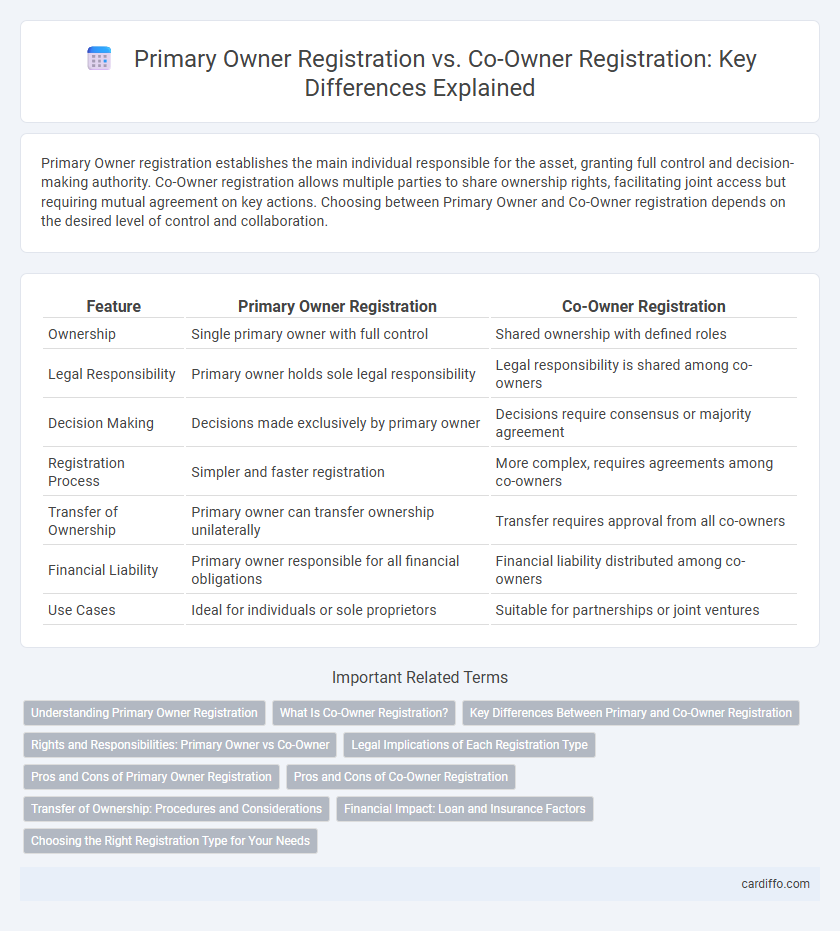
Primary Owner registration establishes the main individual responsible for the asset, granting full control and decision-making authority. Co-Owner registration allows multiple parties to share ownership rights, facilitating joint access but requiring mutual agreement on key actions. Choosing between Primary Owner and Co-Owner registration depends on the desired level of control and collaboration.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Primary Owner Registration | Co-Owner Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Single primary owner with full control | Shared ownership with defined roles |
| Legal Responsibility | Primary owner holds sole legal responsibility | Legal responsibility is shared among co-owners |
| Decision Making | Decisions made exclusively by primary owner | Decisions require consensus or majority agreement |
| Registration Process | Simpler and faster registration | More complex, requires agreements among co-owners |
| Transfer of Ownership | Primary owner can transfer ownership unilaterally | Transfer requires approval from all co-owners |
| Financial Liability | Primary owner responsible for all financial obligations | Financial liability distributed among co-owners |
| Use Cases | Ideal for individuals or sole proprietors | Suitable for partnerships or joint ventures |
Understanding Primary Owner Registration
Primary Owner Registration establishes the main account holder responsible for the asset or service, ensuring clear accountability and exclusive control over decisions and transactions. This registration type assigns legal rights and liabilities solely to the primary owner, simplifying communication with service providers and government entities. Understanding its implications helps avoid conflicts arising from shared ownership and clarifies authority in case of disputes or asset management.
What Is Co-Owner Registration?
Co-Owner Registration allows multiple individuals to share legal ownership and responsibilities of an asset or account, providing equal rights in decision-making and management. This type of registration enhances shared control and accountability, ensuring that all registered co-owners have access to the asset and can participate in transactions. It differs from Primary Owner Registration, where only one individual holds exclusive ownership and control.
Key Differences Between Primary and Co-Owner Registration
Primary owner registration establishes the main legal authority and responsibility for a property or vehicle, often granting full rights to use, sell, or transfer ownership. Co-owner registration shares ownership rights and responsibilities without necessarily providing equal control or decision-making power, depending on the registration terms. The key differences lie in the extent of legal control, liability, and the ability to independently make decisions regarding the registered asset.
Rights and Responsibilities: Primary Owner vs Co-Owner
Primary owner registration grants full legal rights and sole responsibility for decision-making, financial obligations, and liability related to the asset. Co-owner registration distributes rights and responsibilities proportionally, requiring consensus for major decisions and shared liability among owners. Understanding these distinctions ensures clarity in ownership roles and prevents future disputes over control and accountability.
Legal Implications of Each Registration Type
Primary owner registration establishes sole legal responsibility and full control over the asset, granting exclusive rights to make decisions and bear liabilities. Co-owner registration creates shared ownership, dividing legal responsibilities, decision-making authority, and potential liabilities between parties according to their ownership percentage or agreement. Legal disputes or obligations involving the asset require consensus or clear understanding of each co-owner's rights and duties to avoid conflicts or unintended liabilities.
Pros and Cons of Primary Owner Registration
Primary Owner Registration centralizes control and responsibility, ensuring streamlined decision-making and clear legal accountability for the registered asset or account. This registration type simplifies communication and management but may pose challenges if the primary owner becomes unavailable, as co-owners lack formal authority to act independently. While it enhances security by limiting access, it may reduce flexibility and collaboration opportunities compared to Co-Owner Registration.
Pros and Cons of Co-Owner Registration
Co-owner registration allows shared responsibility and access to the asset, which can simplify management and provide added security if one owner is unavailable. However, it may lead to conflicts over decision-making and complicate legal or financial obligations since all co-owners are equally liable. Co-owner registration can also affect credit scores and creditworthiness, as actions by one owner influence the whole account or property.
Transfer of Ownership: Procedures and Considerations
Primary owner registration requires submitting a formal transfer of ownership form signed by the current owner, along with valid identification and proof of purchase, to the relevant authority. Co-owner registration involves additional consent documentation from all registered owners to authorize the transfer, ensuring legal clarity and avoiding disputes. Both procedures must adhere to state-specific regulations, including possible fees and timelines, to complete the transfer effectively and maintain valid ownership records.
Financial Impact: Loan and Insurance Factors
Primary Owner Registration typically establishes sole responsibility for loan repayment and insurance claims, often resulting in clearer credit impact and streamlined communication with lenders and insurers. Co-Owner Registration distributes financial liability and ownership rights among multiple parties, which can affect loan approval chances and insurance premium calculations based on combined creditworthiness and risk assessment. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for managing financial exposure, loan terms, and insurance coverage effectively in property or vehicle registration.
Choosing the Right Registration Type for Your Needs
Selecting between Primary Owner Registration and Co-Owner Registration depends on the intended control and responsibility over the asset. Primary Owner Registration grants full legal authority and decision-making rights to one individual, typically reflecting sole ownership or main accountability. Co-Owner Registration allows shared ownership and responsibilities, which can be advantageous for joint investments, family property, or collaborative projects where multiple parties need recognized authority.
Primary Owner Registration vs Co-Owner Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com