Rust proofing targets metal surfaces to prevent corrosion by applying protective coatings that seal out moisture and contaminants. Undercoating provides a thicker, rubberized layer mainly on the vehicle's undercarriage, shielding it from road debris, salt, and water damage. Choosing rust proofing enhances long-term metal preservation, while undercoating offers robust physical protection against harsh environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
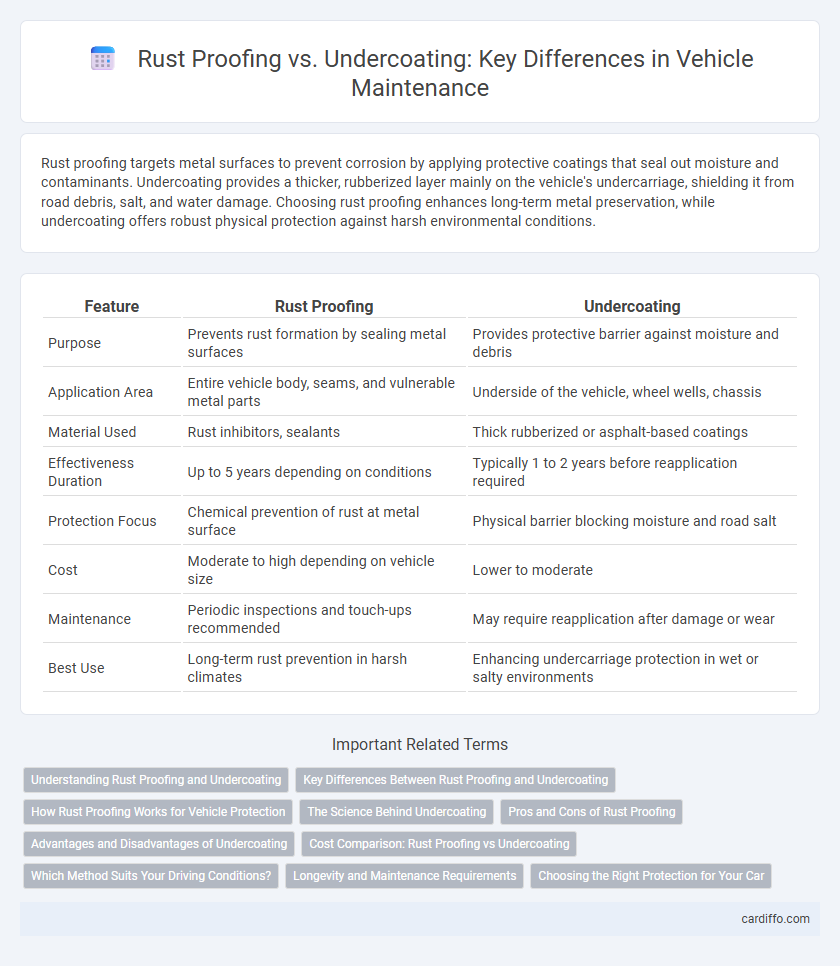
| Feature | Rust Proofing | Undercoating |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents rust formation by sealing metal surfaces | Provides protective barrier against moisture and debris |
| Application Area | Entire vehicle body, seams, and vulnerable metal parts | Underside of the vehicle, wheel wells, chassis |
| Material Used | Rust inhibitors, sealants | Thick rubberized or asphalt-based coatings |
| Effectiveness Duration | Up to 5 years depending on conditions | Typically 1 to 2 years before reapplication required |
| Protection Focus | Chemical prevention of rust at metal surface | Physical barrier blocking moisture and road salt |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on vehicle size | Lower to moderate |
| Maintenance | Periodic inspections and touch-ups recommended | May require reapplication after damage or wear |
| Best Use | Long-term rust prevention in harsh climates | Enhancing undercarriage protection in wet or salty environments |
Understanding Rust Proofing and Undercoating
Rust proofing involves applying chemical treatments like rust inhibitors or sealants to metal surfaces to prevent oxidation and corrosion over time. Undercoating refers to the application of a protective layer, often rubberized or asphalt-based, to the underside of vehicles to shield against moisture, salt, and physical abrasion. Both methods enhance vehicle longevity by addressing rust prevention, but rust proofing targets internal metal protection while undercoating provides an external physical barrier.
Key Differences Between Rust Proofing and Undercoating
Rust proofing involves applying chemical treatments to prevent corrosion by creating a protective barrier on metal surfaces, while undercoating uses thick rubberized or wax-based materials to shield the vehicle's undercarriage from moisture, salt, and debris. Rust proofing targets the internal metal protection, often penetrating seams and crevices, whereas undercoating provides external, physical defense against impacts and environmental damage. Choosing between rust proofing and undercoating depends on climate conditions, vehicle use, and long-term maintenance goals.
How Rust Proofing Works for Vehicle Protection
Rust proofing involves applying a protective chemical coating to a vehicle's metal surfaces, creating a barrier that prevents moisture and salt from causing corrosion. This process targets vulnerable areas such as the undercarriage, wheel wells, and seams, where rust typically begins. By inhibiting oxidation, rust proofing extends the vehicle's lifespan and maintains its structural integrity.
The Science Behind Undercoating
Undercoating creates a durable, flexible barrier by applying a thick, rubberized coating that seals the vehicle's undercarriage against moisture, salt, and road debris, effectively preventing oxidation and corrosion. Unlike rust proofing which uses chemical treatments to neutralize rust-causing agents, undercoating provides physical protection that absorbs impacts and resists chipping, ensuring long-term preservation of metal surfaces. This combination of mechanical shielding and water repellency makes undercoating a scientifically robust method for enhancing vehicle longevity in harsh conditions.
Pros and Cons of Rust Proofing
Rust proofing offers effective protection against corrosion by forming a durable barrier on metal surfaces, extending vehicle lifespan and reducing costly repairs. However, it may require professional application and periodic maintenance to ensure continued effectiveness, which can increase overall costs. Unlike undercoating, rust proofing typically provides a thinner, less insulating layer, making it less effective against physical damage from road debris.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Undercoating
Undercoating provides a protective barrier against moisture, road salt, and debris, significantly reducing underbody corrosion and extending vehicle lifespan. However, improper application can trap moisture underneath, potentially accelerating rust development and requiring careful surface preparation for optimal adhesion. Undercoating may also add weight and need periodic reapplication to maintain effectiveness, posing some maintenance challenges.
Cost Comparison: Rust Proofing vs Undercoating
Rust proofing generally costs between $100 and $400, offering a cost-effective solution focused on treating metal surfaces with protective coatings to prevent corrosion. Undercoating, typically priced from $200 to $800, involves applying a thicker, rubberized shield to the vehicle's undercarriage for enhanced protection against moisture, salt, and road debris. Choosing between rust proofing and undercoating depends on budget considerations and the desired level of protection, with undercoating requiring a higher initial investment but providing more comprehensive defense against rust.
Which Method Suits Your Driving Conditions?
Rust proofing provides a chemical barrier protecting metal surfaces from corrosion, ideal for vehicles driven in humid or coastal areas with high salt exposure. Undercoating offers a thick, rubberized layer that shields the undercarriage from road debris and moisture, best suited for vehicles frequently driven on gravel roads or in snowy regions with salted streets. Choosing between rust proofing and undercoating depends on specific driving conditions, environmental factors, and the level of exposure to corrosive elements.
Longevity and Maintenance Requirements
Rust proofing involves applying protective coatings that penetrate metal surfaces to prevent corrosion and extend vehicle longevity with minimal upkeep. Undercoating offers a thicker, more durable barrier that shields the undercarriage from moisture, salt, and debris but typically requires periodic inspection to maintain effectiveness. Both methods enhance durability, yet rust proofing demands less frequent maintenance while undercoating provides superior protection in harsh environments.
Choosing the Right Protection for Your Car
Choosing the right protection for your car involves understanding the key differences between rust proofing and undercoating. Rust proofing uses chemical treatments to prevent oxidation on the car's metal surfaces, while undercoating applies a thick, protective layer to shield the undercarriage from moisture, salt, and debris. For optimal vehicle longevity, consider your local climate and driving conditions when selecting either rust proofing or undercoating to enhance corrosion resistance effectively.
Rust Proofing vs Undercoating Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com