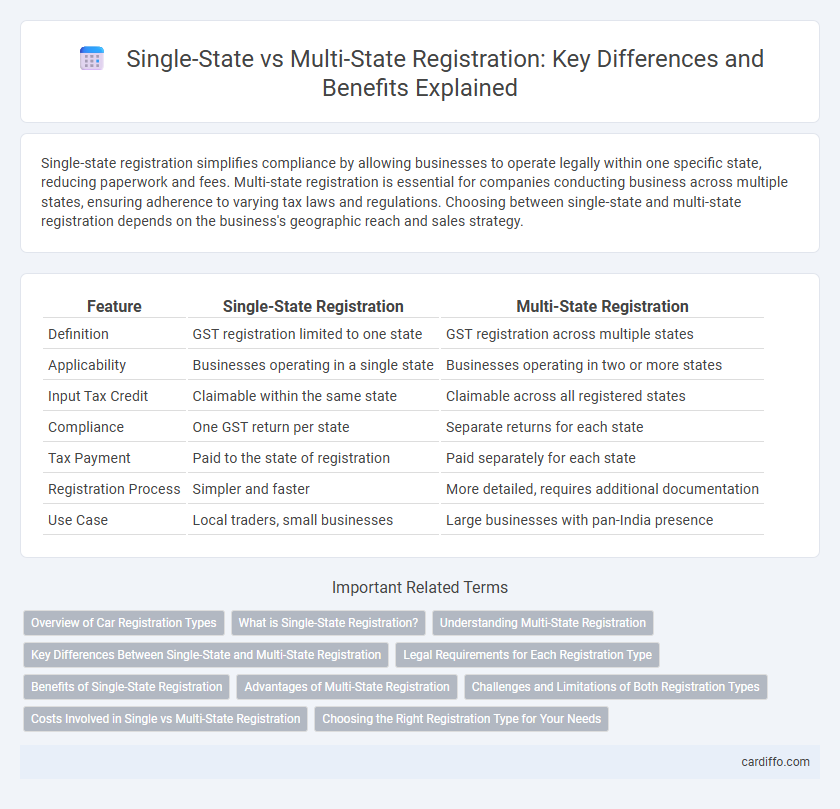
Single-state registration simplifies compliance by allowing businesses to operate legally within one specific state, reducing paperwork and fees. Multi-state registration is essential for companies conducting business across multiple states, ensuring adherence to varying tax laws and regulations. Choosing between single-state and multi-state registration depends on the business's geographic reach and sales strategy.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Single-State Registration | Multi-State Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | GST registration limited to one state | GST registration across multiple states |
| Applicability | Businesses operating in a single state | Businesses operating in two or more states |
| Input Tax Credit | Claimable within the same state | Claimable across all registered states |
| Compliance | One GST return per state | Separate returns for each state |
| Tax Payment | Paid to the state of registration | Paid separately for each state |
| Registration Process | Simpler and faster | More detailed, requires additional documentation |
| Use Case | Local traders, small businesses | Large businesses with pan-India presence |
Overview of Car Registration Types
Car registration types vary primarily between single-state and multi-state registrations, each serving different geographic and administrative needs. Single-state registration applies when a vehicle is registered in one state, complying with that state's legal and tax regulations, suitable for residents who rarely drive outside their home state. Multi-state registration accommodates vehicles frequently used across multiple states, ensuring compliance with varied regional laws and taxes, often necessary for commercial vehicles or individuals with residences in multiple locations.
What is Single-State Registration?
Single-state registration refers to the process where a business registers for tax purposes in only one state where it operates, enabling it to comply with local tax laws and regulations exclusively in that state. This type of registration is suitable for businesses with a physical presence, employees, or sales restricted to a single state. It simplifies tax reporting but limits the company's ability to legally conduct business or collect taxes in other states without obtaining additional registrations.
Understanding Multi-State Registration
Multi-state registration allows businesses to legally operate and comply with tax regulations in multiple states, expanding their market reach beyond a single jurisdiction. This registration requires understanding varying state-specific tax obligations, including sales tax collection, reporting, and payment deadlines. Effective management of multi-state registration ensures seamless interstate commerce and minimizes the risk of penalties for non-compliance.
Key Differences Between Single-State and Multi-State Registration
Single-state registration applies when a business operates exclusively within one state, simplifying tax compliance and limiting reporting obligations to that state's regulations. Multi-state registration is required when a business has a physical presence, employees, or significant sales across multiple states, necessitating adherence to varied tax laws, filing requirements, and nexus standards in each state. Key differences include scope of tax jurisdiction, complexity of compliance, and potential exposure to multiple tax authorities and audits.
Legal Requirements for Each Registration Type
Single-state registration mandates businesses to comply solely with the legal and tax requirements of one state, including obtaining a state-specific business license and adhering to local tax codes. Multi-state registration requires companies to fulfill each state's unique registration processes, tax obligations, and regulatory compliance standards where they operate, which often involves registering for sales tax permits, income tax filings, and employment taxes separately in every state. Understanding the legal nuances for both registration types ensures adherence to state laws, avoiding penalties and enabling seamless business operations across jurisdictions.
Benefits of Single-State Registration
Single-state registration streamlines compliance by limiting regulatory requirements to one jurisdiction, reducing administrative burdens and costs. Businesses benefit from simplified tax filings, fewer reporting obligations, and faster approval processes under a single-state registration framework. This approach is ideal for companies with a localized market presence seeking efficient operations and minimized compliance risks.
Advantages of Multi-State Registration
Multi-state registration enables businesses to legally operate and expand across multiple states, increasing market reach and customer base without the need for separate entity establishment in each state. It simplifies tax compliance by consolidating reporting requirements, reducing administrative burden and minimizing errors associated with handling diverse state regulations. This registration also enhances credibility with suppliers and clients nationwide, facilitating smoother transactions and business relationships.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Registration Types
Single-state registration limits business operations to a specific geographical area, causing challenges like restricted market reach and regulatory compliance constraints. Multi-state registration involves complex paperwork and higher administrative costs, often requiring businesses to navigate varying tax laws and regulations across states. Both registration types face limitations in scalability and operational flexibility, impacting overall business growth potential.
Costs Involved in Single vs Multi-State Registration
Single-state registration typically involves lower costs due to limited application fees, simpler compliance requirements, and reduced administrative overhead. Multi-state registration incurs higher expenses, including multiple state-specific filing fees, varied tax obligations, and increased costs for ongoing compliance and reporting across jurisdictions. Businesses must weigh these cost differences when deciding between single-state registration and multi-state registration to optimize operational efficiency and financial management.
Choosing the Right Registration Type for Your Needs
Choosing the right registration type depends on the scope of your business operations and tax liabilities. Single-state registration suits businesses operating exclusively within one state, simplifying compliance and reporting requirements. Multi-state registration is essential for companies with a physical presence or sales in multiple states, ensuring proper tax collection and adherence to varying state laws.
Single-state Registration vs Multi-state Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com