New car registration typically involves higher fees and requires detailed documentation such as a manufacturer's certificate of origin, while used car registration may demand a bill of sale and proof of previous ownership. Both processes require proof of insurance and a completed application form, but used car registration often includes additional inspections or emissions tests. Understanding the differences ensures a smoother registration experience and compliance with local DMV regulations.
Table of Comparison
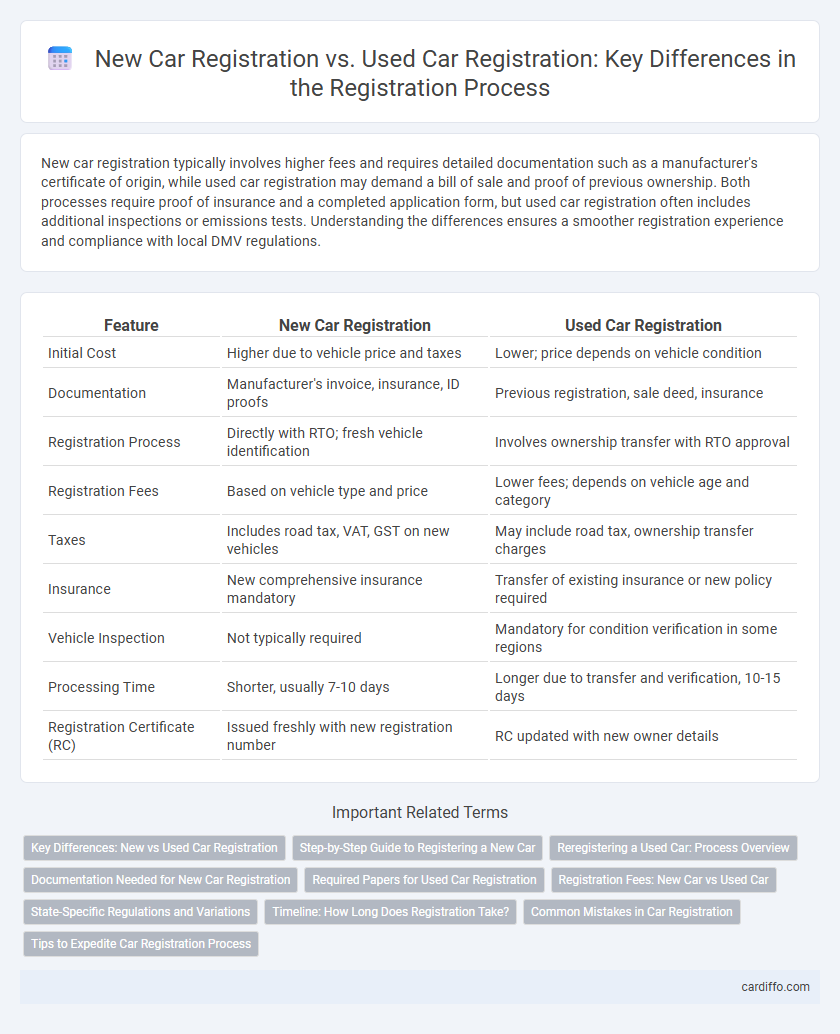
| Feature | New Car Registration | Used Car Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Higher due to vehicle price and taxes | Lower; price depends on vehicle condition |
| Documentation | Manufacturer's invoice, insurance, ID proofs | Previous registration, sale deed, insurance |
| Registration Process | Directly with RTO; fresh vehicle identification | Involves ownership transfer with RTO approval |
| Registration Fees | Based on vehicle type and price | Lower fees; depends on vehicle age and category |
| Taxes | Includes road tax, VAT, GST on new vehicles | May include road tax, ownership transfer charges |
| Insurance | New comprehensive insurance mandatory | Transfer of existing insurance or new policy required |
| Vehicle Inspection | Not typically required | Mandatory for condition verification in some regions |
| Processing Time | Shorter, usually 7-10 days | Longer due to transfer and verification, 10-15 days |
| Registration Certificate (RC) | Issued freshly with new registration number | RC updated with new owner details |
Key Differences: New vs Used Car Registration
New car registration typically involves higher fees due to vehicle value taxes, mandatory inspections, and dealership documentation, while used car registration often requires the submission of a valid title and proof of previous ownership. Vehicle identification number (VIN) verification and emissions testing may be mandated for used cars, but new cars often come pre-certified from manufacturers. Insurance requirements remain consistent, yet registration timelines differ, with new cars generally requiring immediate registration post-purchase and used cars allowing for a brief transfer period.
Step-by-Step Guide to Registering a New Car
Registering a new car involves obtaining the manufacturer's certificate of origin, completing the vehicle title application, and submitting proof of insurance to the state DMV or motor vehicle agency. Buyers must pay applicable registration fees, taxes, and may need to schedule a vehicle inspection depending on state requirements. Upon successful processing, the owner receives license plates, registration stickers, and the official vehicle title.
Reregistering a Used Car: Process Overview
Reregistering a used car involves transferring the vehicle title and registration to a new owner while updating the records with the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV). Key steps include submitting the signed title, completing a bill of sale, providing proof of insurance, and paying applicable fees and taxes. The process ensures legal ownership transfer and compliance with state regulations for road use and taxation.
Documentation Needed for New Car Registration
New car registration requires specific documentation including the Manufacturer's Certificate of Origin (MCO), proof of insurance, valid identification, and a completed application form. Additionally, proof of payment for applicable taxes and fees must be submitted to the local Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) or relevant authority. These documents ensure proper vehicle identification and ownership verification during the registration process.
Required Papers for Used Car Registration
Used car registration requires essential documents such as the original registration certificate (RC), valid insurance, a pollution under control (PUC) certificate, and a no-objection certificate (NOC) from the previous owner. The buyer must also submit proof of identity, address proof, and Form 29 and 30 duly signed by both parties during the transfer of ownership process. Unlike new car registration, used car registration involves verifying the vehicle's history and ownership transfer to ensure legal compliance.
Registration Fees: New Car vs Used Car
New car registration fees typically include higher costs due to vehicle excise duty, registration tax, and sometimes additional manufacturer fees, reflecting its initial market value and emissions standards. Used car registration fees are generally lower, often based on the car's current market value, age, and prior registration history, resulting in reduced excise duties or taxes. These fee differences impact total ownership costs and should be carefully evaluated when registering a new versus a used vehicle.
State-Specific Regulations and Variations
New car registration often requires manufacturer's certificate of origin and initial state inspections, while used car registration typically demands a title transfer and proof of prior ownership. State-specific regulations vary significantly, with some states imposing emissions testing or safety inspections only for used vehicles, whereas others require these checks for all registrations regardless of vehicle age. Variations in fees and required documentation reflect the distinct administrative processes tailored to new versus used car registrations across different states.
Timeline: How Long Does Registration Take?
New car registration typically takes between one to two weeks, as the process involves issuing original documents and updating manufacturer databases. Used car registration can be faster, often completed within a few days, since it mainly requires the transfer of ownership and verification of existing documents. Processing times may vary by state, with online registration options potentially expediting both new and used vehicle registrations.
Common Mistakes in Car Registration
Common mistakes in new car registration often involve failing to submit the Manufacturer's Certificate of Origin or overlooking state-specific emissions and safety inspection requirements. Used car registration errors typically include missing the title transfer, not reporting the mileage accurately, or neglecting to pay applicable taxes and fees. Both processes require careful attention to deadlines and documentation to avoid fines and delays.
Tips to Expedite Car Registration Process
To expedite new car registration, gather all necessary documents including the Manufacturer's Certificate of Origin, proof of insurance, and a valid ID before visiting the DMV. For used car registration, ensure the title is properly signed over, have a bill of sale, and verify emissions testing compliance to avoid delays. Scheduling appointments online and pre-paying fees can significantly reduce wait times for both new and used car registrations.
New Car Registration vs Used Car Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com