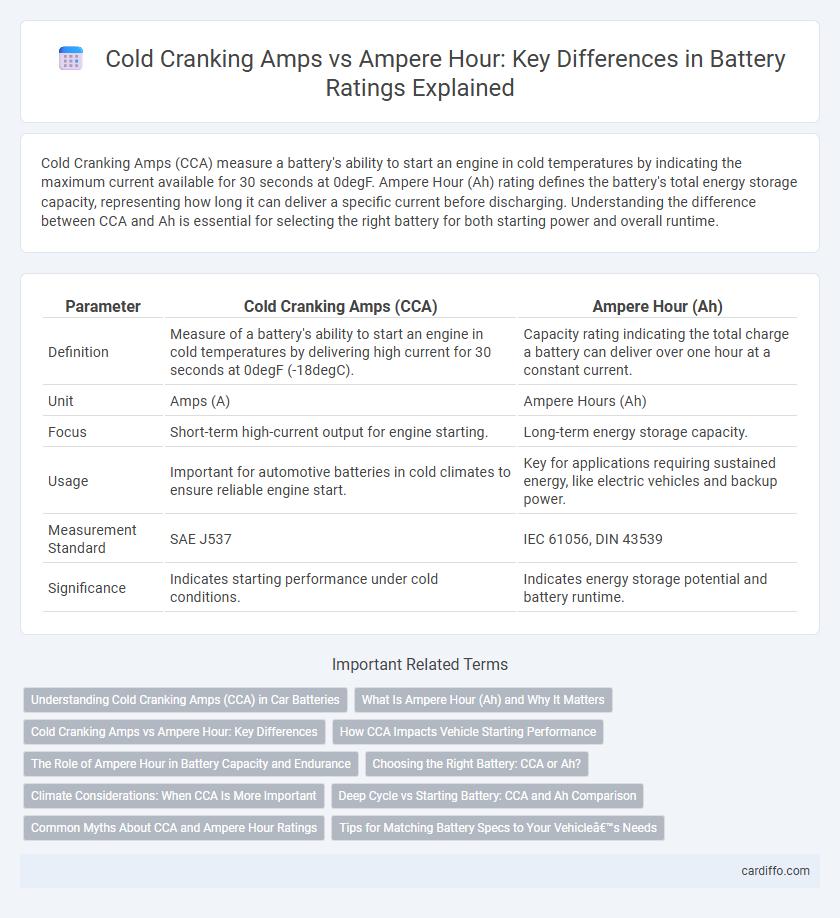
| Parameter | Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) | Ampere Hour (Ah) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measure of a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by delivering high current for 30 seconds at 0degF (-18degC). | Capacity rating indicating the total charge a battery can deliver over one hour at a constant current. |
| Unit | Amps (A) | Ampere Hours (Ah) |
| Focus | Short-term high-current output for engine starting. | Long-term energy storage capacity. |
| Usage | Important for automotive batteries in cold climates to ensure reliable engine start. | Key for applications requiring sustained energy, like electric vehicles and backup power. |
| Measurement Standard | SAE J537 | IEC 61056, DIN 43539 |
| Significance | Indicates starting performance under cold conditions. | Indicates energy storage potential and battery runtime. |
Understanding Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) in Car Batteries
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a car battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by indicating the number of amps it can deliver at 0degF for 30 seconds without dropping below 7.2 volts. Ampere Hour (Ah) rating, on the other hand, shows the battery's total energy storage capacity over time, not its starting power. Understanding CCA is crucial for selecting a battery that ensures reliable engine starts in winter conditions and prevents starting failures due to insufficient current.
What Is Ampere Hour (Ah) and Why It Matters
Ampere Hour (Ah) measures a battery's capacity to deliver current over time, indicating how long a battery can power a device before needing recharge. Unlike Cold Cranking Amps (CCA), which assess a battery's ability to start an engine under cold conditions, Ah is crucial for understanding overall energy storage and battery endurance. Higher Ah ratings enable longer usage periods, making this metric vital for applications requiring sustained power delivery.
Cold Cranking Amps vs Ampere Hour: Key Differences
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by delivering a high burst of current, while Ampere Hour (Ah) indicates the battery's energy storage capacity over time. CCA is critical for ensuring reliable starts in freezing conditions, focusing on the battery's instantaneous power output, whereas Ah reflects the total charge the battery can provide during extended use. Understanding the balance between CCA and Ah helps in selecting the right battery for both starting performance and energy endurance.
How CCA Impacts Vehicle Starting Performance
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to deliver a high burst of current needed to start an engine in cold temperatures, directly impacting vehicle starting performance during harsh weather. Higher CCA ratings ensure reliable ignition by providing sufficient power to overcome engine resistance and battery internal chemical limitations at low temperatures. Ampere Hour (Ah) rating, while indicating overall energy capacity, does not affect the immediate cranking power essential for cold starts.
The Role of Ampere Hour in Battery Capacity and Endurance
Ampere Hour (Ah) measures a battery's capacity to deliver a consistent current over time, defining its endurance during extended use. This metric is crucial for understanding how long a battery can power devices before needing recharge, unlike Cold Cranking Amps (CCA), which focus on immediate power for engine starts. A higher Ah rating indicates greater energy storage, directly impacting the battery's runtime and overall efficiency in applications requiring sustained power.
Choosing the Right Battery: CCA or Ah?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, making it vital for vehicles in harsh climates, while Ampere Hour (Ah) indicates the battery's capacity to deliver power over time, essential for sustained energy needs. Choosing the right battery depends on usage: prioritize high CCA for reliable cold starts and focus on higher Ah rating for longer, consistent power supply in applications like RVs or marine equipment. Understanding the balance between CCA and Ah ensures optimal performance and battery life tailored to specific vehicle or device requirements.
Climate Considerations: When CCA Is More Important
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in low temperatures, making it crucial in cold climates where freezing conditions demand higher starting power. Ampere Hour (Ah) ratings indicate overall battery capacity but do not reflect performance in extreme cold, where high CCA ensures reliable ignition. In regions with harsh winters, prioritizing batteries with high CCA ratings is essential to prevent starting failures caused by sluggish chemical reactions in cold weather.
Deep Cycle vs Starting Battery: CCA and Ah Comparison
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a starting battery's ability to deliver a high burst of current to start an engine in cold temperatures, while Ampere Hour (Ah) rating indicates a deep cycle battery's capacity to provide a steady amount of power over time. Starting batteries prioritize high CCA for quick bursts of power, making them ideal for ignition, whereas deep cycle batteries have higher Ah ratings to support sustained energy output for applications like marine or solar systems. Understanding the balance between CCA and Ah helps in selecting the right battery type based on whether immediate power or long-lasting energy delivery is required.
Common Myths About CCA and Ampere Hour Ratings
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, while Ampere Hour (Ah) indicates the battery's energy storage capacity over time. A common myth is that a higher CCA rating means a longer-lasting battery, but CCA only reflects starting power, not runtime or overall capacity. Many mistakenly believe that Ampere Hour ratings affect engine starting performance, yet Ah primarily determines how long a battery can supply power under normal conditions.
Tips for Matching Battery Specs to Your Vehicle’s Needs
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, making it crucial for vehicles in cold climates, while Ampere Hour (Ah) indicates the battery's energy storage capacity for running electrical systems over time. When matching battery specs to your vehicle, prioritize a CCA rating that meets or exceeds the manufacturer's recommendation to ensure reliable starts in low temperatures. Consider the Ah rating to support your vehicle's electrical demands, such as accessories and electronics, without draining the battery prematurely.
Cold Cranking Amps vs Ampere Hour Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com