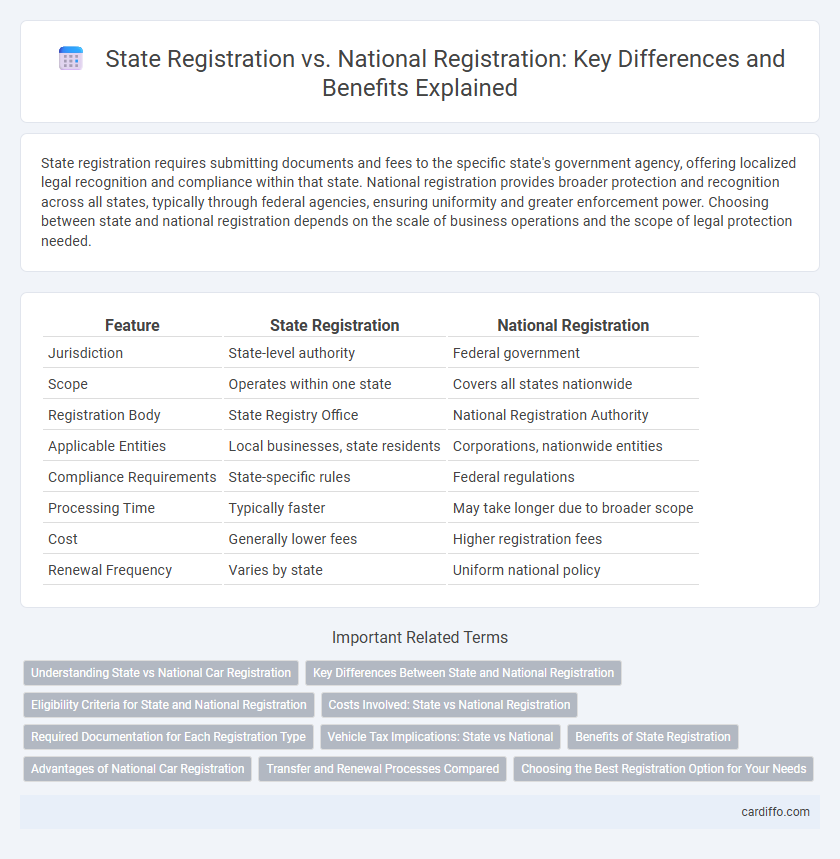
State registration requires submitting documents and fees to the specific state's government agency, offering localized legal recognition and compliance within that state. National registration provides broader protection and recognition across all states, typically through federal agencies, ensuring uniformity and greater enforcement power. Choosing between state and national registration depends on the scale of business operations and the scope of legal protection needed.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | State Registration | National Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Jurisdiction | State-level authority | Federal government |
| Scope | Operates within one state | Covers all states nationwide |
| Registration Body | State Registry Office | National Registration Authority |
| Applicable Entities | Local businesses, state residents | Corporations, nationwide entities |
| Compliance Requirements | State-specific rules | Federal regulations |
| Processing Time | Typically faster | May take longer due to broader scope |
| Cost | Generally lower fees | Higher registration fees |
| Renewal Frequency | Varies by state | Uniform national policy |
Understanding State vs National Car Registration
State registration involves registering a vehicle within a specific state, adhering to state-specific regulations, fees, and requirements, which can vary significantly across states. National car registration, while less common, refers to a centralized registration system managed at the federal level, providing uniform standards and easier vehicle tracking across all states. Understanding the differences between state and national registration is crucial for compliance, transfer procedures, and maintaining valid registration status when moving between states or importing vehicles.
Key Differences Between State and National Registration
State registration applies to businesses operating within a specific state, requiring compliance with local regulations and state tax obligations. National registration involves registering a business or entity at the federal level, enabling operations across multiple states and granting access to federal tax identification numbers and protections. Key differences include the scope of legal authority, tax responsibilities, and regulatory requirements specific to state versus nationwide business activities.
Eligibility Criteria for State and National Registration
State registration eligibility requires applicants to meet specific residency or business operation criteria within the state, often including proof of local address and compliance with state regulations. National registration demands broader qualifications, such as federal tax identification, compliance with national standards, and sometimes prior state registration. Differences in eligibility criteria ensure that state registration caters to localized legal and economic activities, while national registration accommodates entities operating across multiple states or at a federal level.
Costs Involved: State vs National Registration
State registration typically involves lower initial fees and simpler documentation compared to national registration, making it a cost-effective choice for small businesses targeting local markets. National registration generally demands higher application fees, ongoing maintenance costs, and specialized legal support to ensure compliance across all states. Businesses must evaluate the scale of their operations and budget constraints when deciding between the more affordable state registration and the comprehensive but costlier national registration.
Required Documentation for Each Registration Type
State registration requires documentation such as proof of residency, state-issued identification, and local tax identification numbers, while national registration demands federal tax identification, social security numbers, and compliance certificates relevant to national regulations. State registration processes often necessitate additional documents like business licenses or permits issued by local authorities, differing from the national requirement for standardized legal documents such as a certificate of incorporation. Understanding the specific documentation needed for each registration type is critical for ensuring compliance and avoiding delays in processing.
Vehicle Tax Implications: State vs National
State vehicle registration often incurs taxes based on local property values and road use, leading to variations in fees across different states. National vehicle registration typically standardizes tax rates, offering a uniform fee structure but may lack regional tax incentives or deductions available at the state level. Understanding these differences is crucial for vehicle owners to optimize tax liabilities and compliance with applicable regulations.
Benefits of State Registration
State registration offers localized legal recognition, enabling businesses to comply efficiently with regional regulations and access state-specific benefits such as tax incentives and grants. It enhances market credibility within the state, facilitating smoother interactions with local suppliers, customers, and government agencies. State registration also typically involves simpler procedures and lower fees compared to national registration, saving time and costs for small and medium enterprises.
Advantages of National Car Registration
National car registration offers streamlined administrative processes by consolidating vehicle records within a single centralized system, reducing the risk of duplication and errors. It enhances legal enforcement and security measures through uniform identification standards accessible across all states, facilitating easier tracking and recovery of stolen vehicles. Furthermore, national registration simplifies interstate travel and reduces paperwork for vehicle owners, supporting consistent policy application and fee structures nationwide.
Transfer and Renewal Processes Compared
State registration processes for transfer and renewal typically involve localized paperwork and adherence to state-specific regulations, resulting in faster processing times but varying requirements. National registration often standardizes transfer and renewal procedures across states, ensuring uniform documentation and eligibility standards, but may entail longer processing durations due to centralized systems. Comparing the two, state registration offers more agility in updates while national systems provide consistency and broader recognition of transfers and renewals.
Choosing the Best Registration Option for Your Needs
State registration offers localized compliance with specific state regulations, making it ideal for businesses operating primarily within one state. National registration provides broader protection and recognition across all states, beneficial for companies planning to expand or operate interstate. Evaluating business goals, operational scope, and legal requirements will guide you in choosing the most suitable registration option.
State Registration vs National Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com