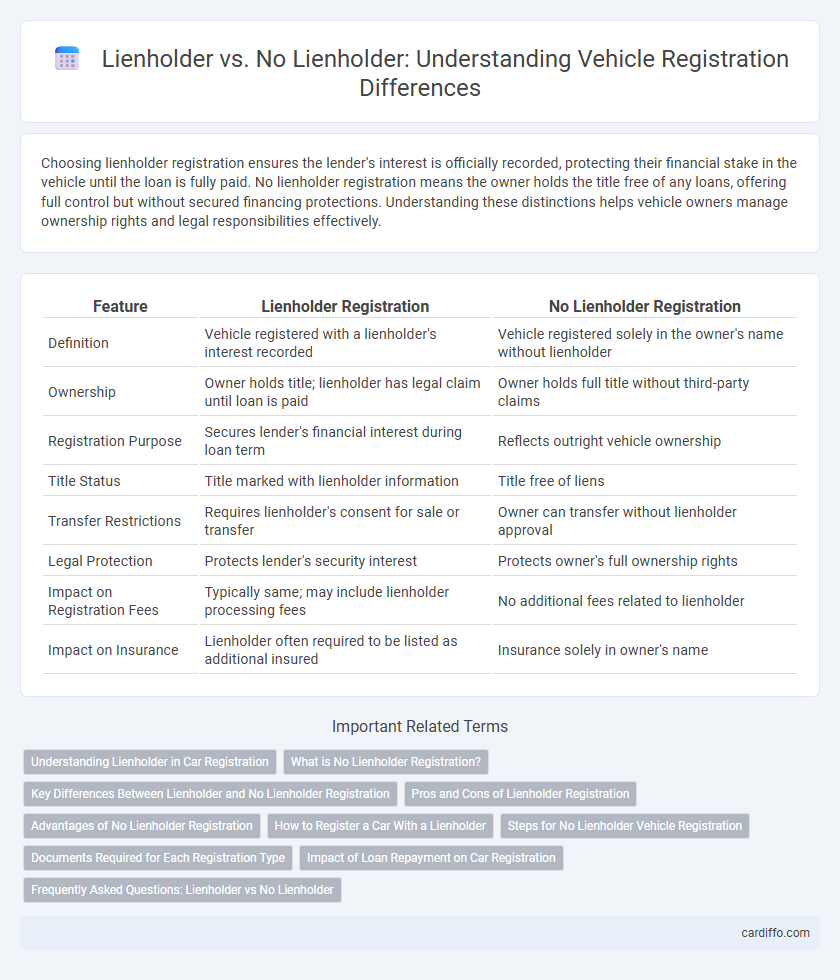
Choosing lienholder registration ensures the lender's interest is officially recorded, protecting their financial stake in the vehicle until the loan is fully paid. No lienholder registration means the owner holds the title free of any loans, offering full control but without secured financing protections. Understanding these distinctions helps vehicle owners manage ownership rights and legal responsibilities effectively.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lienholder Registration | No Lienholder Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vehicle registered with a lienholder's interest recorded | Vehicle registered solely in the owner's name without lienholder |
| Ownership | Owner holds title; lienholder has legal claim until loan is paid | Owner holds full title without third-party claims |
| Registration Purpose | Secures lender's financial interest during loan term | Reflects outright vehicle ownership |
| Title Status | Title marked with lienholder information | Title free of liens |
| Transfer Restrictions | Requires lienholder's consent for sale or transfer | Owner can transfer without lienholder approval |
| Legal Protection | Protects lender's security interest | Protects owner's full ownership rights |
| Impact on Registration Fees | Typically same; may include lienholder processing fees | No additional fees related to lienholder |
| Impact on Insurance | Lienholder often required to be listed as additional insured | Insurance solely in owner's name |
Understanding Lienholder in Car Registration
A lienholder in car registration refers to a financial institution or individual that holds a security interest in the vehicle until the loan is fully paid. When registering a car with a lienholder, their information is listed on the title to indicate their legal claim on the vehicle. No lienholder registration means the vehicle owner has full ownership rights without any outstanding financial obligations tied to the car.
What is No Lienholder Registration?
No Lienholder Registration refers to the process of registering a vehicle without listing a lienholder, indicating that the vehicle is fully owned without any outstanding loan or financial interest from a third party. This type of registration simplifies title processing and ownership verification, as there are no liens associated with the vehicle. It is commonly used by individuals who have paid off their vehicle loans or purchased vehicles outright.
Key Differences Between Lienholder and No Lienholder Registration
Lienholder registration indicates that a financial institution or lender holds a legal claim on the vehicle title until the loan is fully paid, ensuring their interest is protected. No lienholder registration means the vehicle owner holds the title free and clear, with no outstanding claims from creditors or lenders. The key difference lies in title ownership and security interest, impacting title transfer and lien release processes during vehicle registration.
Pros and Cons of Lienholder Registration
Lienholder registration secures the lender's interest by officially recording their claim on the vehicle title, offering legal protection in case of default or repossession. This method can complicate the resale process since the lienholder's approval is required, potentially delaying ownership transfer. Without lienholder registration, vehicle owners have full control over the title but risk losing lender protections, increasing financial exposure if loan terms are violated.
Advantages of No Lienholder Registration
No lienholder registration allows vehicle owners full autonomy over their title, preventing third-party claims or restrictions related to loans or liens. This registration type simplifies the transfer or sale process by eliminating the need for lienholder approval, enhancing ownership flexibility. Vehicle owners benefit from faster, less complicated title management, reducing potential legal or financial entanglements.
How to Register a Car With a Lienholder
Registering a car with a lienholder involves listing the lienholder's name on the title to indicate their legal interest in the vehicle until the loan is paid off. The lienholder will typically provide the necessary documentation required by the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV), such as the loan agreement and lien release forms. Completing the registration requires submitting the title application, proof of insurance, identification, and fees while ensuring the lienholder's information is accurately recorded to avoid future title disputes.
Steps for No Lienholder Vehicle Registration
To register a vehicle with no lienholder, the owner must submit the original title showing clear ownership to the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV). The process involves completing the application for a new title and registration, providing proof of insurance, and paying the applicable registration fees. Finally, the DMV issues the new registration and license plates directly to the owner without lienholder involvement.
Documents Required for Each Registration Type
Lienholder registration requires submission of a lienholder agreement, proof of insurance, and the vehicle title indicating the lienholder's interest, while no lienholder registration demands only the vehicle title in the owner's name and proof of identity. For lienholder registrations, additional documents such as loan agreements and payoff statements might be necessary to verify financial interests. No lienholder registration typically simplifies the process with fewer documents, focusing on ownership verification without third-party claims.
Impact of Loan Repayment on Car Registration
When registering a vehicle with a lienholder, the lender holds a financial interest, requiring the lien to be noted on the title until the loan is fully repaid. No lienholder registration means the owner holds the title outright, simplifying ownership transfer but eliminating lender protection. Loan repayment impacts registration by clearing the lien, allowing the owner to request a lien-free title, which can streamline future sales or transfers.
Frequently Asked Questions: Lienholder vs No Lienholder
A lienholder registration records a financial institution's legal interest in a vehicle, protecting their right if the owner defaults on a loan, whereas no lienholder registration assigns full ownership rights solely to the registrant. Common questions address how lienholder information is displayed on the title, the process for removing a lienholder after loan payoff, and implications for selling or transferring the vehicle. Understanding the difference helps clarify responsibilities, title status, and legal claims during ownership changes.
Lienholder vs No Lienholder Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com