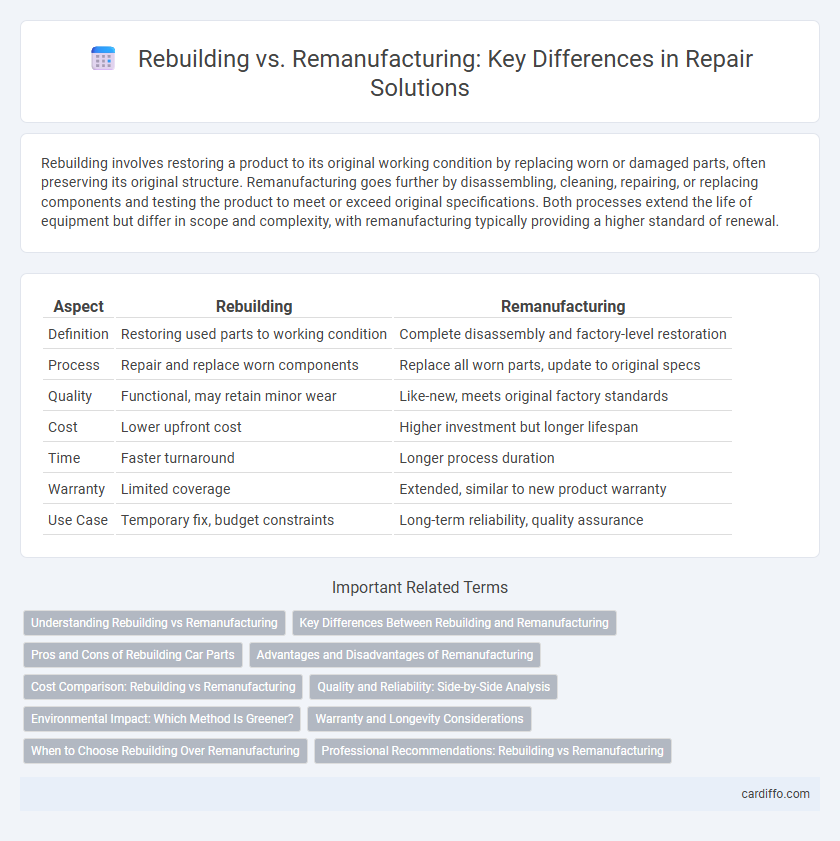
Rebuilding involves restoring a product to its original working condition by replacing worn or damaged parts, often preserving its original structure. Remanufacturing goes further by disassembling, cleaning, repairing, or replacing components and testing the product to meet or exceed original specifications. Both processes extend the life of equipment but differ in scope and complexity, with remanufacturing typically providing a higher standard of renewal.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Rebuilding | Remanufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Restoring used parts to working condition | Complete disassembly and factory-level restoration |
| Process | Repair and replace worn components | Replace all worn parts, update to original specs |
| Quality | Functional, may retain minor wear | Like-new, meets original factory standards |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher investment but longer lifespan |
| Time | Faster turnaround | Longer process duration |
| Warranty | Limited coverage | Extended, similar to new product warranty |
| Use Case | Temporary fix, budget constraints | Long-term reliability, quality assurance |
Understanding Rebuilding vs Remanufacturing
Rebuilding involves restoring a used component to its original condition by replacing worn parts and repairing defects, maintaining the original design specifications. Remanufacturing goes further by disassembling the product, inspecting each part, machining or replacing components, and reassembling it to meet or exceed original factory standards. Both processes extend equipment life, but remanufacturing ensures higher quality and reliability through comprehensive testing and upgrades.
Key Differences Between Rebuilding and Remanufacturing
Rebuilding involves repairing and replacing only the worn or damaged components of a product to restore its functionality, often maintaining the original specifications. Remanufacturing goes beyond by disassembling the entire product, inspecting, cleaning, and restoring all parts to meet or exceed original factory standards, resulting in a like-new condition. Key differences include the scope of work, with remanufacturing providing a comprehensive overhaul, higher quality assurance, and often a longer warranty compared to rebuilding.
Pros and Cons of Rebuilding Car Parts
Rebuilding car parts involves repairing and replacing worn components to restore functionality at a lower cost compared to remanufacturing, which typically requires more extensive processes and higher expenses. Pros of rebuilding include reduced turnaround time and cost savings, while cons include potential compromises in part durability and reliability due to reused components. Choosing rebuilding is ideal for less critical parts where performance demands are moderate, but it may not be suitable for high-stress components requiring guaranteed factory specifications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Remanufacturing
Remanufacturing restores products to like-new condition by completely disassembling, cleaning, and replacing worn components, which ensures high quality and reliability often exceeding standard repairs. It offers significant environmental benefits by reducing waste and resource consumption, while potentially lowering costs compared to new manufacturing. However, remanufacturing requires specialized expertise and equipment, can involve longer turnaround times, and may be limited by product design complexity or component availability.
Cost Comparison: Rebuilding vs Remanufacturing
Rebuilding typically costs 30-50% less than remanufacturing because it involves repairing or replacing only worn components, while remanufacturing requires complete disassembly and factory-level restoration. Labor intensity and part replacement rates are higher in remanufacturing, driving up expenses and turnaround time. Choosing rebuilding over remanufacturing can provide significant cost savings for moderate wear without compromising core functionality.
Quality and Reliability: Side-by-Side Analysis
Rebuilding and remanufacturing offer distinct quality and reliability outcomes, with remanufacturing adhering to original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications and replacing all worn components, resulting in superior product consistency. Rebuilt items often involve selective part replacement and inspection, which can lead to variable quality depending on the technician's expertise and parts used. For long-term reliability and performance, remanufactured products typically deliver greater durability and meet stringent quality standards compared to rebuilt alternatives.
Environmental Impact: Which Method Is Greener?
Rebuilding involves restoring used components to working condition, often conserving more original materials and generating less waste compared to remanufacturing, which replaces or refurbishes parts extensively. Remanufacturing typically demands higher energy consumption and additional raw materials, increasing its environmental footprint. Choosing rebuilding over remanufacturing can significantly reduce resource usage and carbon emissions, making it the greener repair option.
Warranty and Longevity Considerations
Rebuilding typically involves replacing worn components within the original structure, which may offer limited warranty coverage and moderate longevity compared to remanufacturing. Remanufacturing restores the product to like-new condition by thoroughly replacing or upgrading all critical parts, often accompanied by extended warranties that reflect higher durability. Customers seeking long-term reliability and comprehensive warranty protection generally benefit more from remanufactured products.
When to Choose Rebuilding Over Remanufacturing
Rebuilding is ideal when specific components of an engine or machinery can be restored to meet original specifications, allowing cost-effective repairs without complete replacement. Choose rebuilding for systems with minor wear or damage, where retaining original parts offers faster turnaround and preserves equipment history. Remanufacturing suits cases requiring full component overhaul or replacement to ensure like-new performance and extended lifespan.
Professional Recommendations: Rebuilding vs Remanufacturing
Professional recommendations emphasize choosing rebuilding for cost-effective repairs when wear is minimal and original parts remain usable, ensuring reliable restoration without full replacement. Remanufacturing is advised for heavily damaged or obsolete components, offering factory-level precision and extended warranty for critical systems. Both approaches require expert assessment to balance longevity, budget, and performance in industrial or automotive repairs.
Rebuilding vs remanufacturing Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com