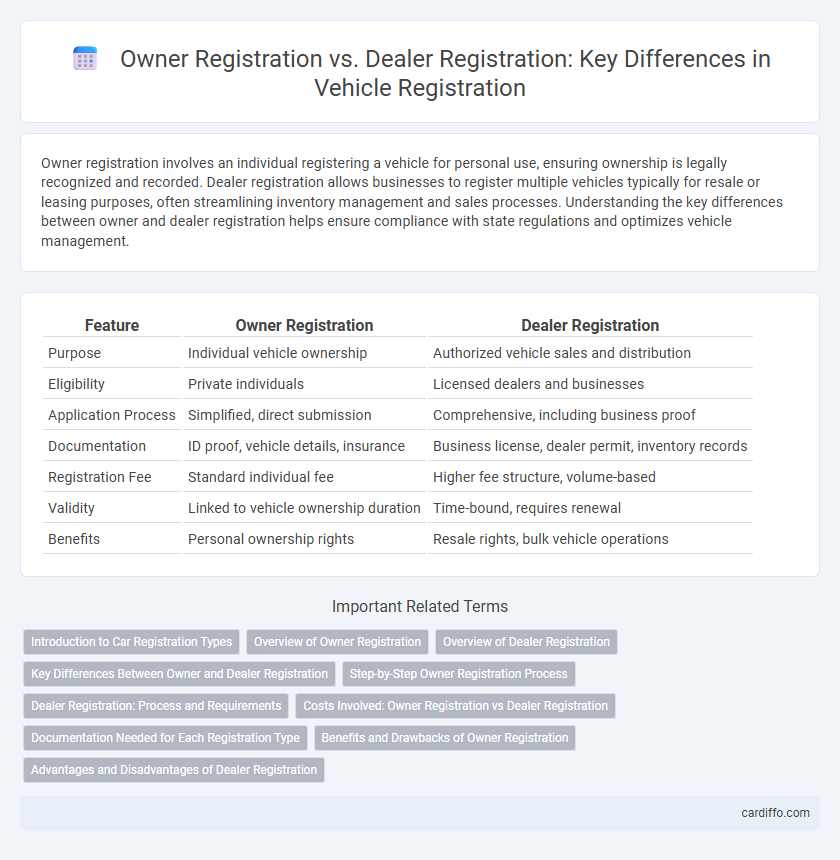
Owner registration involves an individual registering a vehicle for personal use, ensuring ownership is legally recognized and recorded. Dealer registration allows businesses to register multiple vehicles typically for resale or leasing purposes, often streamlining inventory management and sales processes. Understanding the key differences between owner and dealer registration helps ensure compliance with state regulations and optimizes vehicle management.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Owner Registration | Dealer Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Individual vehicle ownership | Authorized vehicle sales and distribution |
| Eligibility | Private individuals | Licensed dealers and businesses |
| Application Process | Simplified, direct submission | Comprehensive, including business proof |
| Documentation | ID proof, vehicle details, insurance | Business license, dealer permit, inventory records |
| Registration Fee | Standard individual fee | Higher fee structure, volume-based |
| Validity | Linked to vehicle ownership duration | Time-bound, requires renewal |
| Benefits | Personal ownership rights | Resale rights, bulk vehicle operations |
Introduction to Car Registration Types
Owner registration involves registering a vehicle under a private individual's name, granting full ownership and responsibility for the car. Dealer registration allows automotive dealers to register vehicles temporarily for inventory management and test drives, often under a dealer plate rather than individual ownership. Understanding these car registration types is crucial for complying with legal requirements and ensuring proper documentation during vehicle transactions.
Overview of Owner Registration
Owner registration involves individuals or private entities officially recording their ownership of a vehicle with the relevant motor vehicle department, establishing legal responsibility and enabling lawful operation. This process requires submission of proof of ownership, identification, and payment of applicable fees, resulting in issuance of a vehicle title and registration certificate. Owner registration differs from dealer registration, which pertains to entities authorized to sell or distribute vehicles, requiring compliance with additional licensing and business regulations.
Overview of Dealer Registration
Dealer registration entails businesses or individuals formally registering with regulatory authorities to legally buy, sell, or lease vehicles. This process requires meeting specific state-mandated criteria, submitting necessary documents, and paying licensing fees to obtain a dealer license. Unlike owner registration, which is for individual vehicle ownership, dealer registration enables commercial transactions and inventory management under a licensed dealership.
Key Differences Between Owner and Dealer Registration
Owner registration involves an individual registering a vehicle for personal use, typically requiring proof of ownership, identity, and residence. Dealer registration is designed for businesses selling multiple vehicles, often necessitating a dealer license, sales tax number, and compliance with state-specific regulations. Key differences include documentation requirements, eligibility criteria, and intended use, with owner registration focused on single-vehicle ownership and dealer registration enabling commercial sales activities.
Step-by-Step Owner Registration Process
Owner registration involves a step-by-step process starting with submitting personal identification documents and proof of vehicle ownership to the relevant motor vehicle department. The applicant must complete the registration form, pay the required fees, and schedule a vehicle inspection if applicable. Once approved, the vehicle owner receives official registration certificates and license plates, ensuring legal compliance and ownership verification.
Dealer Registration: Process and Requirements
Dealer registration requires submitting a completed application form along with proof of business ownership, valid dealer license, and a surety bond as mandated by state law. Applicants must also provide details on the business location, tax identification number, and comply with background checks and vehicle inventory documentation. The process ensures dealers meet regulatory standards to legally buy, sell, and distribute vehicles.
Costs Involved: Owner Registration vs Dealer Registration
Owner registration typically incurs lower costs, including standard title fees, registration charges, and personal transaction taxes. Dealer registration involves higher expenses such as licensing fees, dealer bond costs, and compliance-related charges designed for commercial vehicle sales operations. Understanding these cost differences helps individuals and businesses determine the most budget-appropriate registration type.
Documentation Needed for Each Registration Type
Owner registration typically requires proof of identity, proof of address, vehicle title, and insurance documents, while dealer registration demands additional paperwork such as a dealer license, business registration certificates, inventory list, and surety bonds. Owner registration documents validate personal ownership and vehicle details, whereas dealer registration documents verify business legitimacy and compliance with state regulations. Ensuring all required documentation is accurate and complete is essential for smooth processing in both registration types.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Owner Registration
Owner registration offers direct control over the vehicle, ensuring personal accountability and straightforward title transfer processes. However, it may lack access to bulk purchasing discounts, fleet management advantages, and specialized dealer support services. For individuals prioritizing simplicity and ownership clarity, owner registration is ideal, though it may be less efficient for commercial activities or resale operations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dealer Registration
Dealer registration offers advantages such as streamlined bulk vehicle processing, access to wholesale pricing, and the ability to handle multiple transactions efficiently, which benefits businesses with high sales volumes. However, disadvantages include stricter regulatory compliance, higher initial fees, and increased scrutiny from authorities compared to owner registration. This form of registration requires maintaining detailed records and adhering to dealership-specific legal requirements, which can increase operational complexity.
Owner Registration vs Dealer Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com