Spot welding creates a strong, precise bond by applying pressure and heat to small, overlapping metal surfaces, making it ideal for thin sheets in automotive and manufacturing industries. Plug welding involves filling a hole in one metal piece with weld material to join it to another surface beneath, providing a versatile solution for thicker components or where surface access is limited. Both techniques offer efficient repair options, but spot welding excels in speed and minimal distortion, while plug welding enhances joint strength and stability in complex assemblies.
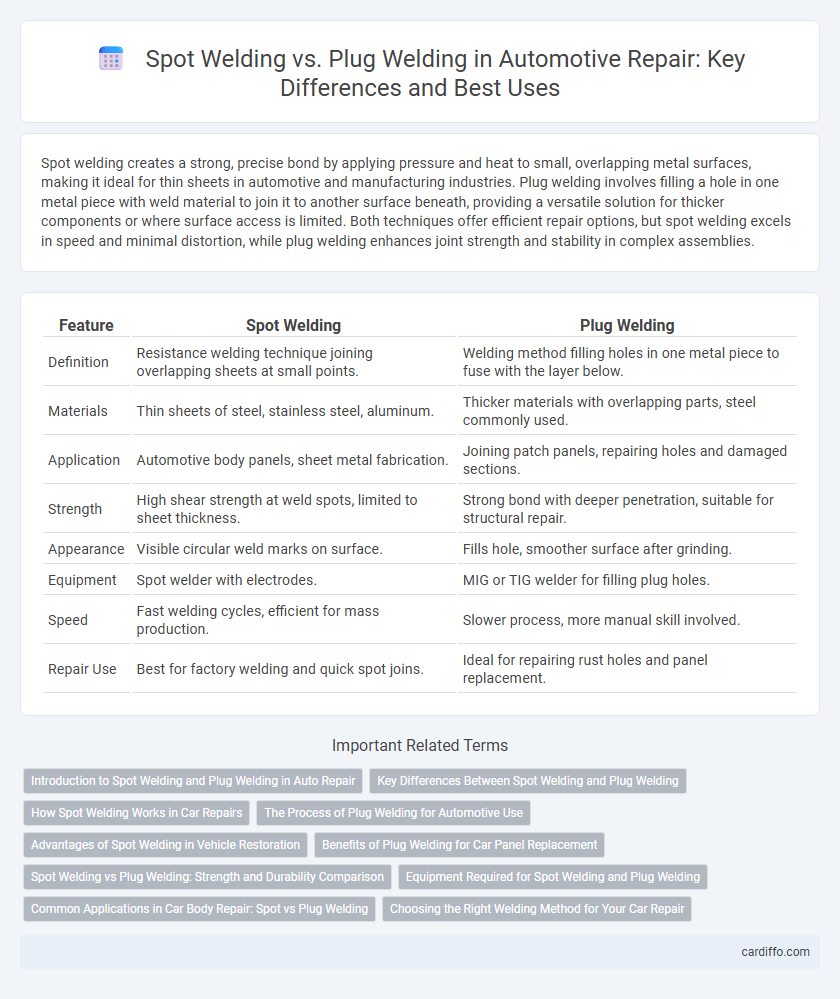
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spot Welding | Plug Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Resistance welding technique joining overlapping sheets at small points. | Welding method filling holes in one metal piece to fuse with the layer below. |
| Materials | Thin sheets of steel, stainless steel, aluminum. | Thicker materials with overlapping parts, steel commonly used. |
| Application | Automotive body panels, sheet metal fabrication. | Joining patch panels, repairing holes and damaged sections. |
| Strength | High shear strength at weld spots, limited to sheet thickness. | Strong bond with deeper penetration, suitable for structural repair. |
| Appearance | Visible circular weld marks on surface. | Fills hole, smoother surface after grinding. |
| Equipment | Spot welder with electrodes. | MIG or TIG welder for filling plug holes. |
| Speed | Fast welding cycles, efficient for mass production. | Slower process, more manual skill involved. |
| Repair Use | Best for factory welding and quick spot joins. | Ideal for repairing rust holes and panel replacement. |
Introduction to Spot Welding and Plug Welding in Auto Repair
Spot welding and plug welding are essential techniques used in auto repair for joining metal components. Spot welding uses electrical resistance to create localized welds by clamping metal sheets between copper electrodes, ideal for thin sheet metals and car body panels. Plug welding involves filling drilled holes in the top metal layer with weld material to bond it to the underlying metal, providing strong joints in thicker materials and structural repairs.
Key Differences Between Spot Welding and Plug Welding
Spot welding creates a weld by applying pressure and electric current to two overlapping metal sheets, resulting in a circular weld nugget typically used for joining thin materials. Plug welding involves filling a drilled or punched hole in one metal piece with weld material to join it to another piece beneath, allowing for thicker materials and providing stronger load-bearing connections. Key differences include the weld shape, joint design, material thickness compatibility, and application scope, with spot welding suited for rapid, thin-sheet assembly and plug welding preferred for thicker, structural repairs.
How Spot Welding Works in Car Repairs
Spot welding in car repairs involves clamping two overlapping metal sheets between copper electrodes and passing a high electric current through them to generate heat at the contact point, which melts the metal and forms a weld nugget. This process creates a strong, localized bond typically used for joining thin automotive body panels with minimal distortion. Spot welding is preferred for its speed, efficiency, and ability to maintain the integrity of painted surfaces during vehicle assembly and repairs.
The Process of Plug Welding for Automotive Use
Plug welding for automotive repair involves drilling or punching holes through overlapping metal sheets, then filling the holes with weld metal to join the parts securely. This process ensures strong structural integrity by fusing the base materials at discrete points, ideal for attaching components like sheet metal panels. Controlled heat input and precise hole size are critical to prevent warping and ensure optimal weld strength in automotive applications.
Advantages of Spot Welding in Vehicle Restoration
Spot welding offers precise and strong joint formation with minimal heat distortion, making it ideal for vehicle restoration where maintaining structural integrity is critical. It enables faster production times due to its automated process, reducing labor costs and improving efficiency in repair shops. The ability to create clean, consistent welds without filler material ensures a seamless finish that preserves the vehicle's original design and appearance.
Benefits of Plug Welding for Car Panel Replacement
Plug welding offers superior structural integrity for car panel replacement compared to spot welding by creating strong, localized welds that effectively join overlapping metal sections. This method reduces distortion risk and ensures better load distribution, which is critical for maintaining vehicle safety and durability. Plug welding also allows for easier access in tight or complex areas, making it a preferred choice for precise, long-lasting repairs.
Spot Welding vs Plug Welding: Strength and Durability Comparison
Spot welding creates strong, localized welds by fusing overlapping metal sheets through resistance heating, ensuring consistent strength in thin materials. Plug welding involves filling holes in one metal piece to join it to another, offering superior strength and durability for thicker sections and load-bearing applications. Comparing both, spot welding excels in speed and thin metal repairs, while plug welding provides enhanced joint integrity where structural demands are higher.
Equipment Required for Spot Welding and Plug Welding
Spot welding requires a spot welder machine equipped with electrodes that deliver high current for quick, localized fusion on sheet metals. Plug welding utilizes a MIG or TIG welder along with drill equipment to create holes for filler metal deposition, ensuring a strong joint through molten metal fill. Both techniques demand precise voltage and amperage control but differ significantly in tooling and application methods.
Common Applications in Car Body Repair: Spot vs Plug Welding
Spot welding is predominantly used in car body repair for joining sheet metal panels quickly and efficiently, especially in areas with limited access and thin materials like door skins and fenders. Plug welding is preferred when repairing or replacing sections with thicker metal or when increased strength is needed, such as chassis components and structural reinforcements. Both techniques complement each other by providing targeted applications that ensure durability and maintain the integrity of vehicle frames during restoration.
Choosing the Right Welding Method for Your Car Repair
Spot welding offers a fast and efficient solution for joining thin metal sheets in automotive repairs, ensuring strong, localized bonds with minimal distortion. Plug welding provides greater flexibility for thicker materials or overlapping joints, creating a solid bond through drilled holes that enhance structural integrity. Selecting the right welding method depends on the metal thickness, joint type, and repair location to achieve optimal durability and safety in your car repair.
Spot welding vs plug welding Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com